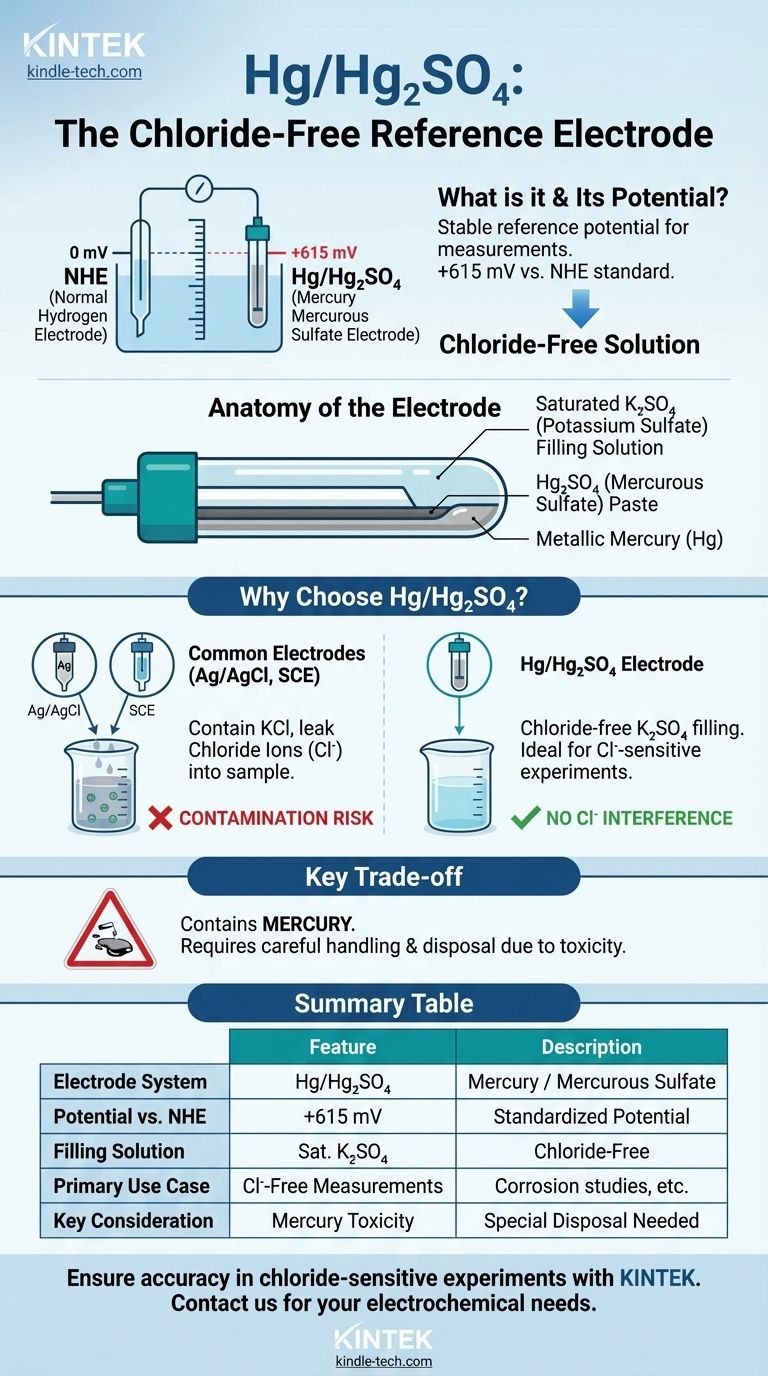
Technically, the mercury/mercurous sulfate (Hg/Hg₂SO₄) system is itself a reference electrode. Its purpose is to provide a stable, known electrochemical potential that other potentials can be measured against. The standard it is referenced to is the Normal Hydrogen Electrode (NHE), against which the Hg/Hg₂SO₄ electrode has a potential of +615 mV.
The Hg/Hg₂SO₄ electrode is a specialized, chloride-free reference electrode. It is used in electrochemical applications where chloride ion contamination from more common electrodes, like Ag/AgCl or Calomel, would interfere with the measurement or damage the sample.

The Role of a Reference Electrode
The Need for a Stable Baseline
In electrochemistry, we can only measure the potential difference between two points, not an absolute potential. A reference electrode acts as one of those points, providing a constant, stable potential.
