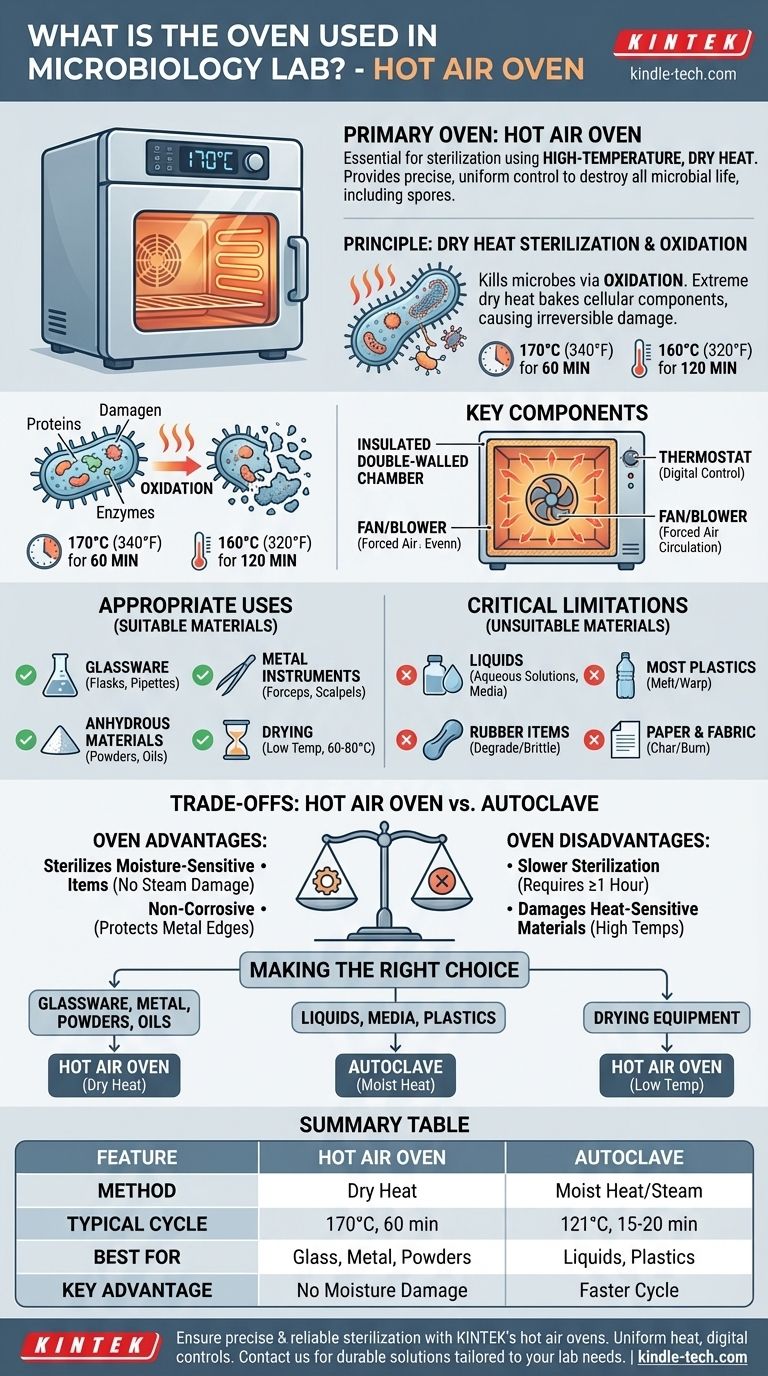
In a microbiology lab, the primary oven used is a hot air oven. This is a piece of essential laboratory equipment designed for sterilization using high-temperature, dry heat. Unlike a standard kitchen oven, it provides precise and uniform temperature control, which is critical for reliably destroying all forms of microbial life, including resilient bacterial spores.
The core function of a hot air oven is to provide dry heat sterilization. It is the go-to instrument for sterilizing materials that can tolerate high temperatures but would be damaged by the moisture and pressure of an autoclave, such as certain glassware, metal instruments, and anhydrous powders or oils.

The Principle of Dry Heat Sterilization
To understand the role of a hot air oven, you must first understand how it works. It doesn't just warm things up; it uses a specific method to achieve sterility.
How It Kills Microbes
A hot air oven kills microorganisms through a process of oxidation. The extreme, dry heat essentially bakes the cellular components—proteins, enzymes, and nucleic acids—causing irreversible damage and leading to cell death. This is a fundamentally different and slower mechanism than the steam coagulation used in an autoclave.
The Role of Temperature and Time
Achieving sterility is a function of both temperature and time. Because dry heat penetrates and kills more slowly than moist heat, higher temperatures and longer exposure times are required.
