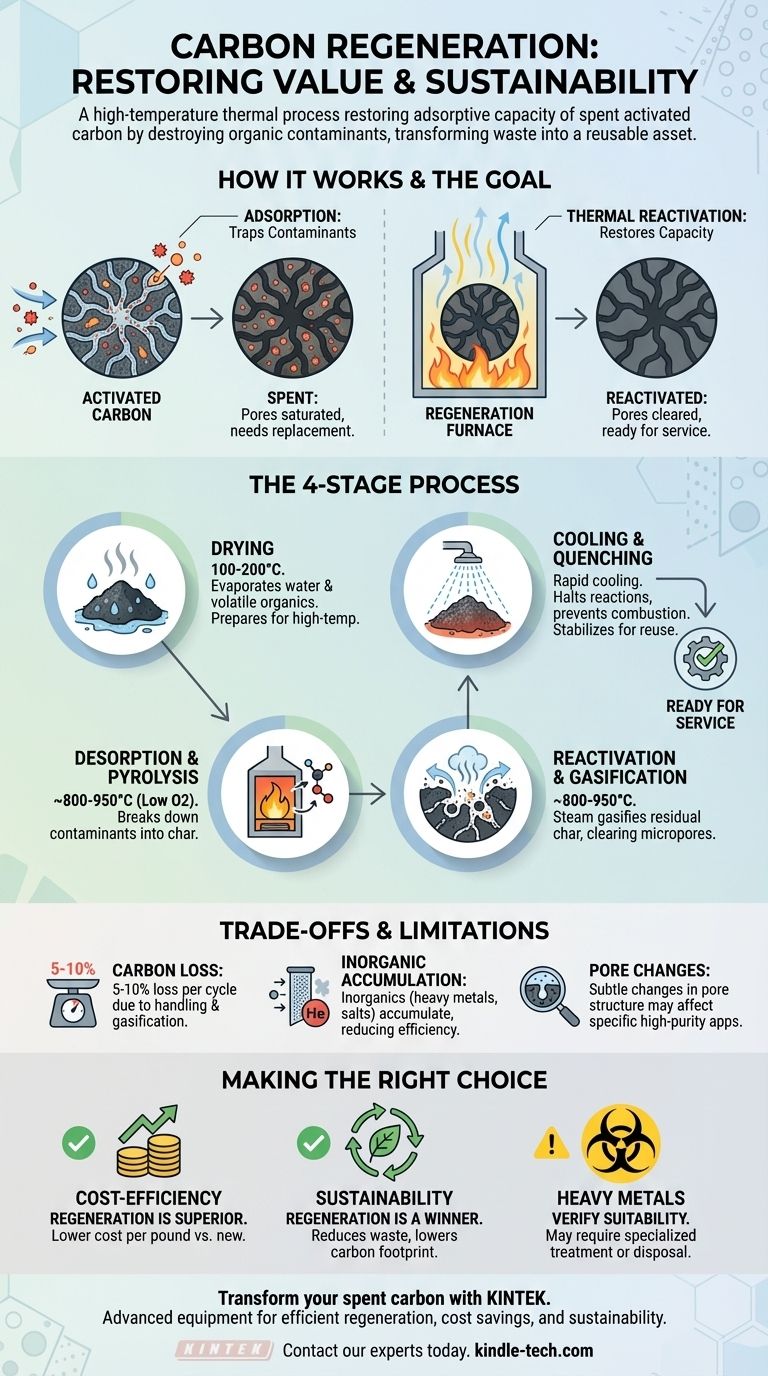
At its core, carbon regeneration is a high-temperature thermal process used to restore the adsorptive capacity of spent activated carbon. It works by using heat in a controlled environment to destroy the organic contaminants that have been captured in the carbon's pores during its operational use. This allows the carbon to be returned to service, functioning almost as effectively as new material.
The central challenge with spent activated carbon is that it represents either a significant waste disposal liability or a valuable, reusable asset. Understanding regeneration is the key to transforming that liability into an asset, offering a cost-effective and environmentally superior alternative to simple disposal.

The Goal of Regeneration: Restoring Adsorption Capacity
To understand regeneration, you must first understand how activated carbon works and why it becomes "spent."
How Activated Carbon Works
Activated carbon possesses a vast internal network of microscopic pores. This structure creates an enormous surface area—a single gram of activated carbon can have the surface area of a football field. Contaminants from a liquid or gas stream are trapped on this surface through a process called adsorption.
Why Carbon Becomes "Spent"
Over time, the carbon's massive internal surface area becomes saturated with adsorbed contaminants. Once the pores are full, the carbon can no longer effectively remove impurities and is considered "spent" or "exhausted." At this point, it must be replaced.