This allows any change in the measured voltage to be confidently attributed to the reaction occurring at the other electrode, known as the working electrode.
The Universal Standard: NHE
The entire electrochemical scale is standardized against the Normal Hydrogen Electrode (NHE), which is assigned a potential of 0.000 volts by definition. All other reference electrode potentials, including that of Hg/Hg₂SO₄, are reported relative to this universal standard.
Anatomy of the Hg/Hg₂SO₄ Electrode
Core Components
The electrode consists of metallic mercury (Hg) in direct contact with a paste of mercurous sulfate (Hg₂SO₄). This equilibrium provides the stable potential.
The Chloride-Free Filling Solution
Its defining characteristic is its filling solution, which is typically saturated potassium sulfate (K₂SO₄). This is fundamentally different from the potassium chloride (KCl) solution used in more common reference electrodes.
Its Standard Potential
The established potential for the mercury/mercurous sulfate electrode is +0.615 V (or +615 mV) compared to the NHE. This value is critical for converting your experimental measurements to a standardized scale.
Why Choose Hg/Hg₂SO₄?
The Problem with Chloride Contamination
The two most common reference electrodes are the silver/silver chloride (Ag/AgCl) and the saturated calomel electrode (SCE). Both rely on a saturated potassium chloride (KCl) filling solution.
A small amount of this solution inevitably leaks from the electrode tip into the sample being tested. For many experiments, this is not a problem.
When to Use a Sulfate Reference
However, if your experiment is sensitive to chloride ions (Cl⁻), this leakage can invalidate your results. The Hg/Hg₂SO₄ electrode is the primary solution for these "chloride-free" applications.
This is especially critical in areas like corrosion studies, where chloride is a known pitting agent, or in solutions where chloride ions could precipitate with other ions in your sample.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Toxicity and Disposal
Like the calomel electrode (SCE), the Hg/Hg₂SO₄ electrode contains mercury. This poses significant toxicity and environmental disposal challenges, making it unsuitable for applications in food, beverage, or certain environmental studies.
Lower Popularity
Compared to the nearly ubiquitous Ag/AgCl electrode, the Hg/Hg₂SO₄ is a more specialized and less common piece of equipment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Experiment
Your choice of reference electrode is critical for ensuring the accuracy and integrity of your data.
- If your primary focus is general aqueous electrochemistry: The Ag/AgCl electrode is the most common, robust, and convenient choice for most applications.
- If your experiment is sensitive to chloride ions or involves silver ions: The Hg/Hg₂SO₄ electrode is the industry-standard alternative to prevent chloride contamination.
- If you must avoid both mercury and chloride: You may need to investigate even more specialized electrodes, such as the copper/copper sulfate (Cu/CuSO₄) electrode, depending on your specific chemical system.
Ultimately, the best reference electrode is the one that provides a stable potential without interfering with the chemistry you intend to study.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Electrode System | Mercury / Mercurous Sulfate (Hg/Hg₂SO₄) |
| Potential vs. NHE | +615 mV |
| Filling Solution | Saturated Potassium Sulfate (K₂SO₄) |
| Primary Use Case | Chloride-free electrochemical measurements |
| Main Advantage | Prevents chloride ion contamination from common electrodes |
| Key Consideration | Contains mercury; requires careful handling and disposal |
Ensure the accuracy of your chloride-sensitive experiments with the right equipment.
Choosing the correct reference electrode is critical for valid results. The Hg/Hg₂SO₄ electrode is essential for applications in corrosion studies and other scenarios where chloride contamination must be avoided.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving all your laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect reference electrode for your specific electrochemical setup.
Contact us today via our [#ContactForm] to discuss your application and find the ideal solution for your research.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Reference Electrode Calomel Silver Chloride Mercury Sulfate for Laboratory Use
- Rotating Platinum Disk Electrode for Electrochemical Applications
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
- Gold Disc Electrode
- Copper Sulfate Reference Electrode for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What is the reference electrode for mercury mercury chloride? Discover the Saturated Calomel Electrode (SCE)
- Which type of electrode can be used as a reference point? Select the Right One for Accurate Measurements
- Which electrode is used as a reference? A Guide to Accurate Electrochemical Measurements
- What are the characteristics of a saturated calomel electrode for neutral solutions? Understanding its stability and limitations.
- What are the four main types of sensors? A Guide to Power Source and Signal Type



















