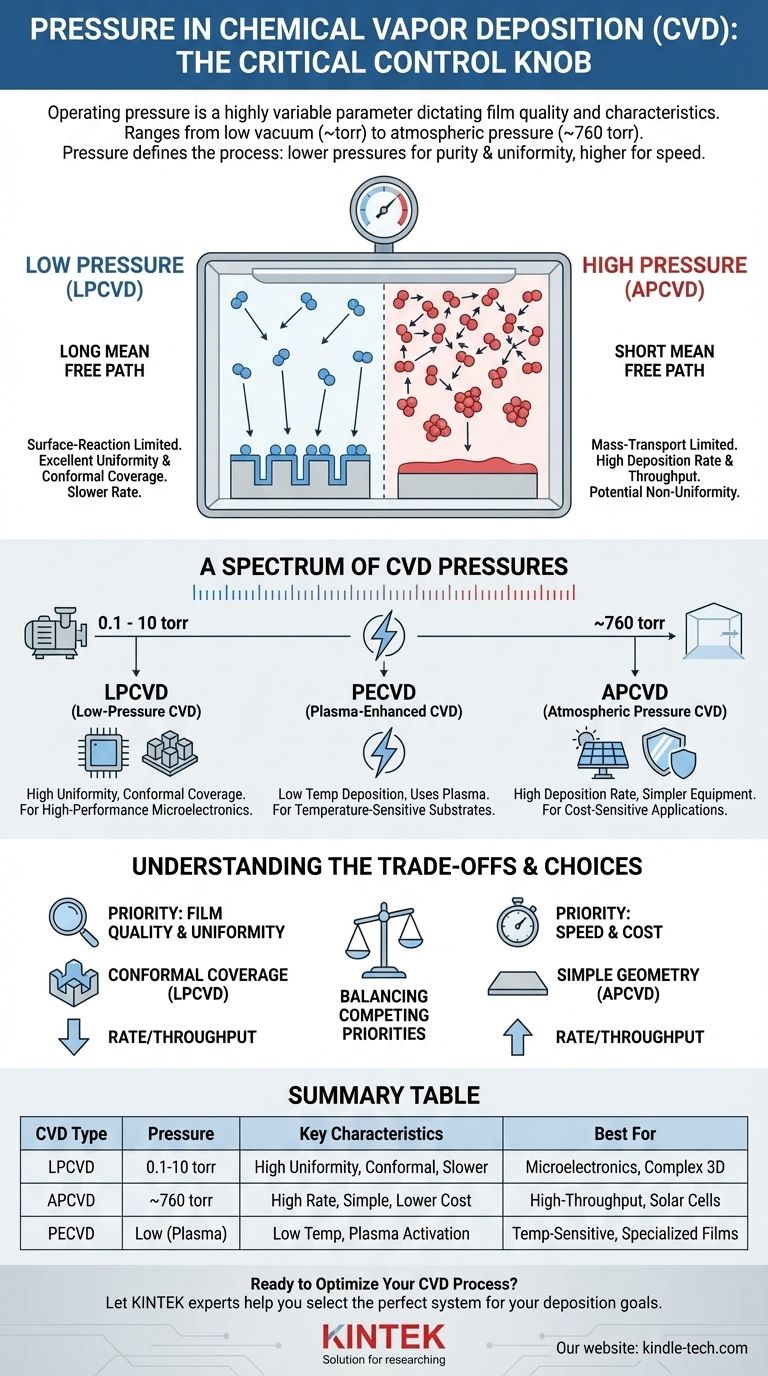
In chemical vapor deposition (CVD), the operating pressure is a critical, highly variable parameter that directly influences the quality and characteristics of the deposited film. The process typically operates in a wide range, from a low vacuum of just a few torr (a unit of pressure) to pressures at or even above standard atmospheric pressure (760 torr).
The choice of pressure in a CVD system is not arbitrary; it fundamentally defines the process itself. Lower pressures promote high-purity, uniform films by controlling molecular interactions, while higher pressures are used to achieve faster deposition rates, often at the expense of that uniformity.

The Role of Pressure in the CVD Process
To understand CVD, you must see pressure as a primary control knob for the entire system. It dictates the environment within the reaction chamber and, therefore, the outcome of the deposition.
Controlling Gas Molecule Behavior
The pressure inside the chamber determines the density of the precursor gas molecules. This, in turn, dictates the mean free path—the average distance a molecule travels before colliding with another.
At low pressure, the mean free path is long. Molecules are more likely to travel unimpeded from the gas inlet to the substrate surface, resulting in highly controlled, surface-driven reactions.
At high pressure, the mean free path is very short. Molecules collide frequently with each other in the gas phase, long before they ever reach the substrate.
Impact on Deposition Mechanism
This difference in molecular behavior directly affects how the film grows.
