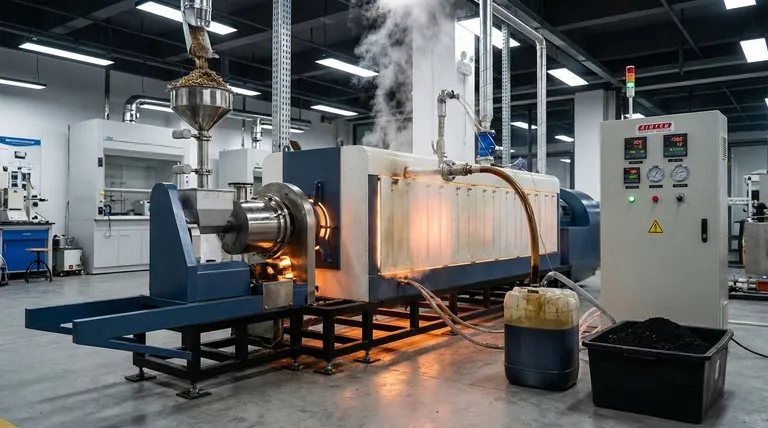
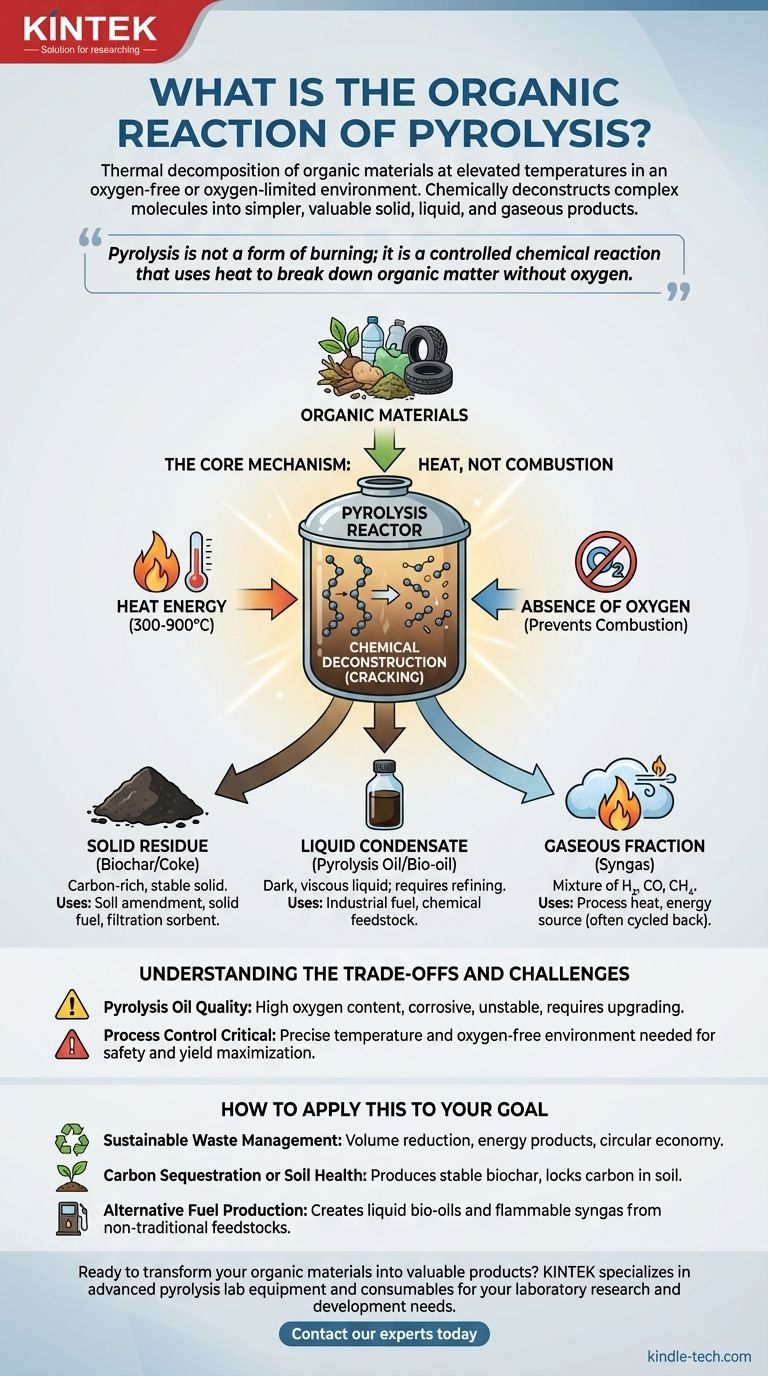
In essence, pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of organic materials at elevated temperatures in an oxygen-free or oxygen-limited environment. Instead of burning and releasing energy as heat through combustion, this process chemically deconstructs complex organic molecules into simpler, often more valuable, solid, liquid, and gaseous products.
Pyrolysis is not a form of burning; it is a controlled chemical reaction that uses heat to break down organic matter without oxygen. This fundamental difference allows it to transform waste materials into useful products like biochar, bio-oil, and fuel gas.

