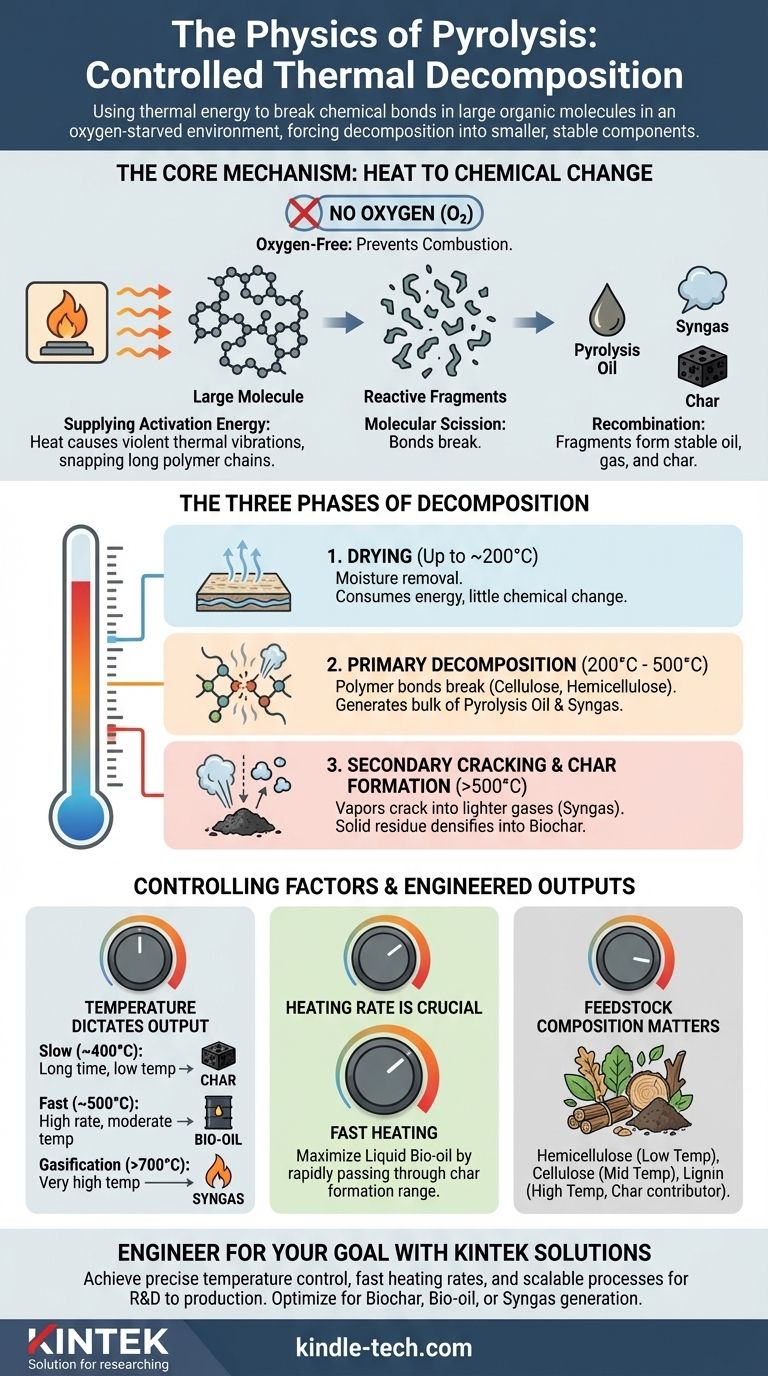
From a physics perspective, pyrolysis is the process of using thermal energy to break the strong chemical bonds within large organic molecules in an oxygen-starved environment. Instead of burning, the material is forced to decompose, or "crack," into a mix of smaller, more stable liquid, gas, and solid molecules. This transformation is driven by supplying enough kinetic energy (heat) to overcome the activation energy of the bonds themselves.
The core principle of pyrolysis is not just heating, but controlled thermal decomposition. By eliminating oxygen, you prevent combustion and instead use thermal vibration to physically break down complex molecules into simpler, valuable components like oils, gases, and char.
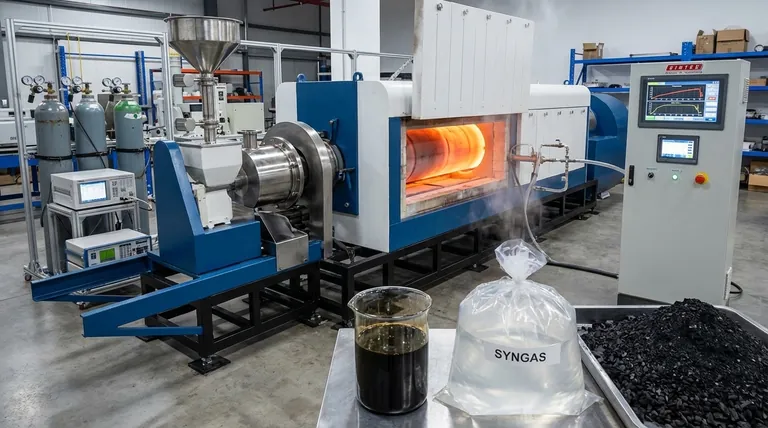

The Core Mechanism: From Thermal Energy to Chemical Change
Supplying Activation Energy
All chemical bonds have an "activation energy"—a minimum amount of energy required to break them. In pyrolysis, heat provides this energy.
