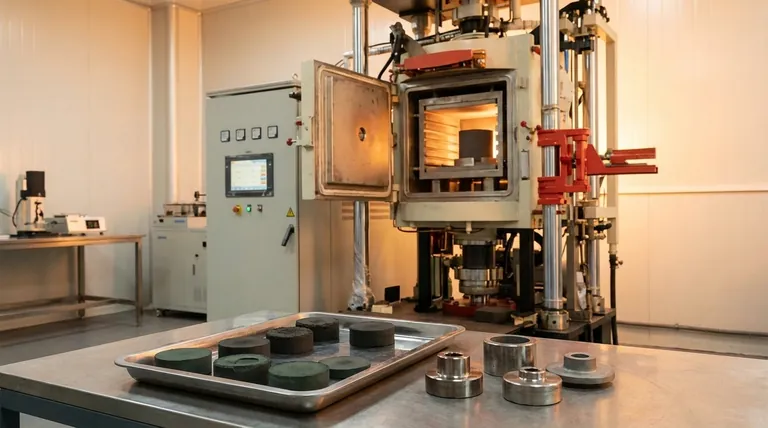
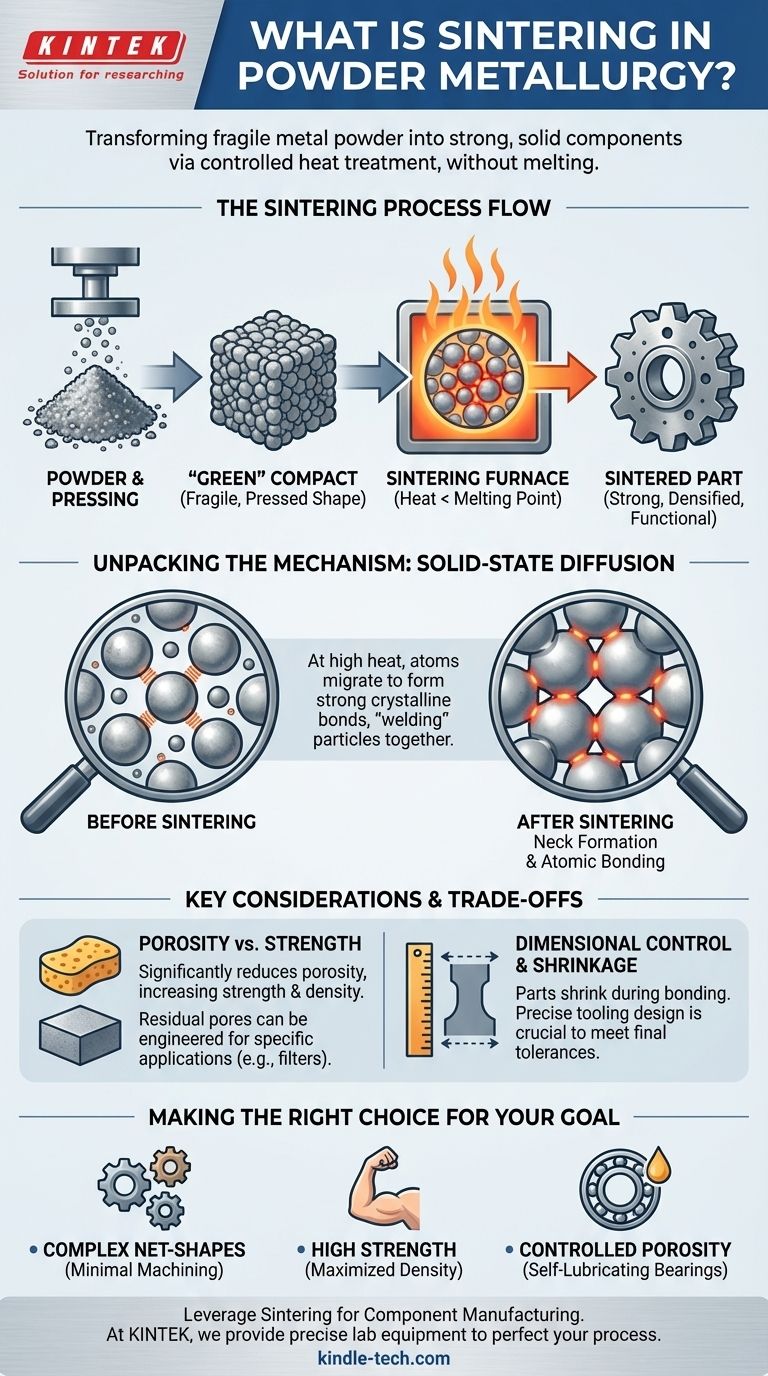
At its core, sintering is a heat treatment process used in powder metallurgy to transform a fragile, compressed powder shape into a strong, solid component. By heating the material in a furnace to a temperature just below its melting point, the individual metal particles fuse, creating strong metallurgical bonds that give the part its final strength and structural integrity.
