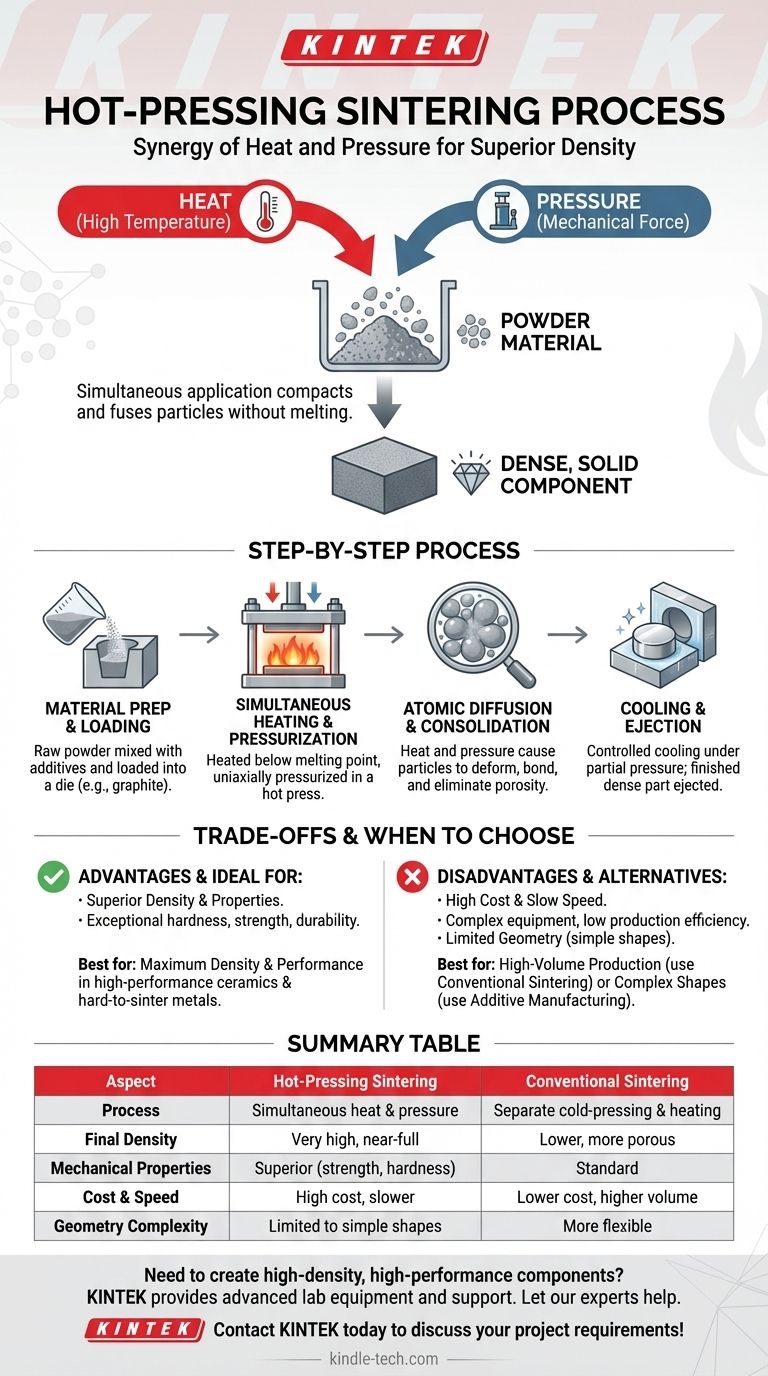
At its core, hot-pressing sintering is a manufacturing process that simultaneously applies high temperature and mechanical pressure to a powder material. This combined action compacts and fuses the powder particles into a dense, solid component without melting the material, achieving superior density and mechanical properties compared to conventional sintering methods.
The crucial distinction of hot-pressing is the simultaneous application of heat and pressure. This synergy overcomes the limitations of separate pressing and heating, making it a powerful tool for creating high-performance components from materials that are otherwise difficult to densify.
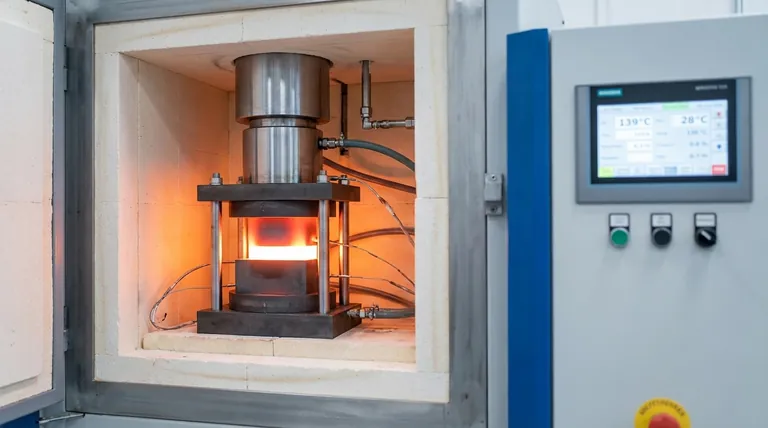

The Fundamental Principle: Synergy of Heat and Pressure
Hot-pressing is an evolution of traditional sintering, designed to achieve results that are not possible with heat alone. The simultaneous action of heat and pressure is the key to its effectiveness.
