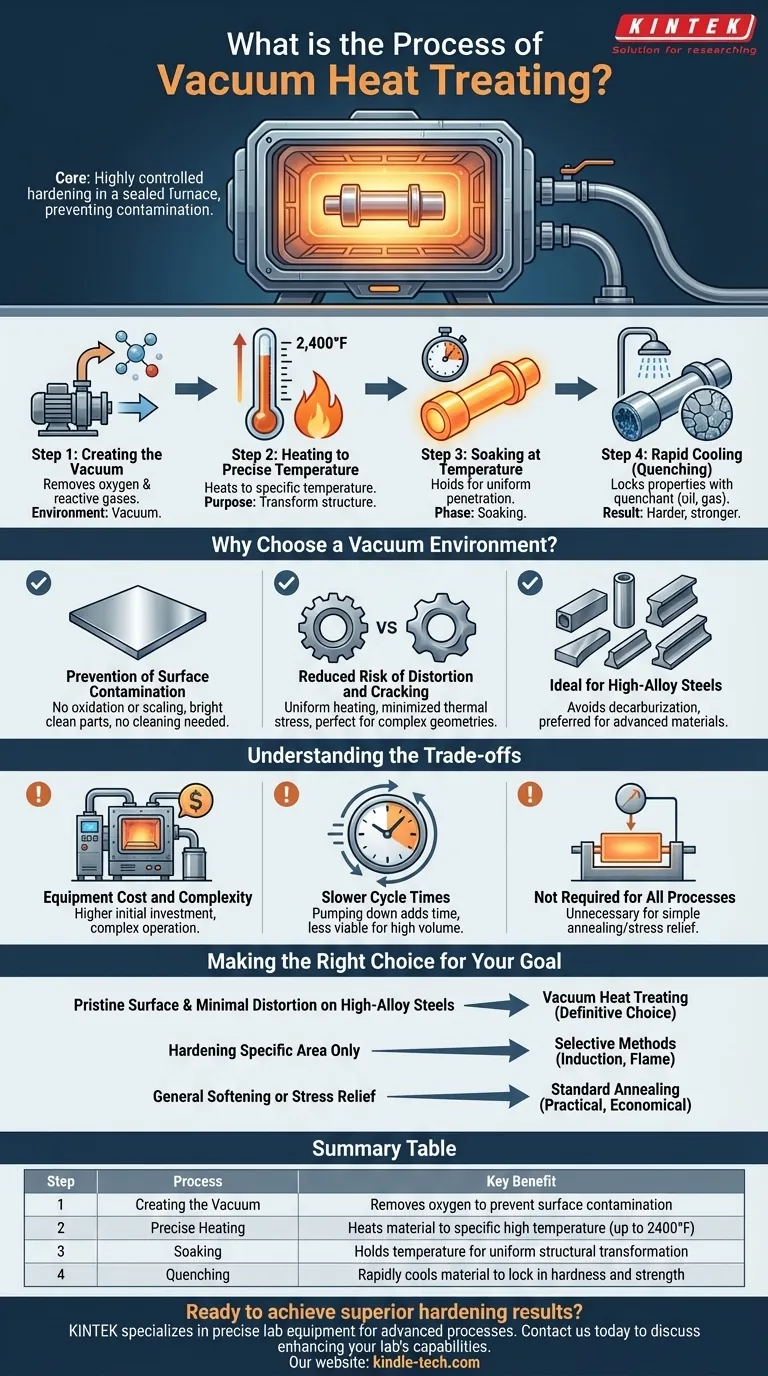
At its core, vacuum heat treating is a highly controlled hardening process. It involves three fundamental steps performed inside a sealed furnace: heating a material to a specific high temperature in a vacuum, holding it at that temperature to alter its internal structure, and then rapidly cooling it (quenching) to lock in the desired properties.
The critical advantage of performing this process in a vacuum is the prevention of surface contamination. By removing atmospheric gases, the vacuum ensures the final part is clean, bright, and less prone to the distortion or cracking that can occur with other methods.

Deconstructing the Vacuum Heat Treating Process
The process is methodical, with each step serving a distinct and critical purpose in transforming the material's properties. It is a refinement of traditional heat treatment, elevated by the controlled environment.