Sintering is not about melting metal. It is the controlled process of using thermal energy to drive solid-state diffusion, causing adjacent powder particles to bond and densify, thereby converting a weakly-held powder compact into a robust, engineered part.

The Role of Sintering in Powder Metallurgy
Sintering is the critical transformation step that gives powder metal parts their useful mechanical properties. Without it, a compacted part would simply crumble.
From "Green" Compact to Finished Part
Before sintering, metal powder is pressed into a mold under high pressure. The resulting shape is called a "green" compact.
This green compact is fragile, held together only by the mechanical interlocking of the particles. It has the desired shape but lacks the strength needed for any application. Sintering is what provides this strength.
The Goal: Strength Through Bonding
The primary objective of sintering is to heat the green compact in a controlled furnace. This thermal energy causes the atoms at the contact points of the particles to diffuse across the boundaries.
This atomic transport creates strong, crystalline bonds, effectively "welding" the particles together on a microscopic level. The result is a significant increase in the part's hardness, strength, and density.
Unpacking the Sintering Mechanism
The process works through a principle known as solid-state diffusion, which occurs without ever melting the bulk material.
The Power of Solid-State Diffusion
At high temperatures, atoms become more mobile. During sintering, atoms from adjacent particles migrate and rearrange to form connections, or "necks," at their points of contact.
Think of how two ice cubes left in a glass of water will slowly fuse at their contact points. Sintering achieves a similar effect for metal particles, but at much higher temperatures and resulting in a far stronger bond.
The Critical Role of Temperature
The sintering temperature is precisely controlled to be below the melting point of the primary metal.
This is crucial because it allows the part to densify and strengthen while maintaining its precise, compacted shape. If the material were to melt, dimensional control would be lost entirely.
A Controlled Furnace Environment
Sintering is performed in specialized furnaces with a carefully controlled atmosphere. This atmosphere is typically inert or reducing, preventing oxidation of the metal surfaces, which would otherwise inhibit proper bonding between particles.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the sintering process involves key considerations that impact the final product.
Porosity vs. Strength
Sintering significantly reduces the empty space (porosity) between powder particles, but it rarely eliminates it completely.
This residual porosity means that a sintered part is often less dense and may have lower ultimate strength than a part made from solid, wrought metal. However, this porosity can be a design advantage for creating products like self-lubricating bearings or filters.
Dimensional Control
As the particles fuse and the pores shrink, the entire component undergoes a degree of shrinkage. This change must be accurately predicted and accounted for during the initial design of the compaction tooling to ensure the final part meets its required dimensional tolerances.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding sintering allows you to leverage the powder metallurgy process to achieve specific engineering outcomes.
- If your primary focus is producing complex, net-shape parts: Sintering is ideal, as it allows you to form intricate geometries that require little to no subsequent machining.
- If your primary focus is achieving high strength: Careful control over powder composition, compaction pressure, and sintering time, temperature, and atmosphere is critical to maximize density.
- If your primary focus is creating controlled porosity: Sintering is a unique process that enables the deliberate engineering of porous materials for applications like filters and oil-impregnated bearings.
Ultimately, sintering is the essential process that unlocks the potential of metal powders, transforming them into precise and durable engineered components.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Transform a fragile 'green' compact into a strong, solid part. |
| Core Mechanism | Solid-state diffusion bonds particles at temperatures below melting. |
| Key Outcome | Increased strength, hardness, and density of the final component. |
| Critical Factor | Controlled furnace atmosphere to prevent oxidation and ensure bonding. |
| Design Consideration | Predictable part shrinkage must be accounted for in tooling design. |
Ready to leverage sintering for your component manufacturing?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precise lab equipment and consumables needed to perfect your powder metallurgy processes. Whether you are developing complex net-shape parts, optimizing for maximum strength, or engineering controlled porosity, our expertise and products support your goals.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you achieve superior results in your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Large Vertical Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is the boiling point of THC under a vacuum? A Guide to Safe Distillation
- What is the impact factor of powder metallurgy progress? A 2022 Analysis & Context
- What are the stages of sintering? A Guide to Mastering the Powder-to-Part Process
- What is a sputtering machine? A Guide to High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What are the challenges of welding stainless steel? Overcome Warping, Sensitization, and Contamination



