Low-pressure processes are often surface-reaction limited. The deposition rate is governed by the chemical reaction speed on the substrate itself, leading to excellent film uniformity and the ability to coat complex shapes.
High-pressure processes tend to be mass-transport limited. The rate is governed by how quickly reactant gases can diffuse through the dense boundary layer of gas above the substrate. This is faster but can lead to non-uniform films.
A Spectrum of CVD Pressures
The wide pressure range mentioned isn't arbitrary; it gives rise to distinct categories of CVD, each optimized for different applications.
Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD)
Operating at pressures typically between 0.1 and 10 torr, LPCVD relies on a vacuum system. The long mean free path ensures that precursor gases can evenly coat all surfaces within the chamber.
This results in films with outstanding uniformity and conformity (the ability to coat intricate, 3D structures), making it essential for fabricating high-performance microelectronics.
Atmospheric Pressure CVD (APCVD)
As the name implies, APCVD operates at or near standard atmospheric pressure (~760 torr). This is its primary advantage, as it eliminates the need for expensive and complex vacuum chambers and pumps.
APCVD systems offer very high deposition rates and high throughput, making them ideal for applications like depositing thick protective coatings or silicon dioxide films in solar cell manufacturing where cost and speed are paramount.
Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD)
While technically a different energy source, PECVD is worth noting as it often operates in the same low-pressure regime as LPCVD. A plasma is used to energize the precursor gases, allowing deposition to occur at much lower temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a pressure regime is a matter of balancing competing priorities. There is no single "best" pressure; there is only the best pressure for a specific goal.
Deposition Rate vs. Film Quality
This is the fundamental trade-off. High pressure (APCVD) delivers high deposition rates but risks lower uniformity and potential particle formation in the gas phase. Low pressure (LPCVD) produces superior, uniform films but at a much slower rate.
Equipment Complexity and Cost
An APCVD reactor is relatively simple. An LPCVD system, however, requires a robust vacuum chamber, expensive pumps, and sophisticated pressure control systems, significantly increasing its cost and complexity. This is why the vacuum system is a core component of many CVD setups.
Conformal Coverage
If you need to coat a complex, non-flat surface with a uniform film, low pressure is non-negotiable. The long mean free path of LPCVD allows precursor gases to penetrate deep into trenches and around corners, a feat that is nearly impossible with the short mean free path of APCVD.
Choosing the Right Pressure for Your Application
Your choice of operating pressure must be directly aligned with your end goal for the material being produced.
- If your primary focus is high film purity and uniformity: Use Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD) for its superior control over surface-limited reactions.
- If your primary focus is high throughput and lower cost: Use Atmospheric Pressure CVD (APCVD) for its fast deposition rates and simpler equipment requirements.
- If your primary focus is coating complex, non-flat surfaces: Choose LPCVD, as the long mean free path is the only way to ensure excellent conformal coverage.
- If your primary focus is deposition on temperature-sensitive substrates: Consider Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD), which uses low pressures but also a plasma to reduce required process temperatures.
Ultimately, controlling pressure is the primary tool for tailoring the CVD process to achieve your specific material properties and economic targets.
Summary Table:
| CVD Type | Typical Pressure Range | Key Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| LPCVD | 0.1 - 10 torr | High uniformity, excellent conformal coverage, slower rate | High-purity films, microelectronics, complex 3D structures |
| APCVD | ~760 torr (atmospheric) | High deposition rate, simpler equipment, lower cost | High-throughput coatings, solar cells, cost-sensitive applications |
| PECVD | Low Pressure (similar to LPCVD) | Lower temperature deposition, uses plasma activation | Temperature-sensitive substrates, specialized films |
Ready to Optimize Your CVD Process?
The right pressure is critical for achieving your specific film properties, whether you prioritize ultimate uniformity or maximum throughput. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise lab equipment—from robust LPCVD vacuum systems to high-throughput APCVD reactors—that your laboratory needs to succeed.
Let our experts help you select the perfect system to meet your deposition goals. Contact us today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- How are tools coated with diamond? Achieve Superior Hardness and Low Friction for Your Tools
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of chemical vapor deposition? A Guide to High-Performance Coating
- What is physical vapor deposition on plastic? Upgrade Plastic Parts with Durable, Functional Coatings
- What are the disadvantages of LPCVD? Understanding the Trade-offs for High-Quality Thin Films
- What is the primary function of CVD equipment for BDD films? Unlock Precision Diamond Synthesis
- What are the main advantages of using CVD in CMOS technology? Unlock Precision in 3D Device Fabrication
- What are the key differences between CVD and PVD? Choose the Best Thin Film Deposition for Your Lab
- How does RF magnetron sputtering work? A Complete Guide to Thin-Film Deposition



















