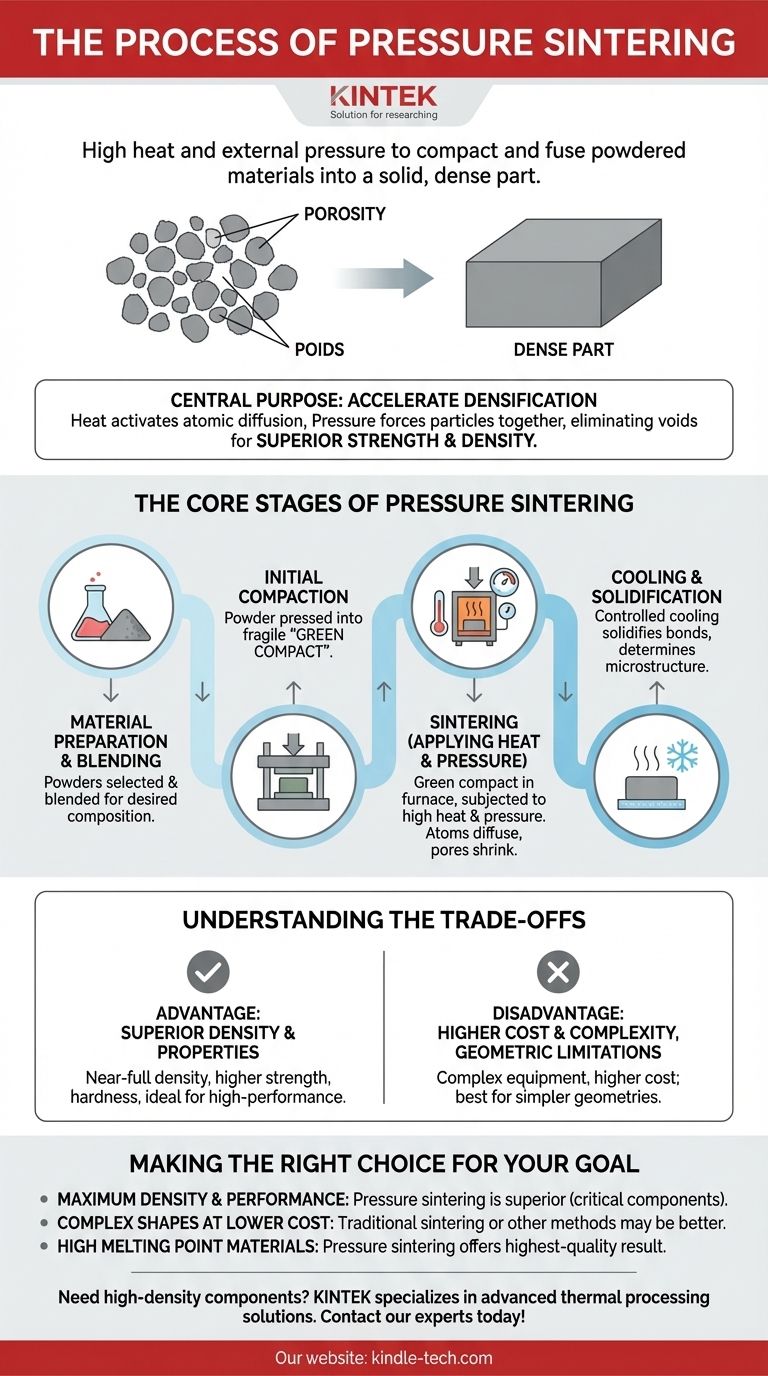
In short, pressure sintering is a manufacturing process that uses a combination of high heat and external pressure to compact and fuse powdered materials into a solid, dense part. Unlike traditional casting, this process occurs at temperatures below the material's melting point, relying on atomic diffusion across particle boundaries to create a strong, unified mass.
The central purpose of applying external pressure during sintering is to accelerate the densification process. While heat provides the energy for atoms to bond, pressure physically forces the powder particles together, eliminating voids more effectively and resulting in a final product with superior strength and density.
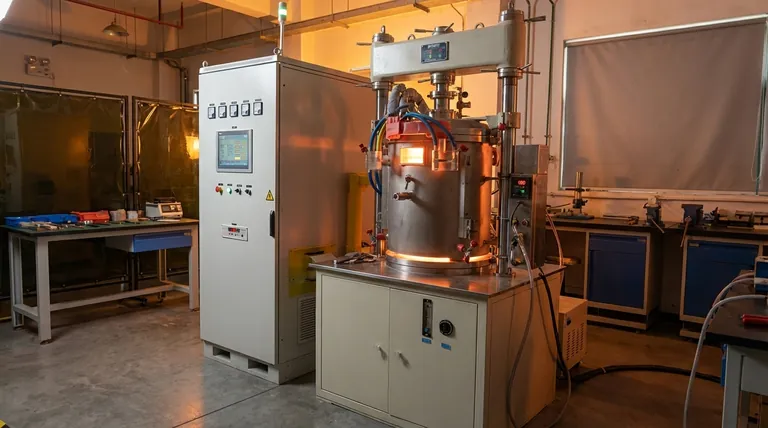

The Fundamental Goal: Overcoming Porosity
The starting point for any sintering process is a collection of fine particles. The primary challenge is eliminating the empty space, or porosity, between these particles to create a fully dense, solid component.