Step 1: Creating the Vacuum
Before any heating begins, air and other gases are pumped out of the sealed furnace chamber. This removal of oxygen and other reactive elements is what fundamentally defines the process.
Step 2: Heating to a Precise Temperature
Once the vacuum is established, the material is heated to a predetermined temperature, which can be as high as 2,400°F. This temperature is carefully selected based on the specific alloy and the desired final characteristics.
Step 3: Soaking at Temperature
The material is then held at this peak temperature for a specific duration, a phase known as "soaking." This allows the heat to penetrate the part uniformly, ensuring its entire crystalline structure transforms as intended.
Step 4: Rapid Cooling (Quenching)
Finally, the part is rapidly cooled using a quenchant such as oil, polymer, or high-pressure gas. This rapid cooling locks the transformed molecular structure in place, resulting in a significantly harder and stronger material.
Why Choose a Vacuum Environment?
The decision to use a vacuum furnace is driven by the need for superior results, especially for high-value or mission-critical components. The environment itself provides several key benefits over conventional atmospheric heat treating.
Prevention of Surface Contamination
The absence of oxygen prevents oxidation, scaling, and other surface reactions. This results in a bright, clean part that does not require subsequent cleaning operations, saving both time and cost.
Reduced Risk of Distortion and Cracking
The uniform heating and controlled cooling inherent in the vacuum process minimize thermal stress. This significantly reduces the tendency for parts, especially those with complex geometries, to warp, distort, or crack during hardening.
Ideal for High-Alloy Steels
Vacuum heat treating is the preferred method for high-alloy tool steels and other advanced materials. These materials are often sensitive to surface decarburization (carbon loss), which is completely avoided in a vacuum environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum heat treating is not a universal solution. Its precision and control come with specific considerations that make it unsuitable for every application.
Equipment Cost and Complexity
Vacuum furnaces are significantly more complex and expensive to purchase and operate than standard atmospheric furnaces. This higher initial investment is a primary factor in its application.
Slower Cycle Times
The process of pumping down the chamber to create a vacuum adds time to the overall treatment cycle. For high-volume, low-cost parts, this can make the process less economically viable.
Not Required for All Processes
Many heat treating goals, such as simple annealing (softening) or stress relieving, do not require the pristine surface finish or a vacuum environment. For these applications, less complex and more cost-effective methods are sufficient.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct heat treatment process depends entirely on the material and the desired outcome for the final component.
- If your primary focus is a pristine surface finish and minimal distortion on high-alloy steels: Vacuum heat treating is the definitive choice for superior hardening results.
- If your primary focus is hardening only a specific area of a component: Selective methods like induction or flame hardening are more efficient and targeted.
- If your primary focus is general softening or stress relief without critical surface requirements: A standard, non-vacuum annealing or stress relief process is the more practical and economical option.
Ultimately, understanding your material's specific needs empowers you to select the most effective and efficient path to achieving your desired performance.
Summary Table:
| Step | Process | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Creating the Vacuum | Removes oxygen to prevent surface contamination |
| 2 | Precise Heating | Heats material to specific high temperature (up to 2400°F) |
| 3 | Soaking | Holds temperature for uniform structural transformation |
| 4 | Quenching | Rapidly cools material to lock in hardness and strength |
Ready to achieve superior hardening results for your high-value components?
KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for advanced processes like vacuum heat treating. Our expertise ensures you get the clean, bright finishes and minimal distortion required for mission-critical parts.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and deliver the material performance you demand.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a furnace used for in industry? Essential Tool for Material Transformation
- What is the temperature used in hardening? Master the Key to Steel Hardening Success
- What are the advantages of an arc furnace? Achieve Flexible, Low-Carbon Steel Production
- What is the function of a vacuum drying oven in catalyst recovery? Maximize Cycle Life and Maintain Active Sites
- What furnace is used for heat treatment? Match Your Process to the Perfect Equipment
- How does a vacuum unit system contribute to the stainless steel nitriding process? Mastering Plasma Environment Control
- What are the benefits of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Material Purity and Process Control
- What type of ore are subjected for calcination? Purify Carbonate & Hydrated Ores



















