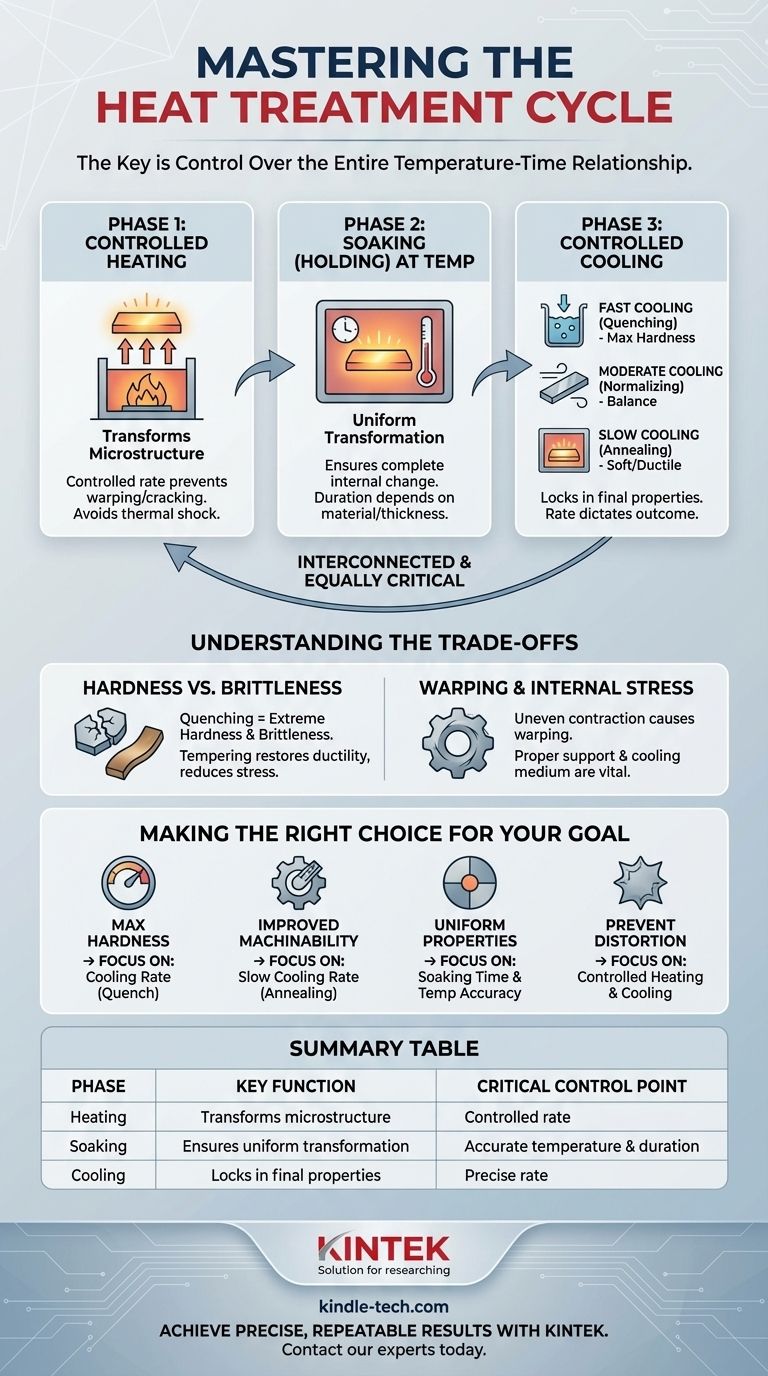
The single most important part of heat treatment is not one specific stage, but the precise and unwavering control over the entire temperature-time cycle. This cycle consists of three interconnected phases—heating, soaking, and cooling—and a failure in any one of them will compromise the final result. The correct execution of this entire profile is what transforms a material to achieve desired properties like hardness or ductility.
While many focus on the rapid cooling of a quench, the true key to successful heat treatment is understanding that every phase—heating, holding, and cooling—is codependent. The "most important part" is the discipline to control this entire relationship between temperature and time for a specific, predetermined outcome.

The Three Pillars of the Heat Treatment Cycle
Every heat treatment process, regardless of the specific goal, is built upon three fundamental and equally critical phases. Thinking of them as separate steps is a mistake; they are a continuous process where each phase sets the stage for the next.
Phase 1: Controlled Heating
The initial heating phase is about bringing the material to a specific target temperature. This temperature is chosen because it allows the material's internal crystal structure, or microstructure, to begin changing into a more malleable and uniform state (for steel, this is typically the formation of austenite).
A controlled, even heating rate is critical. Heating too quickly can induce thermal shock, causing stress, warping, or even cracking, especially in complex or large parts.
