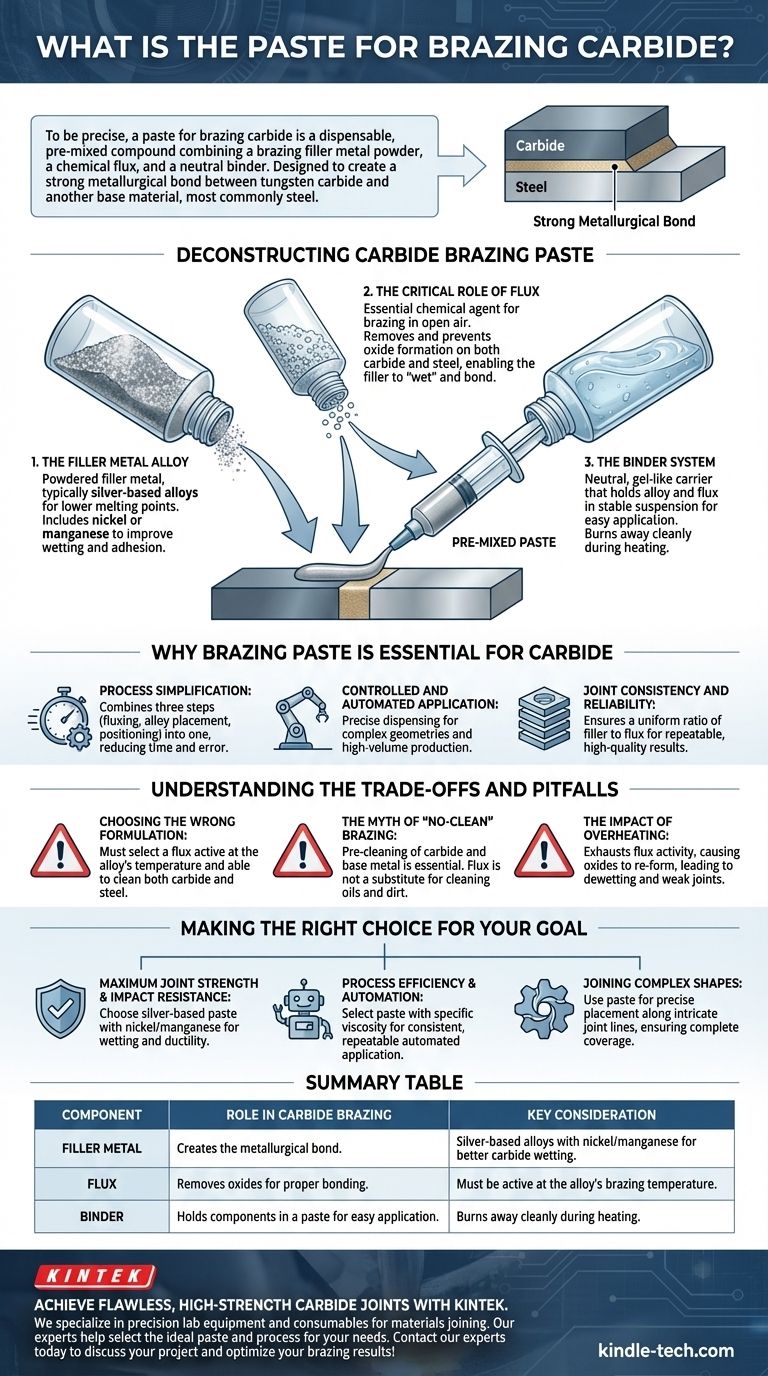
To be precise, a paste for brazing carbide is a dispensable, pre-mixed compound that combines a brazing filler metal powder, a chemical flux, and a neutral binder. This formulation is specifically designed to create a strong metallurgical bond between a tungsten carbide component and another base material, most commonly steel.
The core function of carbide brazing paste is to simplify the joining process by delivering the two most critical components—filler alloy and flux—in a single, controlled application. Success depends entirely on choosing a paste with an alloy and flux system engineered for the unique challenges of wetting both carbide and steel.
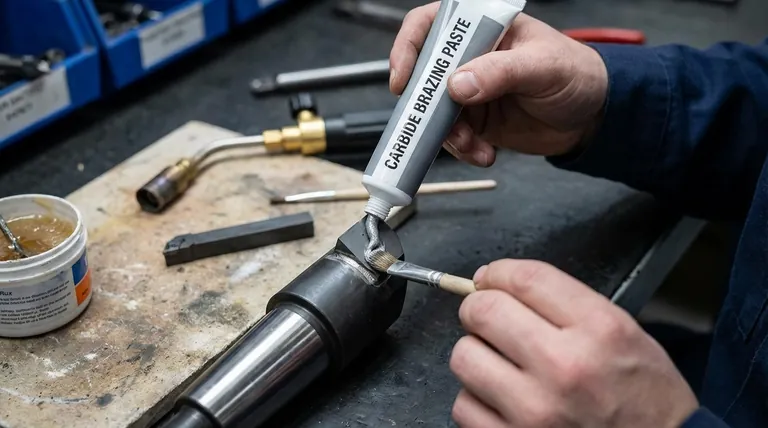

Deconstructing Carbide Brazing Paste
To understand how to use it effectively, you must first understand its three primary components. Each plays a distinct and critical role in the success of the braze joint.
