In short, the microwave heating technique is an advanced thermal process that uses microwave radiation to heat materials rapidly and uniformly. Unlike conventional ovens that heat from the outside-in, microwave energy penetrates the material, causing it to heat from within its entire volume at once, which significantly shortens processing times and improves energy efficiency.
Microwave heating offers a powerful alternative to conventional methods by delivering fast, clean, and volumetric heat. However, its effectiveness is not universal; it depends critically on the material's ability to absorb microwave energy and the specific technical demands of the application, such as process control and scale.

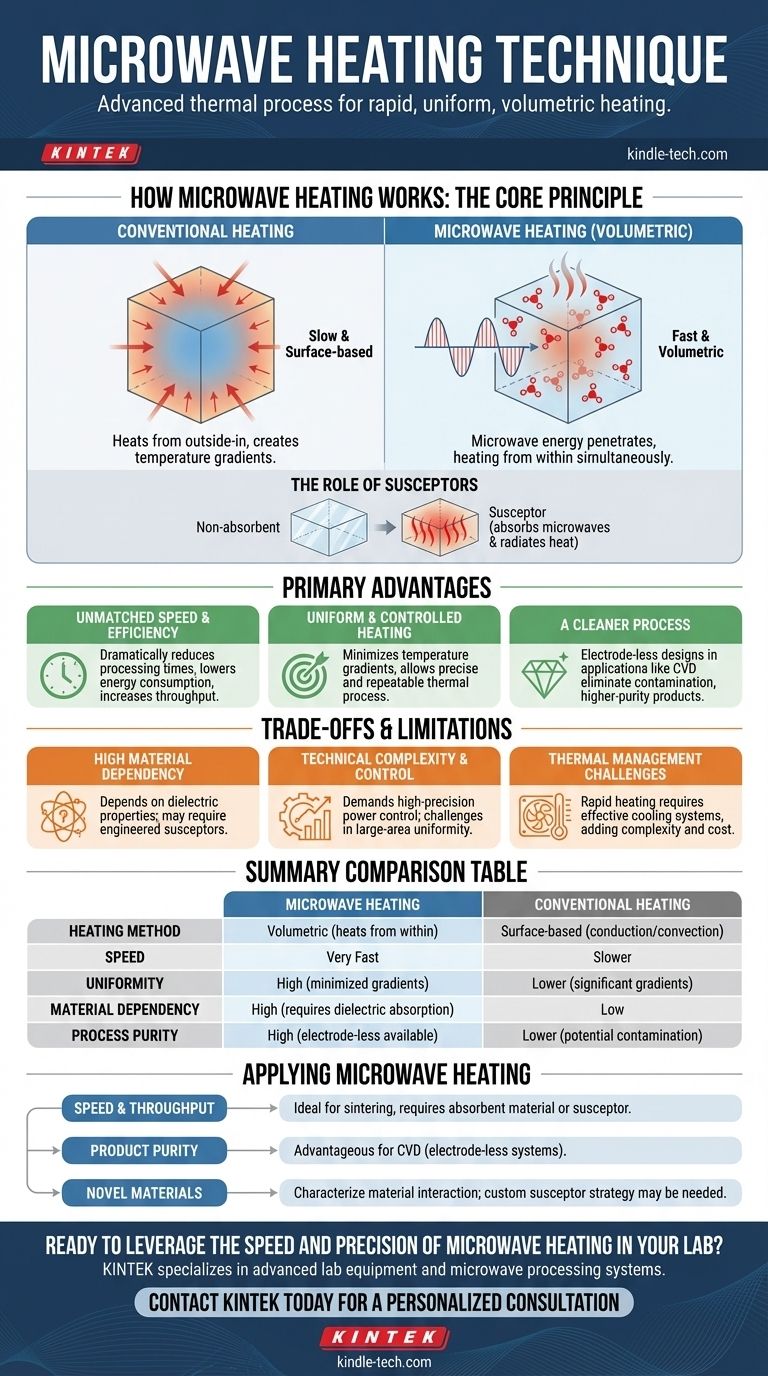
How Microwave Heating Works: The Core Principle
Microwave heating is fundamentally different from the conduction and convection methods used in traditional furnaces. Understanding this difference is key to leveraging its unique advantages.