Phase 2: Soaking (Holding) at Temperature
Once the target temperature is reached, the material is "soaked," or held at that temperature for a specific duration. The purpose of soaking is to ensure the internal structural changes occur uniformly throughout the entire volume of the part.
If the soaking time is too short, the core of the material may not fully transform, leading to inconsistent and unpredictable properties. The required time depends on the material's composition, its cross-sectional thickness, and the specific process.
Phase 3: Controlled Cooling
This is often the most dramatic and visibly distinct phase. The rate at which the material is cooled from the soaking temperature "locks in" a specific final microstructure, which directly dictates its mechanical properties.
- Fast cooling (Quenching): Plunging the material into water, oil, or polymer solution traps a hard, brittle structure like martensite.
- Moderate cooling (Normalizing): Cooling in still air produces a mix of hardness and ductility.
- Slow cooling (Annealing): Cooling slowly inside the furnace creates a soft, ductile, and easily machinable structure.
The cooling rate isn't "more important" than heating or soaking; its success is entirely dependent on the previous two phases being executed correctly.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Heat treatment is not a magic bullet; it is a precise science of balancing competing properties. Understanding these trade-offs is essential for avoiding failure and achieving your actual goal.
Hardness vs. Brittleness
The most fundamental trade-off is between hardness and brittleness. A process like quenching that creates extreme hardness also makes the material very brittle and susceptible to fracture.
This is why a secondary heat treatment process called tempering is almost always performed after quenching. Tempering involves reheating the part to a much lower temperature to relieve stress and restore some ductility, reducing brittleness at the cost of a small amount of hardness.
Warping and Internal Stress
Any time you heat and cool a material, you introduce stress. If this process is not controlled, especially during cooling, different parts of the component will contract at different rates.
This uneven contraction can cause the part to warp, distort, or even crack. Proper support in the furnace and selection of the right cooling medium are critical to mitigating these risks.
The Goal Dictates the Process
There is no universally "best" heat treatment cycle. The desired outcome dictates the exact parameters. As the benefits show, the goals can be vastly different:
- Increasing strength requires a very different cycle (e.g., quenching and tempering) than relieving stresses to improve machinability (e.g., annealing).
- Improving wear resistance on a surface is different from changing the properties of the entire part.
Because the goal changes the process, the "most critical" control point also changes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine what part of the process requires your closest attention, you must first be clear about your objective.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum hardness: The cooling rate during the quench is your most critical variable and must be aggressively controlled.
- If your primary focus is improving machinability or ductility: The slow, carefully controlled cooling rate during an annealing cycle is the most important phase.
- If your primary focus is ensuring uniform properties in a thick or complex part: The soaking time and temperature accuracy are paramount to guarantee a complete internal transformation.
- If your primary focus is preventing distortion: The controlled heating and cooling rates, along with proper part support, are the most vital elements to manage.
Ultimately, successful heat treatment is achieved by mastering the relationship between the material, temperature, and time.
Summary Table:
| Heat Treatment Phase | Key Function | Critical Control Point |
|---|---|---|
| Heating | Transforms material microstructure | Controlled rate to prevent warping/cracking |
| Soaking (Holding) | Ensures uniform transformation | Accurate temperature and duration |
| Cooling | Locks in final properties | Precise rate (quench, air, or furnace cool) |
Achieve precise, repeatable heat treatment results with KINTEK.
Whether your goal is maximum hardness, improved ductility, or stress relief, the right equipment is essential for controlling the critical temperature-time cycle. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces, ovens, and quenching systems that deliver the accuracy and reliability your laboratory demands.
Our heat treatment solutions help you:
- Eliminate guesswork with precise digital temperature controllers.
- Ensure uniform results with consistent heating and soaking performance.
- Prevent part failure by accurately managing cooling rates.
Ready to master your heat treatment process? Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect equipment for your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the five methods of synthesis of nanoparticles? A Guide to Top-Down & Bottom-Up Approaches
- What is the difference between batch and continuous reactor for pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Needs
- What are the waste products of biomass? Uncover Byproducts from Ash to Biochar
- Why is it necessary to use a mechanical stirrer or shaker during azo dye degradation experiments? Optimize Your Results
- Which is used for elemental analysis? XRF for Fast, Non-Destructive Material Testing
- What are the advantages of centrifugal extraction? Achieve High-Speed, High-Purity Separations
- What is a rotary flash evaporator used for? Gentle Solvent Removal for Heat-Sensitive Compounds
- What is the source of energy for pyrolysis? From External Heat to Self-Sustaining Systems



















