At its core, brazing is a highly relevant industrial process used to create strong, permanent, and often leak-proof joints between two or more metal parts. It accomplishes this by melting and flowing a filler metal into the joint, which has a lower melting point than the adjoining base metals. Brazing is the go-to method for assembling complex components, joining dissimilar materials, and applications where the high heat of welding would cause unacceptable distortion or damage.
The true relevance of brazing lies not in its ability to replace welding, but in its unique capacity to solve joining problems that welding cannot. It enables the creation of high-precision, multi-material components that are foundational to modern aerospace, automotive, and electronics industries.

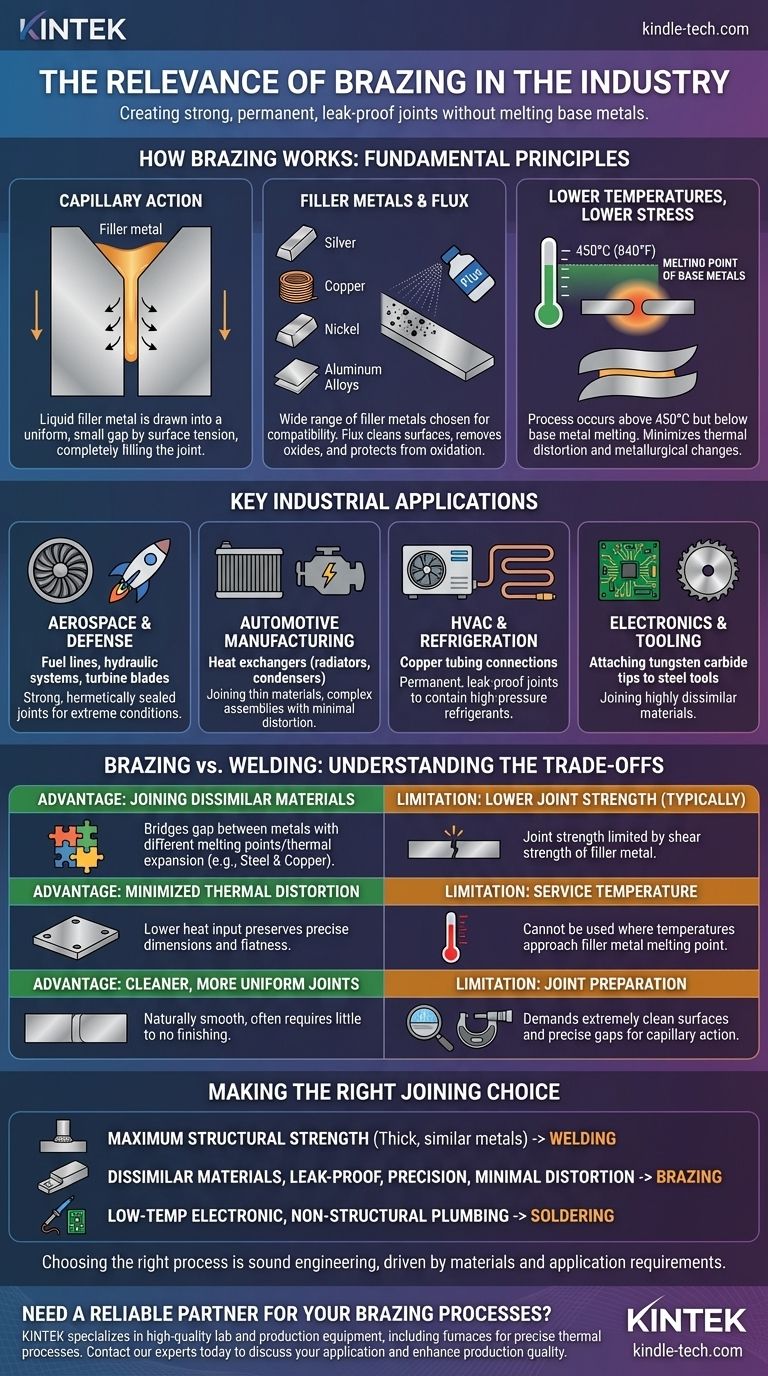
The Fundamental Principle: How Brazing Works
Brazing is a thermal joining process defined by a specific set of principles. Understanding these fundamentals is key to appreciating its role in manufacturing.
Capillary Action: The Core Mechanism
The success of a brazed joint depends on capillary action. The parts are designed with a very small, uniform gap between them. When the filler metal melts, surface tension pulls the liquid metal into this gap, completely filling the joint regardless of gravity.
The Role of Filler Metals and Flux
Brazing uses a wide range of filler metals, such as silver, copper, nickel, and aluminum alloys. The choice depends on the base metals and the required service conditions of the joint.