Commonly accepted standards for sterilization in a hot air oven are:
- 170°C (340°F) for 60 minutes
- 160°C (320°F) for 120 minutes
These time periods begin only after the contents of the oven have reached the target temperature.
Key Components of the Oven
A laboratory hot air oven is more than just a heated box. It typically includes:
- An insulated double-walled chamber to maintain high temperatures efficiently.
- A thermostat for precise digital control of the internal temperature.
- A fan or blower for forced air circulation, ensuring heat is distributed evenly throughout the chamber to eliminate cold spots.
Appropriate Uses and Critical Limitations
Knowing what to put in a hot air oven is just as important as knowing what not to. Using it incorrectly can destroy valuable materials or fail to achieve sterility.
Suitable Materials
The hot air oven is the ideal choice for sterilizing:
- Glassware: Empty flasks, beakers, pipettes, and Petri dishes.
- Metal Instruments: Forceps, scalpels, and scissors.
- Anhydrous Materials: Heat-stable powders, waxes, and oils that steam cannot penetrate.
It is also frequently used for drying washed glassware at lower temperatures (e.g., 60-80°C) before sterilization.
Unsuitable Materials
You must never place the following items in a hot air oven for sterilization:
- Liquids: Aqueous solutions like culture media or water will simply evaporate.
- Most Plastics: The high temperatures will melt or warp almost all plastics, including most storage containers and pipette tips.
- Rubber Items: Tubing and stoppers will be degraded and become brittle.
- Paper and Fabric: While sometimes used in highly specialized depyrogenation cycles, these materials will typically char or burn at standard sterilization temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Hot Air Oven vs. Autoclave
The hot air oven does not exist in a vacuum. Its primary counterpart in a microbiology lab is the autoclave, which sterilizes using high-pressure saturated steam (moist heat).
Advantage: Sterilizes Moisture-Sensitive Items
This is the oven's chief advantage. It is the only reliable way to sterilize powders, oils, and other materials that would be ruined by moisture or are impermeable to steam.
Advantage: Non-Corrosive
The dry environment does not promote rust, making it an excellent choice for protecting the sharp edges and finish of fine metal instruments over the long term.
Disadvantage: Slower Sterilization Cycle
Dry heat sterilization is significantly less efficient than moist heat. A standard autoclave cycle might run for 15-20 minutes at 121°C, while a hot air oven requires at least an hour at a much higher temperature.
Disadvantage: Damages Heat-Sensitive Materials
The very high temperatures required for sterilization limit the oven's use to only glass, metal, and certain heat-proof substances. The vast majority of lab plastics cannot be sterilized this way.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct sterilization method is fundamental to good laboratory practice. Your choice between a hot air oven and an autoclave depends entirely on the material you need to sterilize.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing glassware, metal instruments, powders, or oils: Use the hot air oven to ensure sterility without damage from moisture.
- If your primary focus is sterilizing culture media, liquid solutions, biohazardous waste, or autoclavable plastics: Use the autoclave for its speed and effectiveness with moisture-tolerant items.
- If your primary focus is simply drying clean lab equipment: Use the hot air oven at a much lower, non-sterilizing temperature (e.g., 80°C).
Understanding when and why to use each tool is a foundational skill for achieving reliable and reproducible results in microbiology.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Hot Air Oven | Autoclave |
|---|---|---|
| Sterilization Method | Dry Heat | Moist Heat (Steam) |
| Typical Cycle | 170°C for 60 min | 121°C for 15-20 min |
| Best For | Glassware, metal, powders, oils | Liquids, culture media, plastics |
| Key Advantage | No moisture damage | Faster cycle |
Ensure precise and reliable sterilization in your lab with KINTEK's hot air ovens. Our laboratory ovens are designed with uniform heat distribution and digital controls to meet the rigorous demands of microbiology. Whether you need to sterilize glassware, metal instruments, or heat-stable powders, KINTEK provides durable, efficient solutions tailored to your laboratory needs. Contact us today to find the perfect oven for your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- Rubber Vulcanizer Vulcanizing Machine Plate Vulcanizing Press for Lab
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Laboratory High Throughput Tissue Grinding Mill Grinder
People Also Ask
- Why do we use sputter coating? For Superior Thin Film Uniformity and Adhesion
- What is the sintering process? A Guide to Manufacturing with Powdered Materials
- Which type of water should be used in water bath for laboratory? Protect Your Equipment and Experiments
- Why is debinding important? The Critical Step for Strong, Dense Metal and Ceramic Parts
- Why is biomass a better alternative to oil? Unlock a Sustainable, Circular Energy Future
- Do diamond testing machines work? Choose the Right Tester for Accurate Results
- Why magnets are placed behind the target in sputtering? To Trap Electrons for Faster, Purer Coatings
- What is ramp rate and how does that affect a melting point measurement? Master the Key to Accurate Thermal Analysis



