As a material is heated, its molecules vibrate more and more violently. At a specific temperature, these thermal vibrations become strong enough to snap the long polymer chains that make up materials like plastic or biomass.
The Critical Role of an Oxygen-Free Environment
If oxygen were present, this process would be called combustion. The heated molecules would rapidly react with oxygen in a highly exothermic reaction, releasing energy and forming simple oxides like carbon dioxide (CO₂) and water (H₂O).
By removing oxygen, you remove the key ingredient for burning. The molecules have no choice but to break apart under the thermal stress, a process known as thermal cracking.
Molecular Scission and Recombination
Once the large polymer chains are broken (scission), they form smaller, often unstable molecular fragments.
These highly reactive fragments immediately seek stability by recombining into new, smaller molecules. This rearrangement is what produces the final outputs: pyrolysis oil (a liquid), syngas (a non-condensable gas), and char (a solid carbon residue).
The Three Phases of Pyrolytic Decomposition
The process does not happen all at once. As temperature increases, the material passes through distinct physical and chemical stages.
Phase 1: Drying (Up to ~200°C)
The initial application of heat drives off any free or trapped water within the feedstock. This phase consumes significant energy but does not yet cause major chemical decomposition of the core material.
Phase 2: Primary Decomposition (200°C - 500°C)
This is the heart of pyrolysis. The primary chemical bonds of the feedstock's polymers—such as cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin in biomass—begin to break apart.
This stage generates the bulk of the condensable vapors that, when cooled, form the valuable pyrolysis oil. Non-condensable gases are also released.
Phase 3: Secondary Cracking and Char Formation (>500°C)
As temperatures rise further, the process continues. The vapors produced in Phase 2 can break down even more (secondary cracking) if they remain in the hot reactor, creating lighter, simpler gas molecules.
Simultaneously, the remaining solid residue continues to densify and release any remaining volatile compounds, ultimately forming a stable, carbon-rich solid known as biochar.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Controlling Factors
The final product distribution is not random; it is a direct result of the physical conditions you control.
Temperature Dictates the Output
The final temperature is the most critical control parameter.
- Slow Pyrolysis (Low Temp, ~400°C): Longer residence times and lower temperatures favor the production of char.
- Fast Pyrolysis (Moderate Temp, ~500°C): High heating rates and moderate temperatures maximize the yield of liquid oil.
- Gasification (High Temp, >700°C): Very high temperatures favor the secondary cracking of all components into syngas.
Heating Rate is Crucial for Liquids
To maximize liquid bio-oil, you must heat the material as quickly as possible. A fast heating rate ensures the material passes rapidly through the lower temperature ranges where char is formed, pushing the reaction toward vaporization instead.
Feedstock Composition Matters
The physics is consistent, but the starting material changes the outcome. In biomass, for example, hemicellulose decomposes at the lowest temperature, followed by cellulose. Lignin is the most resilient and is the primary contributor to the final char yield.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the physics of pyrolysis allows you to engineer the process for a specific outcome. By precisely controlling the physical parameters, you can dictate the chemical result.
- If your primary focus is producing biochar for agriculture: Use slow pyrolysis with lower temperatures and longer residence times to maximize the final solid yield.
- If your primary focus is creating liquid biofuels (bio-oil): Use fast pyrolysis with rapid heating rates and carefully controlled peak temperatures (around 500°C) to maximize vaporization and subsequent condensation.
- If your primary focus is generating syngas for energy: Use very high temperatures (>700°C) to ensure complete secondary cracking of vapors into simple, non-condensable gas molecules.
By mastering these physical principles, you can manipulate the pyrolysis process to transform diverse feedstocks into a precisely targeted set of valuable resources.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Phase | Temperature Range | Key Process | Primary Outputs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drying | Up to ~200°C | Moisture removal | Water vapor |
| Primary Decomposition | 200°C - 500°C | Polymer bond breaking | Pyrolysis oil, syngas |
| Secondary Cracking & Char Formation | >500°C | Vapor breakdown & solid densification | Syngas, biochar |
Ready to engineer your pyrolysis process for maximum efficiency and targeted output?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. Whether you're focused on optimizing bio-oil yield, producing high-quality biochar, or maximizing syngas generation, our precise heating systems and reactors are engineered to give you the control you need.
We help our laboratory customers:
- Achieve precise temperature control for consistent results
- Implement fast heating rates to maximize liquid yields
- Scale your process from R&D to production with reliable equipment
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can advance your pyrolysis projects. Get in touch via our contact form to speak with an expert.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products



