A flux is also critical. This chemical agent is applied before heating to clean the base metals, remove oxides, and protect the joint from oxidation during the brazing process, ensuring the filler metal can properly wet and bond to the surfaces.
Lower Temperatures, Lower Stress
Brazing occurs at temperatures above 450°C (840°F), but always below the melting point of the base metals. Unlike welding, the parent materials are only heated, not melted.
This lower heat input is a significant advantage, as it minimizes thermal distortion, residual stresses, and changes to the base metals' metallurgical properties.
Key Industrial Applications Where Brazing Excels
Brazing is not a niche process; it is a critical enabler in some of the most demanding industries. Its unique characteristics make it the only viable option for many high-performance applications.
Aerospace and Defense
In aerospace, reliability is non-negotiable. Brazing is used to join fuel lines, hydraulic systems, and critical engine components like turbine blades. The process creates strong, hermetically sealed joints that can withstand extreme temperatures and vibration.
Automotive Manufacturing
Brazing is essential for producing heat exchangers like radiators, condensers, and oil coolers. The ability to join thin aluminum sheets and tubes into a complex, leak-proof assembly with minimal distortion is something welding cannot easily achieve.
HVAC and Refrigeration
The vast majority of copper tubing in air conditioning and refrigeration units is joined by brazing. The process creates permanent, leak-proof connections required to contain high-pressure refrigerants safely and reliably for years.
Electronics and Tooling
Brazing is the standard method for attaching tungsten carbide tips to steel tool bodies for saw blades, drill bits, and mining tools. This is a classic example of its power to join highly dissimilar materials with vastly different properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Brazing vs. Welding
To fully grasp brazing's relevance, it's best understood in comparison to welding. The choice between them is a classic engineering trade-off.
Advantage: Joining Dissimilar Materials
This is brazing's greatest strength. Welding metals with very different melting points and thermal expansion rates (like steel and copper) is often impossible. Brazing easily bridges this gap.
Advantage: Minimized Thermal Distortion
Because the base metals are not melted, brazing introduces far less heat. This is crucial for maintaining the precise dimensions and flatness of complex or delicate assemblies.
Advantage: Cleaner, More Uniform Joints
Brazed joints are naturally smooth and uniform, often requiring little to no finishing. A welded joint, by contrast, frequently requires grinding or other post-processing.
Limitation: Lower Joint Strength (Typically)
While a well-designed brazed joint is very strong, it generally does not match the strength of a fully fused welded joint. The joint's strength is limited by the shear strength of the filler metal itself.
Limitation: Service Temperature
A brazed component cannot be used in an environment where temperatures approach the melting point of the filler metal. This is a primary design constraint.
Limitation: Joint Preparation
Brazing is less forgiving than welding. It demands extremely clean surfaces and a precise, consistent gap between parts for capillary action to work effectively.
Making the Right Joining Choice
The decision to use brazing, welding, or another method is dictated by the specific demands of the project.
- If your primary focus is maximum structural strength in thick, similar metals: Welding is almost always the superior and more cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar materials, creating leak-proof assemblies, or maintaining dimensional precision with minimal heat distortion: Brazing is the indispensable and technically correct solution.
- If your primary focus is low-temperature electronic connections or simple, non-structural plumbing: Soldering, a lower-temperature cousin of brazing, is the appropriate method.
Ultimately, choosing the right joining process is a hallmark of sound engineering, driven by a clear understanding of the materials and the final application's requirements.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Why It Matters for Brazing |
|---|---|
| Process | Uses capillary action to draw a filler metal into a joint, bonding parts without melting them. |
| Primary Advantage | Excellent for joining dissimilar materials (e.g., steel to copper) and complex, delicate assemblies. |
| Ideal For | Applications requiring leak-proof seals, minimal heat distortion, and high-precision components. |
| Common Industries | Aerospace, Automotive, HVAC, Electronics, and Tool Manufacturing. |
Need a reliable partner for your brazing processes? The right equipment is crucial for achieving strong, consistent, and leak-proof joints. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab and production equipment, including furnaces and systems designed for precise thermal processes like brazing. Whether you are in aerospace, automotive, or electronics manufacturing, our solutions help you join dissimilar materials with confidence. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific application and enhance your production quality.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the cost of a vacuum brazing furnace? A guide to key factors and investment strategy
- Where are vacuum furnaces used? Essential for High-Purity Heat Treatment in Critical Industries
- What is the difference between welding and vacuum brazing? Choose the Right Joining Method for Your Project
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining



















