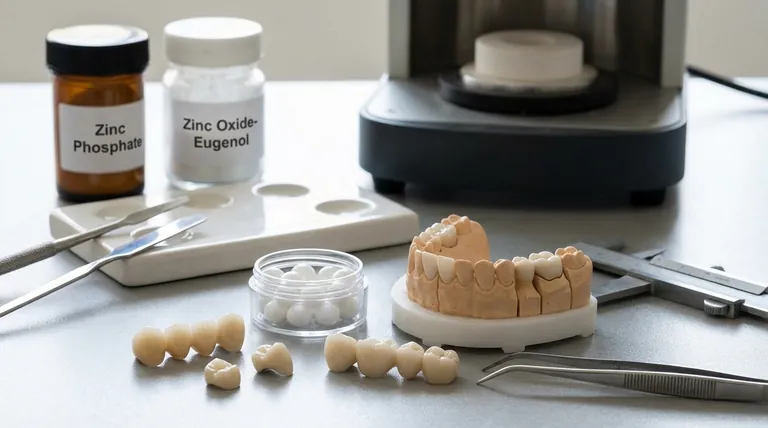
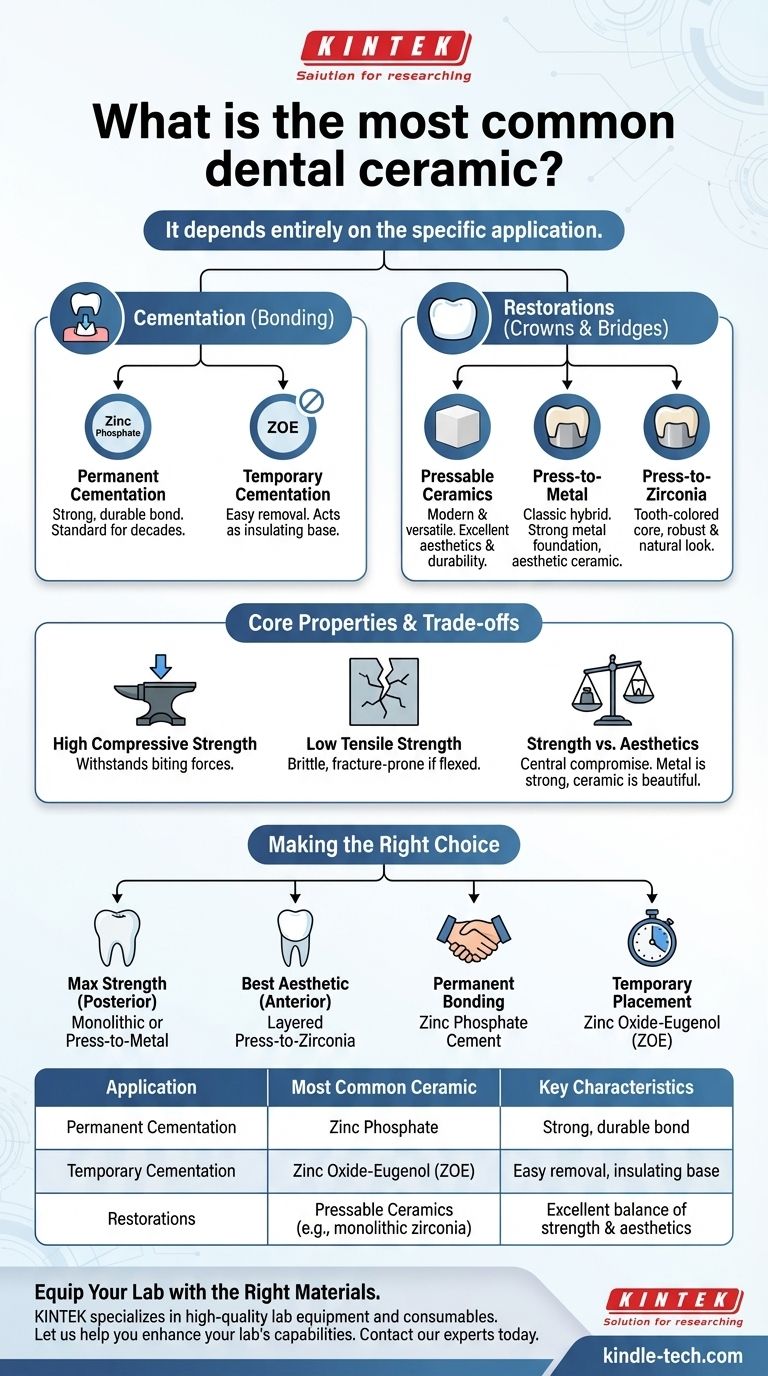
The most common dental ceramic depends entirely on its specific application. For cementing permanent crowns and bridges, zinc phosphate is a prevalent choice, while for temporary cementation, zinc oxide-eugenol (ZOE) is the standard. For the restorations themselves, such as crowns, modern pressable ceramics (like monolithic zirconia or layered materials) are extremely common due to their excellent aesthetics and durability.
The term "dental ceramic" is not monolithic; it describes a class of materials used for different purposes. The most common type is dictated by the clinical need, forcing a strategic choice between materials designed for strength, aesthetics, permanent bonding, or temporary placement.

