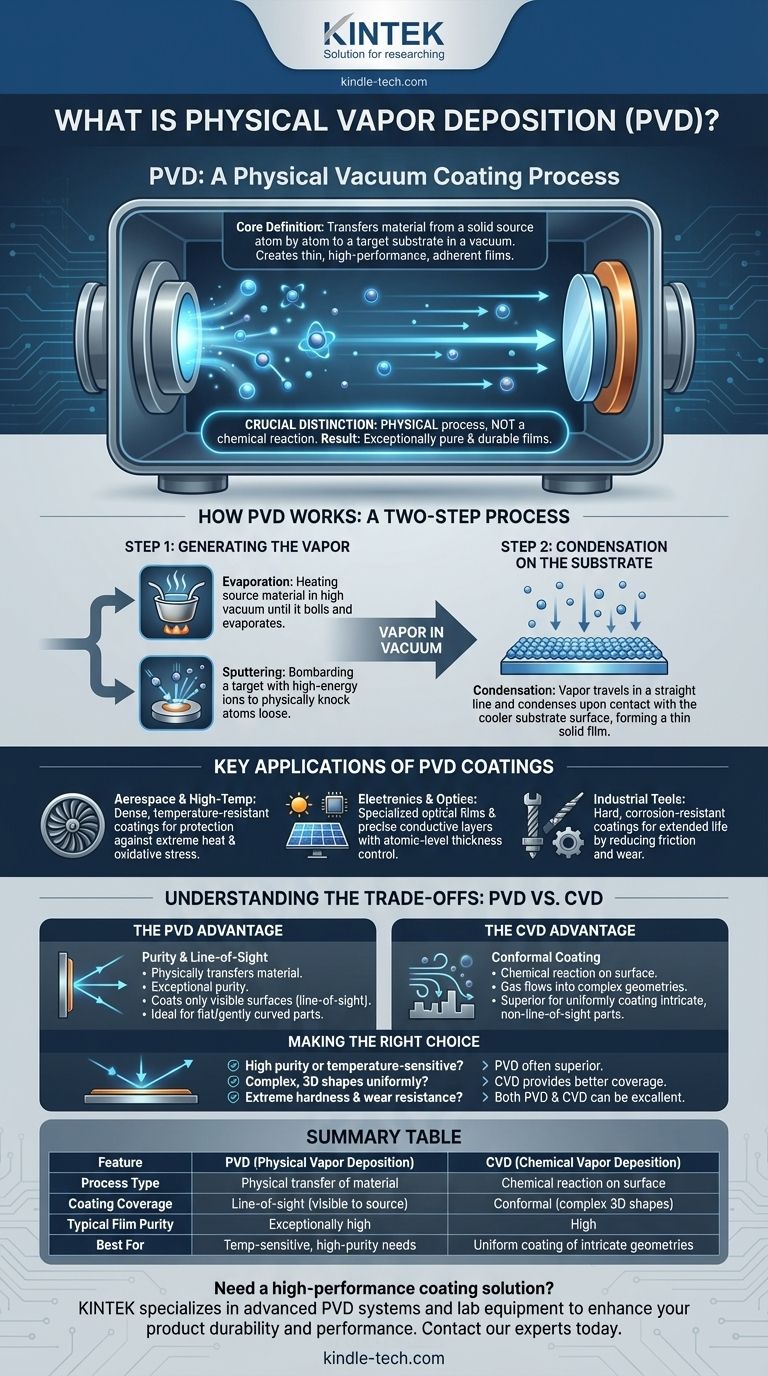
At its core, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a vacuum coating process that transfers a material from a solid source onto a target object, known as a substrate, atom by atom. This method involves vaporizing the source material and allowing it to condense as a thin, high-performance film on the substrate's surface. PVD is renowned for creating coatings with excellent adhesion that can be applied to materials with very high melting points.
The crucial distinction of PVD is that it is a physical process, not a chemical one. Unlike other methods that rely on chemical reactions, PVD physically transports material from a source to a surface, resulting in exceptionally pure and durable thin films.

