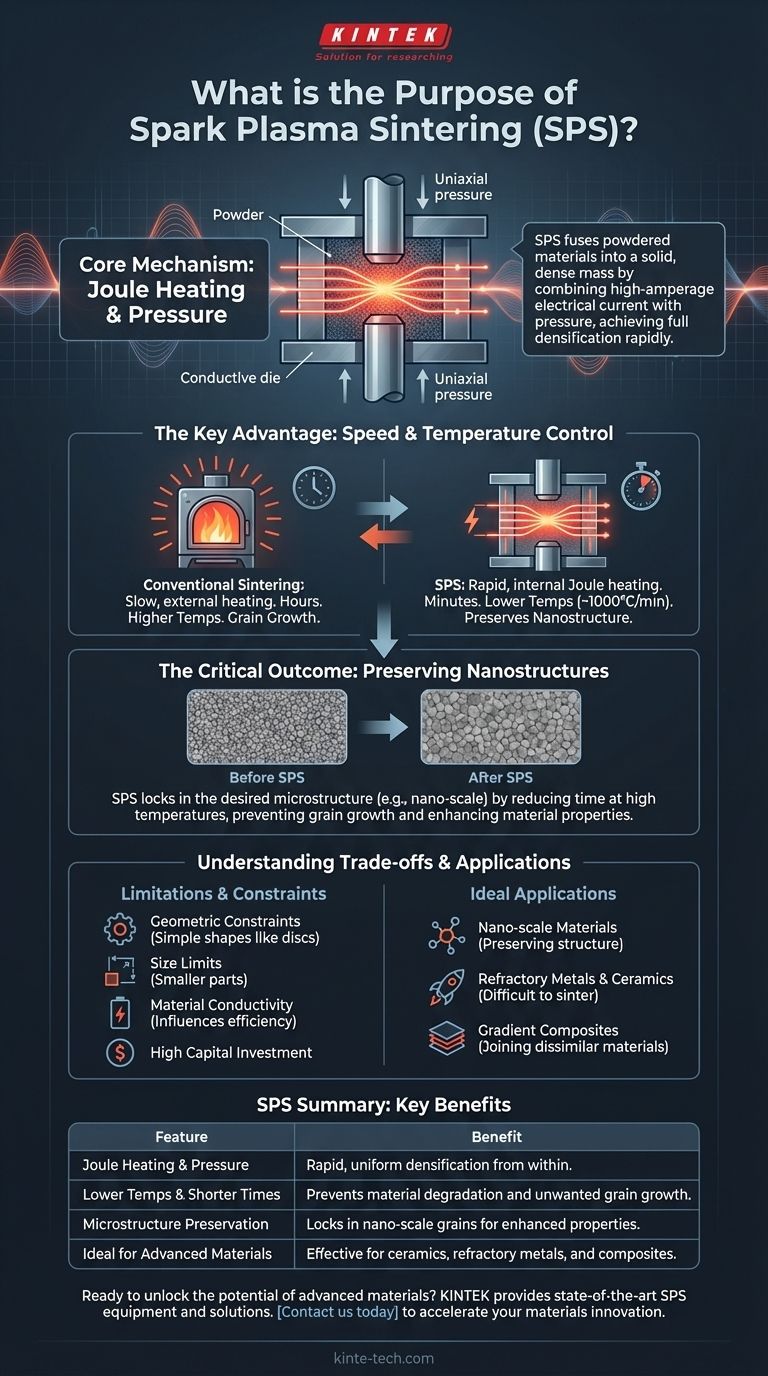
At its core, the purpose of spark plasma sintering (SPS) is to fuse powdered materials into a solid, dense mass using a radically different approach from conventional heating. It combines high-amperage electrical current with uniaxial pressure to achieve full densification at lower temperatures and in a fraction of the time, making it a critical tool for developing advanced materials.
Spark plasma sintering solves a fundamental problem in materials science: how to consolidate powders into a fully dense solid without destroying their unique, carefully engineered microstructures. Its speed prevents unwanted grain growth, preserving the properties of nano-scale and other advanced materials.

How SPS Redefines Material Consolidation
To understand the purpose of SPS, you must first understand its unique mechanism, which sets it apart from traditional furnace-based sintering that slowly "bakes" material from the outside-in.