What Defines a Dental Ceramic?
The Core Properties
Dental ceramics are inorganic, non-metallic materials created by heating minerals to high temperatures. This process gives them their signature characteristics.
They are defined by very high compressive strength, meaning they can withstand immense biting forces. However, they typically have low tensile strength and are brittle, which means they can fracture if flexed or subjected to sharp, focused stress.
The Major Categories of Use
It is critical to understand that ceramics are used in several distinct ways in dentistry, which is why a single "most common" type is impossible to name.
These materials are used for fixed prostheses like crowns and bridges, as cementation agents to bond those prostheses to teeth, and even as fillers within resin-composite restorative materials.
Ceramics for Restorations (Crowns and Bridges)
Pressable Ceramic Systems
The most modern and versatile options for creating durable, aesthetic restorations fall under the category of pressable ceramics. These materials are fabricated using heat and pressure to fit a mold perfectly.
Monolithic Restorations
A monolithic restoration is crafted from a single, uniform block of ceramic material. This approach is valued for its exceptional strength and is often used for molars where biting forces are greatest.
Press-to-Metal Restorations
This is a classic hybrid approach. A strong metal substructure is fabricated to provide foundational strength, and then a layer of aesthetic ceramic is pressed over it. This combines the durability of metal with the tooth-like appearance of ceramic.
Press-to-Zirconia Restorations
This is a more modern evolution of the press-to-metal concept. Instead of a metal alloy, a core is made from extremely strong, tooth-colored zirconia. Aesthetic ceramic is then layered on top, providing both a robust foundation and a highly natural look.
Ceramics for Dental Cementation
Zinc Phosphate: The Permanent Standard
For the permanent cementation of crowns, bridges, and other restorations, zinc phosphate has been a reliable and widely used material for decades. It creates a strong, durable bond.
Zinc Oxide-Eugenol (ZOE): The Temporary Solution
When a restoration only needs to be placed temporarily, ZOE is the most common choice. Its formulation allows for secure placement but also easy removal by the dentist later.
An Insulating Base
Both zinc phosphate and ZOE can also serve a secondary purpose as an insulating base. When placed inside a deep filling, they protect the sensitive inner pulp of the tooth from thermal shock caused by hot or cold foods and drinks.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Strength vs. Aesthetics
This is the central compromise in restorative dentistry. A press-to-metal crown is incredibly strong but the underlying metal can sometimes create a dark line at the gumline. A fully ceramic crown may be more beautiful but might not be suitable for a patient who grinds their teeth heavily.
The Brittleness Factor
While ceramics excel under compression (biting down), their brittleness makes them susceptible to fracture from shearing forces or sharp impacts. The choice of material and the design of the restoration must account for this inherent property to ensure long-term success.
Application-Specific Design
A material that works perfectly for one task is often unsuitable for another. ZOE is designed for easy removal, making it a poor choice for permanent cementation. Likewise, the high-strength monolithic zirconia used for a back molar might lack the subtle translucency needed for a front tooth.
Making the Right Choice for the Application
Understanding the distinct roles of these materials is key to appreciating modern dental care. Each one is a specialized tool selected for a specific job.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength for a posterior crown: A monolithic ceramic or a press-to-metal restoration is often the most reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is the best possible aesthetic for an anterior crown: A layered press-to-zirconia or another highly translucent ceramic system is typically selected.
- If your primary focus is permanently bonding a restoration: A ceramic cement system like zinc phosphate provides a proven, long-lasting solution.
- If your primary focus is temporary placement or tissue insulation: Zinc oxide-eugenol (ZOE) is the standard and most effective material for the task.
Ultimately, selecting the right dental ceramic is a precise decision that balances the mechanical demands of the mouth with the desired aesthetic outcome.
Summary Table:
| Application | Most Common Ceramic Type | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Permanent Cementation | Zinc Phosphate | Strong, durable bond for crowns and bridges |
| Temporary Cementation | Zinc Oxide-Eugenol (ZOE) | Easy removal, also acts as an insulating base |
| Restorations (Crowns/Bridges) | Pressable Ceramics (e.g., monolithic zirconia) | Excellent balance of strength and aesthetics |
Equip Your Lab with the Right Materials from KINTEK
Choosing the correct dental ceramic is crucial for successful patient outcomes. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to the precise needs of dental laboratories. Whether you are fabricating strong monolithic zirconia crowns or require reliable cementation materials, our products support excellence in restorative dentistry.
Let us help you enhance your lab's capabilities. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK can be your trusted partner in dental ceramics.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Advanced Engineering Fine Ceramics Boron Nitride (BN) Ceramic Parts
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- Why are zirconia grinding balls preferred for NiCrAlY-Mo-Ag powders? Ensure Maximum Purity and Durability
- What are alloys in simple words? Unlock the Power of Engineered Materials
- Why are high-purity zirconia grinding balls recommended for LATP ceramic powders? Ensure Purity and High Conductivity.
- What is the purpose of using high-hardness zirconia grinding balls? Ensure Purity & Power in Electrolyte Milling
- What are the applications of zirconia ceramics? Unlock High-Performance Solutions for Extreme Environments