The Filler Metal Alloy
The heart of the paste is the powdered filler metal. For carbide applications, these are typically silver-based alloys.
Silver alloys are chosen for their lower melting temperatures, which reduces the risk of thermal shock and cracking the brittle carbide. They often include elements like nickel or manganese to improve wetting and adhesion to the carbide surface.
The Critical Role of Flux
Flux is the essential chemical agent that makes brazing possible in open-air heating. Its job is to remove and prevent the formation of oxides on both the carbide and the steel surfaces.
Without flux, the molten filler metal cannot "wet" the parent materials. Instead of flowing smoothly and bonding, it would bead up like water on a waxed surface, resulting in a failed joint.
The Binder System
The binder is a neutral, gel-like substance that holds the alloy powder and flux in a stable, paste-like suspension.
This carrier makes the material easy to apply manually with a brush or automatically with dispensing equipment. During the heating cycle, the binder simply burns away completely, leaving only the active alloy and flux behind.
Why Brazing Paste is Essential for Carbide
While you can braze using separate flux and solid wire or shims, a paste offers distinct advantages, especially for the precise requirements of joining carbide.
Process Simplification
A paste combines three steps (fluxing, alloy placement, and positioning) into a single action. This reduces application time and minimizes the chance of operator error, such as missing a spot with the flux.
Controlled and Automated Application
The consistency of a paste allows for highly precise application. You can dispense an exact amount of material directly where it's needed, which is ideal for complex joint geometries or high-volume, automated production lines.
Joint Consistency and Reliability
Using a pre-mixed paste ensures a perfect, uniform ratio of filler metal to flux for every joint. This consistency is a key factor in achieving repeatable, high-quality results across a production run.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
While paste simplifies the process, it does not eliminate the need for proper procedure and understanding. Certain pitfalls can still lead to joint failure.
Choosing the Wrong Formulation
"Carbide brazing paste" is a category, not a single product. Using a paste designed for copper will fail on carbide. You must select a formulation where the flux is active at the alloy's specific brazing temperature and is powerful enough to clean both steel and carbide.
The Myth of "No-Clean" Brazing
Paste does not remove the need for pre-cleaning. Both the carbide and the base metal must be mechanically or chemically cleaned to remove all oils, grease, and dirt before the paste is applied. The flux is designed to handle metal oxides, not workshop contaminants.
The Impact of Overheating
Overheating is a common and critical mistake. If you heat the joint too high or for too long, you can exhaust the chemical activity of the flux before the braze is complete. This allows oxides to re-form, causing the filler metal to dewet and resulting in a weak, porous joint.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The right approach depends entirely on the desired outcome for your specific application.
- If your primary focus is maximum joint strength and impact resistance: Choose a paste with a silver-based alloy that includes nickel or manganese, as this promotes wetting on carbide and adds ductility to the finished joint.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency and automation: Select a paste with a specific viscosity and dispensing characterstic engineered for your automated equipment to ensure consistent, repeatable application.
- If your primary focus is joining complex shapes or dissimilar thicknesses: Use a paste to ensure the alloy and flux are placed precisely along intricate joint lines, preventing voids and ensuring complete coverage.
Ultimately, selecting the correct brazing paste is the first step in a process that demands control over cleanliness, application, and heat.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role in Carbide Brazing | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Filler Metal | Creates the metallurgical bond. | Silver-based alloys with nickel/manganese for better carbide wetting. |
| Flux | Removes oxides for proper bonding. | Must be active at the alloy's brazing temperature. |
| Binder | Holds components in a paste for easy application. | Burns away cleanly during heating. |
Achieve flawless, high-strength carbide joints with the right materials and expertise. KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables for materials joining applications. Our team can help you select the ideal brazing paste and process for your specific carbide tooling or component needs, ensuring maximum joint strength and production efficiency. Contact our experts today to discuss your project and optimize your brazing results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Purity Zinc Foil for Battery Lab Applications
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Laboratory High Throughput Tissue Grinding Mill Grinder
- Aluminum Foil Current Collector for Lithium Battery
- Stainless Steel Quick Release Vacuum Chain Three-Section Clamp
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between PPF and coating? Armor vs. Slick Shell for Your Car
- What are the three types of coating? A Guide to Architectural, Industrial, and Special Purpose
- What is the purpose of laminating? Protect and Enhance Your Documents for Long-Term Use
- What are the barriers to plastic recycling? The Economic, Material, and Technical Hurdles Explained
- What are the two methods that can be used to prevent corrosion of a metal? Barrier vs. Sacrificial Protection Explained








