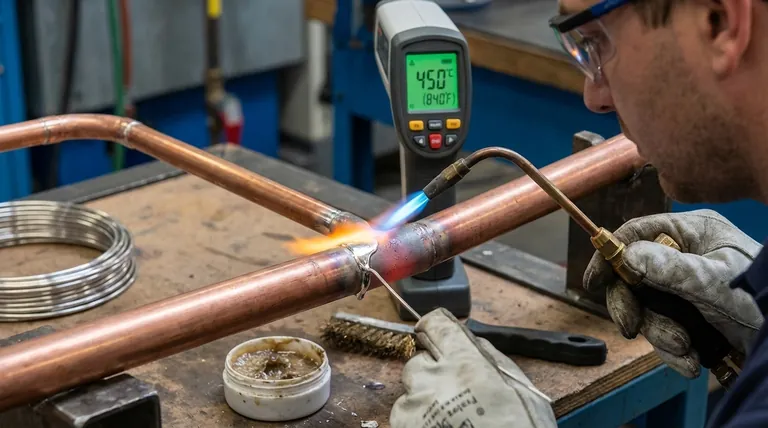
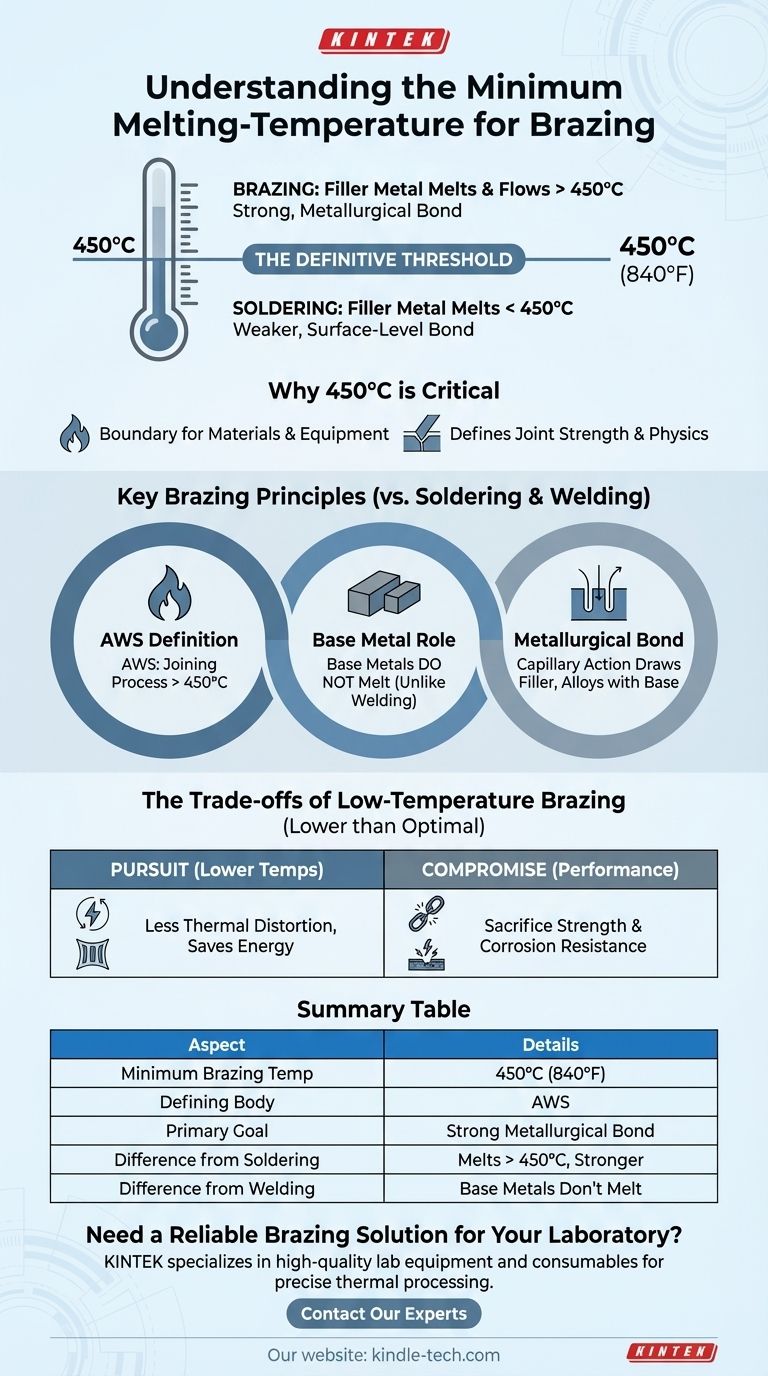
The definitive minimum melting temperature for a filler material to be classified for brazing is 450°C (840°F). This temperature is the internationally recognized dividing line that separates brazing from the lower-temperature process of soldering. For a process to be considered brazing, the filler metal must melt and flow above this point, but always below the melting point of the base metals being joined.