The Core Mechanism: Heat, Not Combustion
Pyrolysis is fundamentally a process of chemical deconstruction. Understanding its core conditions reveals why it is a powerful tool for material transformation rather than simple disposal.
Defining the Reaction Conditions
The defining characteristic of pyrolysis is the absence of oxygen. When organic material is heated with oxygen, the result is combustion—a rapid oxidation that produces carbon dioxide, water, and ash.
By removing oxygen, pyrolysis prevents combustion. Instead, the applied heat energy breaks the chemical bonds within the large organic molecules, causing them to decompose into smaller, more stable components.
The Chemical Transformation
The process targets large organic polymers found in materials like biomass, plastics, or tires. The intense heat (typically 300-900°C) provides the energy to fracture these long molecular chains.
This "cracking" results in a mixture of products. Some molecules recombine into a stable, carbon-rich solid, while others become condensable liquids or non-condensable gases. The exact product distribution depends heavily on the temperature, heating rate, and feedstock material.
The Primary Products of Pyrolysis
The output of a pyrolysis reaction is never a single substance but a mixture of three distinct fractions: a solid, a liquid, and a gas.
The Solid Residue: Biochar and Coke
The primary solid product is a stable, carbon-rich material known as biochar (from biomass) or coke (from other sources). This is not the same as ash from combustion.
Biochar is highly valued in agriculture as a soil amendment to improve water retention and nutrient availability. Both biochar and coke can also be used as sorbents for filtration or as a solid fuel source.
The Liquid Condensate: Pyrolysis Oil
When the hot vapor produced during pyrolysis is cooled, a portion condenses into a liquid commonly called pyrolysis oil or bio-oil.
This dark, viscous liquid can be used as an industrial fuel or further refined to produce transportation fuels like biodiesel and other valuable chemicals. It is a way to create liquid fuel from solid waste.
The Gaseous Fraction: Syngas
The remaining non-condensable gases are a mixture often referred to as syngas or pyrolysis gas. This gas is rich in hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and methane.
In most pyrolysis plants, this gas is not wasted. It is typically cycled back into the system and burned to provide the heat energy required to sustain the pyrolysis reaction, making the process more energy-efficient.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While pyrolysis is a powerful technology, it is not without its complexities and limitations. The quality and handling of its products present real-world engineering challenges.
The Issue with Pyrolysis Oil Quality
Pyrolysis oil is not a direct substitute for crude petroleum. It has a high oxygen content, which makes it corrosive to standard pipes and engines, thermally unstable, and immiscible with conventional fossil fuels.
This means it often requires significant upgrading or refining before it can be used in standard infrastructure, adding cost and complexity to the overall process.
Process Control is Critical
Unlike simply burning waste, pyrolysis requires a highly controlled reactor environment. Maintaining the correct temperature and ensuring a truly oxygen-free atmosphere is essential for maximizing the yield of desired products and ensuring safety. This technical requirement makes it more complex and capital-intensive than incineration.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
Understanding the outputs of pyrolysis allows you to see its potential application for different objectives.
- If your primary focus is sustainable waste management: Pyrolysis dramatically reduces the volume of waste while converting it into energy products, fitting a circular economy model.
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration or soil health: Pyrolysis is a premier method for producing stable biochar, which locks carbon into the soil for centuries.
- If your primary focus is alternative fuel production: Pyrolysis provides a pathway to create liquid bio-oils and flammable syngas from non-traditional, solid feedstocks.
Ultimately, pyrolysis offers a sophisticated method to unlock the chemical value stored within organic materials rather than simply destroying them.
Summary Table:
| Product Type | Key Characteristics | Primary Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Solid (Biochar/Coke) | Carbon-rich, stable solid | Soil amendment, solid fuel, filtration sorbent |
| Liquid (Pyrolysis Oil) | Dark, viscous liquid; requires refining | Industrial fuel, chemical feedstock |
| Gas (Syngas) | Mixture of H₂, CO, CH₄ | Process heat, energy source |
Ready to transform your organic materials into valuable products?
KINTEK specializes in advanced pyrolysis lab equipment and consumables, helping you precisely control the reaction to maximize yields of biochar, bio-oil, and syngas. Whether your goal is sustainable waste management, carbon sequestration, or alternative fuel production, our solutions are designed for your laboratory's research and development needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our pyrolysis technology can help you achieve your goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- CVD Diamond for Thermal Management Applications
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the process of catalytic pyrolysis? Upgrade Biomass and Plastic Waste into High-Quality Fuel
- How is biochar made from pyrolysis? Unlock the secrets of turning biomass into valuable carbon
- How long does it take to produce biochar? From Seconds to Hours, Based on Your Goal
- What are the main parts of a rotary kiln? A Guide to Its Core Components and Functions
- What is temperature controlled pyrolysis? Master Heat to Turn Waste into Fuel, Char, or Gas
- What does a rotary calciner do? Achieve Uniform Thermal Processing for Your Materials
- Why is the rotary kiln inclined? To Control Material Flow and Reaction Time
- What are the materials used in the refractory lining of kilns? Choose the Right Lining for Maximum Durability

