The Role of Heat
Heat is the primary catalyst in sintering. It provides the thermal energy needed to activate atomic diffusion, the mechanism by which atoms migrate across the boundaries of adjacent particles. This migration is what ultimately fuses the individual grains into a single, coherent piece.
The Critical Role of Pressure
In pressure sintering, external mechanical pressure is applied simultaneously with heat. This force physically closes the gaps between particles, reducing the distance atoms need to travel. This synergy of heat and pressure dramatically speeds up the bonding process and achieves a level of density that is often impossible with heat alone.
The Core Stages of Pressure Sintering
While specific techniques vary, the process generally follows four distinct stages.
Stage 1: Material Preparation & Blending
The process begins with the raw materials in powdered form. These powders are carefully selected and blended to achieve the desired chemical composition and properties in the final part. Additives or binding agents may also be introduced at this stage.
Stage 2: Initial Compaction
The blended powder is loaded into a die or mold and pressed into the desired shape. This step, often performed at room temperature, creates a fragile, porous part referred to as a "green compact." The green compact has enough structural integrity to be handled and moved to the sintering furnace.
Stage 3: Sintering (Applying Heat & Pressure)
This is the heart of the process. The green compact is placed in a controlled-atmosphere furnace where it is subjected to both high temperatures and significant external pressure. The atoms diffuse, the pores between particles shrink and close, and the material densifies into a solid mass.
Stage 4: Cooling & Solidification
Once the desired density is achieved, the component is carefully cooled. This controlled cooling solidifies the newly formed atomic bonds and determines the final microstructure and properties of the material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Pressure sintering is a powerful technique, but it comes with specific advantages and disadvantages that are critical to understand.
Advantage: Superior Density & Properties
The primary benefit is the ability to produce parts with near-full density. This lack of porosity leads directly to superior mechanical properties, including higher strength, hardness, and durability, making it ideal for high-performance applications.
Disadvantage: Higher Cost & Complexity
The equipment required for pressure sintering, such as a hot press or a hot isostatic press (HIP), is significantly more complex and expensive than a conventional sintering furnace. This increases both capital investment and operational costs.
Disadvantage: Geometric Limitations
Applying uniform pressure to a complex shape can be challenging. As a result, pressure sintering is often best suited for simpler geometries, whereas more intricate parts may require alternative manufacturing methods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right manufacturing process depends entirely on the requirements of the final component.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum material density and mechanical performance: Pressure sintering is the superior choice, especially for critical components that cannot tolerate internal defects.
- If your primary focus is producing complex shapes at a lower cost: Traditional pressureless sintering or other manufacturing methods like metal injection molding may be more suitable.
- If your primary focus is processing materials with extremely high melting points (like ceramics or tungsten): Sintering is an essential technology, and pressure sintering offers the path to the highest-quality result.
Ultimately, pressure sintering is the definitive method for transforming powdered materials into solid parts with uncompromising strength and integrity.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Preparation | Blending powdered materials | Achieve desired chemical composition |
| 2. Compaction | Pressing powder into a shape (green compact) | Create a handleable pre-form |
| 3. Sintering | Applying heat & pressure in a furnace | Densify the part by atomic diffusion |
| 4. Cooling | Controlled solidification | Lock in final microstructure and properties |
Need to produce high-density, high-strength components from powders? KINTEK specializes in advanced thermal processing solutions, including equipment for pressure sintering. Our expertise in lab equipment and consumables ensures you have the right tools to achieve superior material properties for your most demanding applications. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's sintering needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- How does the pressure loading system of a vacuum hot press furnace affect the density of Cu-Ti3SiC2? Boost Densification
- What is the SPS process of spark plasma sintering? A Guide to Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification
- What pressurization methods are employed in a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Choose the Right Method for Your Materials
- What are the benefits of a vacuum hot press for yttrium oxide? Achieve High-Density, Transparent Ceramics
- What roles do graphite molds play during vacuum hot pressing? Optimize Alloy Powder Densification & Precision
- How does a vacuum hot pressing furnace contribute to the densification of (Ti,M)3AlC2 solid solution ceramics?
- What is the principle of hot pressing? Achieve Superior Density for High-Performance Components
- Why is short-duration HIP used for Al-LLZ ceramics? Master Densification While Preserving Phase Purity



