The Principle of Thermal Reactivation
Regeneration, also called reactivation, reverses this process. By heating the carbon to very high temperatures (typically 800-950°C) in a low-oxygen environment, the adsorbed organic compounds are thermally destroyed. They are broken down, vaporized, and driven out of the pore structure, clearing the surface area and restoring the carbon's adsorptive function.
The Multi-Stage Regeneration Process
Effective regeneration is a precise, multi-stage process typically carried out in a rotary kiln or multiple hearth furnace.
Step 1: Drying
The spent carbon, which is often saturated with water, is first heated to approximately 100-200°C. This initial stage gently evaporates any residual water and some of the most highly volatile organic compounds that were adsorbed.
Step 2: High-Temperature Desorption and Pyrolysis
Next, the temperature is raised significantly in a controlled, oxygen-starved atmosphere. In this stage, the less volatile organic contaminants are desorbed from the carbon surface and then broken down (pyrolyzed) into smaller molecules and a residual layer of char.
Step 3: Reactivation and Gasification
This is the most critical stage. The temperature is held at its peak while a controlled agent, typically steam, is introduced into the furnace. The steam selectively reacts with and gasifies the residual char left behind by the pyrolyzed contaminants, clearing out the micropores without significantly damaging the carbon itself. This re-exposes the original pore structure, "reactivating" the carbon.
Step 4: Cooling and Quenching
Finally, the hot, reactivated carbon is discharged from the furnace and carefully cooled, often through a water quench. This rapid cooling is necessary to stop the gasification reaction and prevent the hot carbon from combusting upon contact with the oxygen in the open air.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, regeneration is not a perfect process. Objectivity requires acknowledging its limitations.
Inevitable Carbon Loss
Each regeneration cycle results in a loss of approximately 5-10% of the carbon mass. This is due to a combination of physical handling (attrition) and the partial gasification of the base carbon material during the reactivation stage. This loss must be factored into economic calculations.
Accumulation of Inorganics
Thermal regeneration is highly effective for organic contaminants but does not remove inorganic materials like heavy metals or mineral salts. These compounds can accumulate in the carbon's pore structure over multiple cycles, gradually reducing its overall efficiency.
Changes to Pore Structure
Repeated regeneration can subtly alter the pore size distribution of the activated carbon. While often minor, this could impact its performance for adsorbing very specific target molecules, making it slightly less effective than virgin carbon for certain high-purity applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to regenerate or dispose of spent carbon depends on your operational scale, contaminant type, and strategic priorities.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency at scale: Regeneration is almost always the superior choice for large volumes, as the cost per pound to reactivate is significantly lower than purchasing new carbon and paying for disposal.
- If your primary focus is environmental sustainability: Regeneration is the clear winner, as it dramatically reduces solid waste, minimizes landfill impact, and lowers the carbon footprint associated with producing and transporting new material.
- If you are dealing with heavy metals or other inorganics: You must verify that thermal regeneration is appropriate, as these contaminants may accumulate and require specialized treatment or eventual disposal of the carbon.
By understanding the principles of regeneration, you can effectively manage your activated carbon as a renewable resource rather than a disposable commodity.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Temperature Range | Key Action | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drying | 100-200°C | Evaporates water and volatile organics | Prepares carbon for high-temperature treatment |
| Desorption & Pyrolysis | ~800-950°C | Breaks down contaminants into char in low-oxygen environment | Removes organic impurities from pores |
| Reactivation & Gasification | ~800-950°C | Steam gasifies residual char, clearing micropores | Restores carbon's adsorption capacity |
| Cooling & Quenching | Rapid cooling | Water quench halts reactions, prevents combustion | Stabilizes carbon for safe handling and reuse |
Transform your spent activated carbon from a disposal liability into a reusable asset with KINTEK.
Our advanced lab equipment and consumables are designed to support efficient, large-scale carbon regeneration processes, helping you achieve significant cost savings and enhance your environmental sustainability. By choosing regeneration over disposal, you can reduce waste, lower your carbon footprint, and maximize the value of your materials.
Ready to optimize your carbon management strategy? Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can meet your laboratory's specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What temperature is a carbon regeneration kiln? Master the 650°C-800°C Range for Optimal Results
- Can you restore activated carbon? Understanding the Industrial Reactivation Process
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What temperature is needed for porcelain? A Guide to Cone 6 and Cone 10 Firing
- What is the temperature of a carbon regeneration kiln? Mastering the 750-800°C Reactivation Process



















