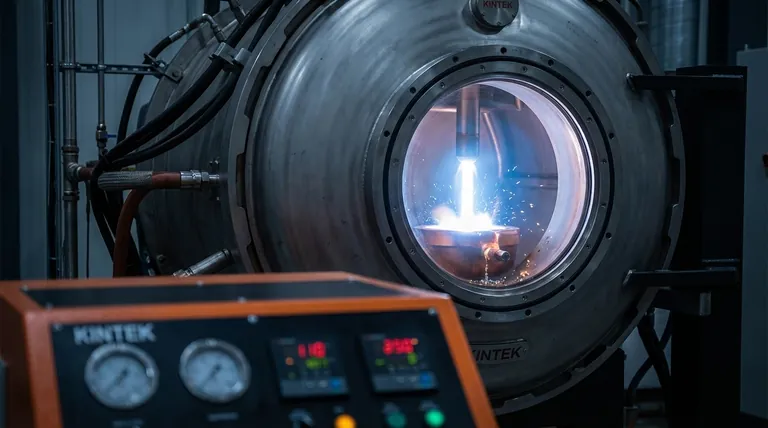
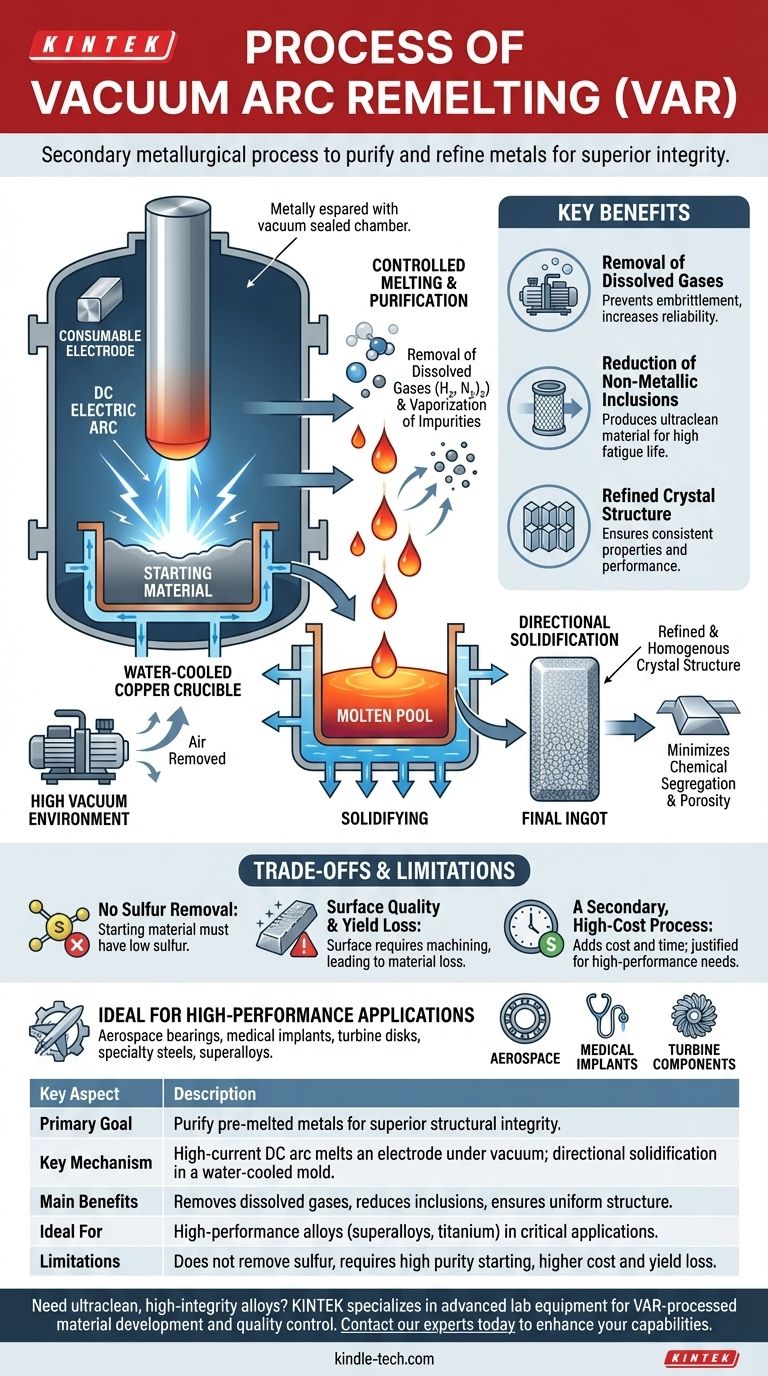
At its core, Vacuum Arc Remelting (VAR) is a secondary metallurgical process designed to purify and refine metals and alloys that have already been melted once. It operates by using a high-current DC electric arc to progressively melt a solid cylindrical electrode of the material under a high vacuum. The molten metal drips down and re-solidifies in a water-cooled copper mold, producing a final ingot with vastly superior purity and structural integrity.
The essential purpose of VAR is not to create a metal, but to perfect it. By remelting an alloy in a vacuum, the process removes dissolved gases and vaporizes impurities while controlling solidification to create an exceptionally clean and uniform final product.