How It Differs from Conventional Sintering
Conventional sintering typically involves two distinct steps: first, a powder is cold-pressed into a desired shape (a "green compact"), and second, that compact is heated in a furnace to fuse the particles.
Hot-pressing combines these into a single, integrated step. The powder is heated while under pressure inside a die, which fundamentally changes the densification dynamics.
The Role of Simultaneous Application
Heat provides the thermal energy necessary for atoms to become mobile and diffuse across the boundaries of adjacent powder particles. This is the core mechanism of sintering.
Pressure provides a powerful mechanical assist. It helps break down any oxide films on the powder surfaces that inhibit bonding, rearranges particles to eliminate gaps, and enhances the driving force for atomic diffusion.
Activating the Sintering Process
This combined force is especially effective for materials with crystal defects. The applied stress activates these defects, accelerating the diffusion process and allowing the material to reach a much higher final density than it would under heat alone.
The Hot-Pressing Process: A Step-by-Step View
The hot-pressing process is a highly controlled operation where temperature, pressure, and time are carefully managed to achieve the desired outcome.
Step 1: Material Preparation and Loading
The process begins with the raw powder, which may be a metal, ceramic, or composite. This powder is often mixed with additives and then loaded into a durable mold or die, typically made of graphite or a refractory material.
Step 2: Simultaneous Heating and Pressurization
This is the defining step. The mold containing the powder is placed in a hot press, where it is heated to a temperature just below the material's melting point. At the same time, uniaxial pressure is applied to the powder through a ram or plunger.
Step 3: Atomic Diffusion and Consolidation
Under the combined influence of heat and pressure, the powder particles deform and begin to fuse. Atoms migrate across particle boundaries, progressively eliminating the porous spaces between them. The material consolidates into a dense, solid mass.
Step 4: Cooling and Ejection
Once the desired density and hold time are achieved, the component is cooled in a controlled manner, often while still under partial pressure to prevent defects. After cooling, the finished, dense part is ejected from the die.
Understanding the Trade-offs of Hot-Pressing
While powerful, hot-pressing is a specialized technique with a distinct set of advantages and disadvantages that make it suitable for specific applications.
Key Advantage: Superior Density and Properties
The primary reason to use hot-pressing is to achieve near-full density. This results in components with exceptional hardness, strength, and durability. It is the preferred method for high-performance ceramics like silicon carbide and hard-to-sinter metals.
Key Disadvantage: Cost and Production Rate
The benefits come at a cost. Hot-pressing machinery is complex and expensive. Molds must withstand extreme conditions and have a limited lifespan. The process itself is slow, resulting in low production efficiency and high per-part costs.
Limitation: Geometric Simplicity
Due to the nature of applying pressure uniaxially within a rigid die, hot-pressing is generally limited to producing parts with relatively simple geometries, such as discs, blocks, or cylinders.
When to Choose Hot-Pressing Sintering
Selecting the right manufacturing process requires aligning the method's capabilities with your project's primary goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and performance: Use hot-pressing for critical applications where achieving near-zero porosity and superior mechanical properties is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production and cost efficiency: Conventional sintering or powder injection molding are far more suitable choices for less demanding applications.
- If your primary focus is creating complex shapes: Explore additive manufacturing (3D printing) or injection molding, as hot-pressing is restrictive for intricate geometries.
Ultimately, choosing hot-pressing is a strategic decision to prioritize final material quality over manufacturing cost and speed.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Hot-Pressing Sintering | Conventional Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Simultaneous heat and pressure | Separate cold-pressing and heating steps |
| Final Density | Very high, near-full density | Lower, more porous |
| Mechanical Properties | Superior (strength, hardness) | Standard |
| Cost & Speed | High cost, slower production | Lower cost, higher volume |
| Geometry Complexity | Limited to simple shapes (discs, blocks) | More flexible for complex shapes |
Need to create high-density, high-performance components? The hot-pressing process is ideal for achieving superior material properties in ceramics, composites, and hard-to-sinter metals. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the advanced lab equipment and expert support you need to master this technique.
Let our experts help you select the right solution for your R&D or production goals. Contact KINTEL today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
People Also Ask
- What conditions does a Vacuum Hot Pressing Furnace provide for Copper-MoS2-Mo composites? Achieve Peak Densification
- How does the uniaxial pressing function of a vacuum hot press furnace influence the microstructure of ZrC-SiC ceramics?
- What advantages does hot pressing sintering equipment provide for NASICON? Achieve 100% Dense Solid Electrolyte Plates
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot press sintering furnace? Achieve 99.1% Density in CuW30 Composites
- Why is a vacuum essential for sintering metal-ceramic composites? Achieve Pure, High-Density Results



