The Core Mechanism: Joule Heating and Pressure
Unlike a conventional furnace that relies on external radiation, SPS passes a pulsed direct current (DC) through a conductive die (typically graphite) and, if conductive, the material powder itself.
This direct electrical resistance generates instantaneous, uniform heat throughout the material, a phenomenon known as Joule heating.
Simultaneously, mechanical pressure is applied by punches, squeezing the powder together. This combination of an electric field, thermal field, and mechanical pressure dramatically accelerates the bonding between particles.
The Key Advantage: Speed and Temperature Control
The most significant advantage of SPS is its speed. The direct Joule heating allows for incredibly rapid heating rates, sometimes as high as 1000°C per minute.
This means a sintering process that might take many hours in a conventional furnace can be completed in minutes with SPS.
Furthermore, this rapid process allows for densification at temperatures that are often hundreds of degrees lower than those required for traditional methods, preventing material degradation.
The Critical Outcome: Preserving Nanostructures
This combination of speed and lower temperature is essential for modern materials science. Many advanced materials derive their unique properties from a nano-scale or finely refined grain structure created through processes like cryogenic milling.
Slow, high-temperature sintering causes these fine grains to grow and coarsen, destroying the very properties you sought to create.
Because SPS is so fast, it effectively "locks in" the desired microstructure before it has a chance to change, preserving the material's enhanced strength, conductivity, or other engineered characteristics.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, SPS is a specialized tool with specific constraints. It is not a universal replacement for all sintering methods.
Geometric and Size Constraints
The SPS process relies on a rigid punch-and-die setup. This means that component shapes are typically limited to simple geometries like discs and rectangles.
Furthermore, the size of the final component is constrained by the practical size limits of the graphite die and the massive pressures required, making it less suitable for producing very large parts.
Material Conductivity Matters
The efficiency of the SPS heating mechanism is influenced by the electrical conductivity of the powder being sintered.
While non-conductive powders like many ceramics can be sintered successfully (heated indirectly by the conductive die), the most uniform and rapid heating occurs when the current can pass through the powder itself.
Cost and Complexity
SPS systems are specialized, high-performance machines. They represent a significantly higher capital investment compared to conventional sintering furnaces. The decision to use SPS is a trade-off between higher equipment cost and the unique ability to produce materials that would otherwise be impossible to make.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
SPS is a solution for specific, high-value challenges. Use this guide to determine if it aligns with your objective.
- If your primary focus is preserving a nano-scale or refined microstructure: SPS is the definitive choice, as its speed prevents the grain growth that destroys the properties of these materials.
- If your primary focus is sintering refractory metals or advanced ceramics: SPS is highly effective, as it can achieve full density at lower temperatures and shorter times for these difficult-to-sinter materials.
- If your primary focus is creating gradient composites or joining dissimilar materials: SPS provides a unique capability for bonding materials like ceramic-to-metal that are challenging to join with other methods.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production of large, simple metal parts: Conventional sintering or hot pressing will likely be a more economical and scalable solution.
Ultimately, spark plasma sintering empowers engineers and researchers to move beyond the limitations of traditional heating to create the next generation of high-performance materials.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Joule Heating & Pressure | Rapid, uniform densification from within the material. |
| Lower Temperatures & Shorter Times | Prevents material degradation and unwanted grain growth. |
| Microstructure Preservation | Locks in nano-scale grains for enhanced material properties. |
| Ideal for Advanced Materials | Effective for ceramics, refractory metals, and composites. |
Ready to unlock the potential of advanced materials in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in providing state-of-the-art lab equipment, including sintering solutions, to help you achieve superior material densification and preserve critical microstructures. Our expertise supports researchers and engineers in developing high-performance materials efficiently.
Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can meet your specific laboratory needs and accelerate your materials innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the vapor phase material? Unlock Faster, Denser Sintering with SPS Technology
- What is the difference between hot press and SPS? Choose the Right Sintering Method for Your Lab
- What is the SPS process of spark plasma sintering? A Guide to Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification
- What are the parameters for spark plasma sintering? Master Speed, Pressure & Temperature Control
- What are the steps in spark plasma sintering? Achieve Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification



