The core principle is not just the temperature itself, but what it represents. The 450°C (840°F) threshold distinguishes brazing—a process that creates a strong, metallurgically-bonded joint via capillary action—from soldering, which typically results in a weaker, surface-level bond.

Why 450°C is the Critical Threshold
Understanding this specific temperature reveals the fundamental physics that defines the entire joining process. It's the boundary condition that dictates the materials, equipment, and resulting strength of the final assembly.
Defining Brazing vs. Soldering
The American Welding Society (AWS) formally defines brazing as a group of joining processes that use a filler metal with a liquidus (melting) temperature above 450°C (840°F).
Conversely, any similar process using a filler metal that melts below this temperature is defined as soldering. This distinction is crucial for material selection and engineering specifications.
The Role of the Base Metal
A key principle of brazing is that the base metals being joined do not melt. The process relies on heating a joint to a temperature high enough to melt the filler alloy, but low enough to keep the parent parts—such as steel, copper, or brass—solid.
This is the primary difference between brazing and welding, where the base metals are melted and fused together.
How the Metallurgical Bond Forms
The heat used in brazing (above 450°C) is sufficient to create a strong metallurgical bond between the filler and base metals.
At these temperatures, the liquid filler metal is drawn into the tight-fitting joint by capillary action. It then alloys with a thin layer of the base metal, creating a permanent bond upon cooling that is often stronger than the filler metal itself.
The Trade-offs of Low-Temperature Brazing
While 450°C is the minimum, there is a constant engineering drive to develop alloys that work at the lowest possible temperatures within the brazing range. This pursuit, however, involves significant compromises.
The Pursuit of Lower Temperatures
Operating at lower temperatures reduces the risk of thermal distortion in the base parts, saves energy, and can speed up production cycles. This makes the development of effective, low-temperature brazing alloys a highly desirable goal.
The Compromise in Performance
As noted in laboratory research, many experimental low-temperature brazing alloys have not yet met industrial requirements.
These specialized alloys often sacrifice critical properties like corrosion resistance and mechanical strength to achieve a lower melting point. This makes them unsuitable for many demanding applications.
The Importance of Flux
Flux is a chemical compound used to clean and protect the base metals from oxidation during heating, which is essential for proper filler metal flow.
The flux must have a melting and activation range that is compatible with the filler metal. For example, some common fluxes activate around 565°C (1049°F), meaning they are only suitable for brazing alloys that melt at or above that temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice of joining process depends entirely on the required strength, operating conditions, and material properties of the final assembly.
- If your primary focus is maximum joint strength and high-temperature performance: Brazing is the correct choice, using alloys that operate well above the 450°C minimum.
- If your primary focus is joining heat-sensitive components or minimizing thermal distortion: Soldering, which operates below the 450°C threshold, is the appropriate process.
- If you are exploring specialized, low-heat applications: Be aware that experimental low-temperature brazing alloys require careful validation of their mechanical and chemical properties before industrial use.
Understanding this fundamental temperature threshold is the first step toward selecting a reliable and effective joining strategy for your project.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Minimum Brazing Temperature | 450°C (840°F) |
| Defining Body | American Welding Society (AWS) |
| Primary Goal | Create a metallurgical bond via capillary action |
| Key Difference from Soldering | Filler metal melts above 450°C, creating stronger joints |
| Key Difference from Welding | Base metals do not melt; only the filler metal does |
Need a Reliable Brazing Solution for Your Laboratory?
Choosing the right brazing materials and equipment is critical for achieving strong, durable joints in your research or production. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your precise thermal processing needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can help you optimize your brazing processes, ensure consistent results, and enhance the integrity of your assemblies.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electrode Polishing Material for Electrochemical Experiments
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Containers
- Conductive Carbon Cloth Carbon Paper Carbon Felt for Electrodes and Batteries
- High Shear Homogenizer for Pharmaceutical and Cosmetic Applications
People Also Ask
- Why are an electrolytic polishing system and specific electrolytes necessary for Inconel 625? Expert Analysis
- What is the importance of electrolytic polishing and electrolytic cells in FeCrAl sample prep? Reveal true structures.
- What is the purpose of using electrolytic polishing on copper foils? Optimize Your CVD Graphene & hBN Growth Surface
- What are the advantages of an electrolytic polishing device for EK-181 steel TEM samples? Ensure Peak Sample Integrity
- What is the purpose of alumina polishing powder in GCE pretreatment? Master Surface Prep for Electrochemistry



