From Microwaves to Heat
The process uses a magnetron to generate microwaves, which are directed into a chamber containing the target material. The oscillating electromagnetic field of the microwaves interacts with polar molecules within the material, causing them to rotate rapidly and generate heat through molecular friction.
Volumetric vs. Conventional Heating
Conventional heating transfers energy from a hot surface to the cooler interior of an object. This is a slow process that creates significant temperature gradients.
Microwave heating is volumetric. The energy penetrates the material and excites molecules throughout its bulk simultaneously, resulting in faster and more uniform temperature distribution.
The Role of Susceptors
Not all materials interact with microwaves. Materials with low dielectric loss, like monoclinic zirconia, are effectively transparent to them.
In these cases, a susceptor material is used. The susceptor is a secondary material that strongly absorbs microwave energy and converts it into thermal energy, which it then radiates to heat the primary, non-absorbent material.
The Primary Advantages of Microwave Processing
When applied to the right materials and processes, microwave heating offers distinct benefits over traditional thermal methods.
Unmatched Speed and Efficiency
The ability to heat the entire volume of a material at once dramatically reduces processing times. Sintering, for example, can be completed much faster, which in turn lowers energy consumption and increases production throughput.
Uniform and Controlled Heating
By heating from the inside out, the technique minimizes the temperature differences between the surface and the core of the material. This uniformity, combined with automatic ON/OFF power control, allows for a highly precise and repeatable thermal process.
A Cleaner Process
In certain applications, such as Microwave Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), the equipment design avoids internal electrodes. This eliminates a common source of contamination, leading to higher-purity end products like high-quality diamond films.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No technique is a universal solution. The objectivity of a technical advisor requires a clear-eyed view of the potential challenges.
High Material Dependency
The success of microwave heating is entirely dependent on the dielectric properties of the material being processed. If a material does not absorb microwave energy, the process is ineffective without a properly engineered susceptor system.
Technical Complexity and Control
Systems like microwave CVD demand high-precision power control. The physics of microwave energy can also make it difficult to achieve uniform deposition over very large areas, limiting its use in some mass-production scenarios.
Thermal Management Challenges
The same rapid heating that makes the process efficient can create engineering challenges. Cooling the equipment effectively can be difficult and may require auxiliary cooling systems to manage the thermal load, adding complexity and cost.
Applying Microwave Heating to Your Process
Your decision to use microwave heating should be based on a clear understanding of its strengths relative to your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is speed and throughput: Microwave heating is an exceptional choice for processes like sintering, provided your material is microwave-absorbent or compatible with a susceptor.
- If your primary focus is product purity: For applications like CVD, the electrode-less nature of a microwave plasma system offers a significant advantage in avoiding process contamination.
- If you are exploring novel materials: You must first characterize the material's interaction with microwaves before investing in equipment, as a custom susceptor strategy may be required.
By aligning the unique characteristics of microwave heating with your specific application, you can make an informed decision that capitalizes on its strengths while mitigating its limitations.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Microwave Heating | Conventional Heating |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Volumetric (heats from within) | Surface-based (conduction/convection) |
| Speed | Very Fast | Slower |
| Uniformity | High (minimized gradients) | Lower (significant gradients) |
| Material Dependency | High (requires dielectric absorption) | Low |
| Process Purity | High (electrode-less systems available) | Lower (potential for contamination) |
Ready to leverage the speed and precision of microwave heating in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including microwave processing systems for sintering, CVD, and more. Our experts can help you determine if microwave technology is right for your specific materials and processes, ensuring you achieve superior results in efficiency and product purity.
Contact KINTEL today for a personalized consultation and discover the right thermal solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Super Sealed Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory drying oven play in the processing and chemical analysis of aluminum dross?
- Does pyrolysis affect the environment? A Dual-Sided Look at Waste Reduction and Pollution Risks
- How do you prepare samples for SEM analysis? Achieve Clear, Accurate Imaging Every Time
- How does heat treatment affect strength? Tailor Material Properties for Maximum Performance
- What does HIP process do? Eliminate Porosity for Superior Material Performance
- What is an example of a continuous furnace? Discover the Conveyor Belt Furnace for High-Volume Production
- Do diamond testing machines work? Choose the Right Tester for Accurate Results
- How do magnetic stirrers and vacuum drying ovens work together to optimize catalyst performance? Expert Prep Guide



