How PVD Works: A Two-Step Process
PVD fundamentally operates by turning a solid material into a vapor, transporting it through a vacuum, and condensing it onto a part to form a coating. This is generally accomplished in two main stages.
Step 1: Generating the Vapor
The initial step is to convert the solid coating material into a gaseous vapor phase. The two most common methods for this are evaporation and sputtering.
Evaporation involves heating the source material in a high vacuum until it boils and evaporates. These evaporated particles then travel through the vacuum chamber.
Sputtering (referred to as spraying in some contexts) uses a different mechanism. A target made of the source material is bombarded with high-energy ions, which physically knock atoms loose from the target's surface, ejecting them into the vacuum chamber.
Step 2: Condensation on the Substrate
Once the material is in a vapor state, it travels in a straight line through the vacuum chamber until it strikes the substrate.
Upon contact with the cooler substrate surface, the vaporized atoms condense and form a thin, solid film. The vacuum environment is critical because it prevents these atoms from colliding with air or other particles, ensuring a pure and uniform coating.
Key Applications of PVD Coatings
The characteristics of PVD films—purity, hardness, and temperature resistance—make them essential in several high-tech industries.
Aerospace and High-Temperature Environments
Aerospace companies utilize PVD to apply dense, temperature-resistant coatings to critical components. These films protect parts from the extreme temperatures and oxidative stress they encounter during operation, significantly enhancing durability.
Electronics and Optics
PVD is used to apply specialized optical films for solar panels and precise conductive layers in semiconductors. The ability to control film thickness at the atomic level is essential for the performance of these devices.
Industrial Tools and Components
For cutting tools, molds, and other components used in harsh industrial settings, PVD provides hard, corrosion-resistant coatings. This dramatically extends the life and performance of the tools by reducing friction and wear.
Understanding the Trade-offs: PVD vs. CVD
To fully grasp PVD, it is helpful to compare it to the other major category of vapor deposition: Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
The PVD Advantage: Purity and Line-of-Sight
Because PVD physically transfers the source material, the resulting film is exceptionally pure. It is also a line-of-sight process, meaning the coating is only applied to surfaces that can be "seen" directly from the source. This is excellent for coating flat or gently curved surfaces with high precision.
The CVD Advantage: Conformal Coating
CVD, by contrast, exposes the substrate to a volatile precursor gas that undergoes a chemical reaction on the surface to create the film. This gas can flow around and into complex geometries, making CVD superior for uniformly coating intricate, non-line-of-sight surfaces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct deposition method depends entirely on the requirements of your application and the geometry of the part you are coating.
- If your primary focus is high-purity coatings or temperature-sensitive parts: PVD is often the superior choice due to its lower processing temperatures and direct material transfer.
- If your primary focus is coating complex, three-dimensional shapes uniformly: CVD's gas-based process provides better conformal coverage than the line-of-sight nature of PVD.
- If your primary focus is extreme hardness and wear resistance: Both PVD and CVD can produce excellent results, so the decision will depend on the specific coating material and substrate involved.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental difference between PVD's physical transfer and CVD's chemical reaction is the key to selecting the right technology for your specific needs.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) | CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) |
|---|---|---|
| Process Type | Physical transfer of material | Chemical reaction on surface |
| Coating Coverage | Line-of-sight (surfaces visible to source) | Conformal (coats complex 3D shapes) |
| Typical Film Purity | Exceptionally high | High |
| Best For | Temperature-sensitive parts, high-purity needs | Uniform coating of intricate geometries |
Need a high-performance coating solution for your lab or production line?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including PVD systems, to meet your specific coating requirements. Whether you need the extreme purity of PVD for sensitive components or are exploring other deposition methods, our expertise can help you enhance product durability and performance.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can provide the right equipment and consumables for your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the advantages of plasma enhanced CVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition


