How the VAR Process Works: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
The VAR process is a highly controlled sequence designed to systematically improve the quality of a pre-existing alloy. It is a batch process, refining one electrode at a time.
The Consumable Electrode
The process begins with a "consumable electrode," which is a large, solid cylinder of the alloy that needs refinement. This electrode is often produced by a primary melting process like vacuum induction melting (VIM).
Striking the Electric Arc
The electrode is suspended inside a vacuum-sealed, water-cooled copper crucible. It is positioned just above a small amount of starting material at the bottom of the crucible, acting as the negative terminal (cathode). A powerful DC arc is then struck between the electrode tip and the base material (anode).
Controlled Melting and Purification
The intense heat of the arc, reaching nearly 5000 Kelvin, melts the tip of the electrode. As the metal liquefies and forms droplets, it is exposed to the vacuum environment.
This exposure is critical. The vacuum pulls out dissolved gases like hydrogen and nitrogen, and other elements with high vapor pressure are vaporized and removed. This is the primary purification step.
Directional Solidification
The molten droplets fall from the electrode into the shallow pool of liquid metal at the bottom of the crucible. Because the crucible is actively water-cooled, the metal begins to solidify immediately upon contact with the cooled walls and base.
As the electrode is continuously consumed, the ingot grows from the bottom up. This controlled, progressive solidification minimizes chemical segregation and porosity, resulting in a highly uniform and dense ingot.
The Primary Goal: Achieving Ultimate Purity and Structure
VAR is specified when the performance requirements of a material demand the highest possible level of cleanliness and structural integrity. The process is engineered to achieve several key outcomes.
Removal of Dissolved Gases
Gases like hydrogen can cause embrittlement, a catastrophic failure mode in high-stress components. The vacuum environment is exceptionally effective at reducing these dissolved gases to extremely low levels.
Reduction of Non-Metallic Inclusions
The remelting process allows non-metallic inclusions, such as oxides, to float to the top of the molten pool where they can be contained. This produces an "ultraclean" material, which is critical for components subjected to high fatigue, like ball bearings or turbine disks.
Refined and Homogenous Crystal Structure
The controlled, directional solidification inherent to the VAR process prevents the different alloying elements from separating (segregating). This results in a final ingot with a consistent chemical composition and a fine, uniform grain structure, which directly translates to predictable and reliable mechanical properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While VAR produces exceptionally high-quality material, it is not a universal solution. It has specific limitations that are important to understand.
No Sulfur Removal
The VAR process does not provide a mechanism for removing sulfur. Therefore, the starting consumable electrode must already have a very low sulfur content. This places a significant constraint on the initial material selection and processing.
Surface Quality and Yield Loss
During the process, some molten metal can splash against the cold mold wall, creating a rough and sometimes porous ingot surface. This surface layer often has a higher concentration of certain impurities and must be machined away, or "peeled," before further processing, resulting in a loss of material yield.
A Secondary, High-Cost Process
VAR is a secondary refining step, not a primary melting method. It adds significant cost and time to the manufacturing cycle. Its use is only justified for high-performance applications where the benefits of extreme purity outweigh the added expense. It is used for materials like specialty VAR steels, superalloys, titanium, and zirconium.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Specifying a VAR-processed material is a decision driven entirely by the performance demands of the final component.
- If your primary focus is extreme fatigue life and reliability (e.g., aerospace bearings, medical implants): VAR is the definitive choice for producing the ultraclean material necessary to prevent inclusion-initiated failures.
- If your primary focus is material homogeneity and predictable properties (e.g., high-performance tool steels, superalloy turbine components): VAR's controlled solidification ensures a uniform structure free from segregation, which is essential for consistent performance under extreme conditions.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency for standard structural applications: VAR is an unnecessary and expensive step; conventional air-melted or vacuum-degassed steels will be sufficient.
Ultimately, choosing VAR is an investment in achieving the highest possible level of material integrity for the most demanding applications.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Purify and refine pre-melted metals for superior structural integrity. |
| Key Mechanism | High-current DC arc melts an electrode under vacuum; molten metal solidifies directionally in a water-cooled mold. |
| Main Benefits | Removes dissolved gases (H₂, N₂), reduces non-metallic inclusions, and ensures uniform grain structure. |
| Ideal For | High-performance alloys (e.g., superalloys, titanium) used in aerospace, medical implants, and turbine components. |
| Limitations | Does not remove sulfur; requires high-purity starting electrode; higher cost and yield loss due to surface machining. |
Need ultraclean, high-integrity alloys for your critical applications? KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables that support the development and quality control of VAR-processed materials. Whether you're refining superalloys for aerospace or ensuring the purity of medical implants, our solutions help you achieve the highest standards of material performance. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is VAR in metallurgy? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Performance
- What is the remelting process? Achieve Ultimate Purity and Performance for High-Strength Alloys
- How does vacuum arc remelting work? Achieve Ultra-Clean, High-Performance Metal Alloys
- What is a remelting process? A Guide to High-Purity Metal Refinement
- What is the benefit of vacuum arc remelting? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Structural Integrity



















