At its core, the remelting process is a secondary melting technique designed to purify and refine an already-formed metal or alloy. In the most common method, Vacuum Arc Remelting (VAR), a solid metal bar called an electrode is re-melted using a high-temperature electric arc inside a vacuum, allowing the molten metal to re-solidify in a controlled manner to produce a final product with superior purity and structure.
The fundamental purpose of remelting is not simply to melt metal again, but to leverage a highly controlled environment—specifically a vacuum and a concentrated heat source—to remove impurities and dictate the crystal structure in a way that primary melting cannot achieve.

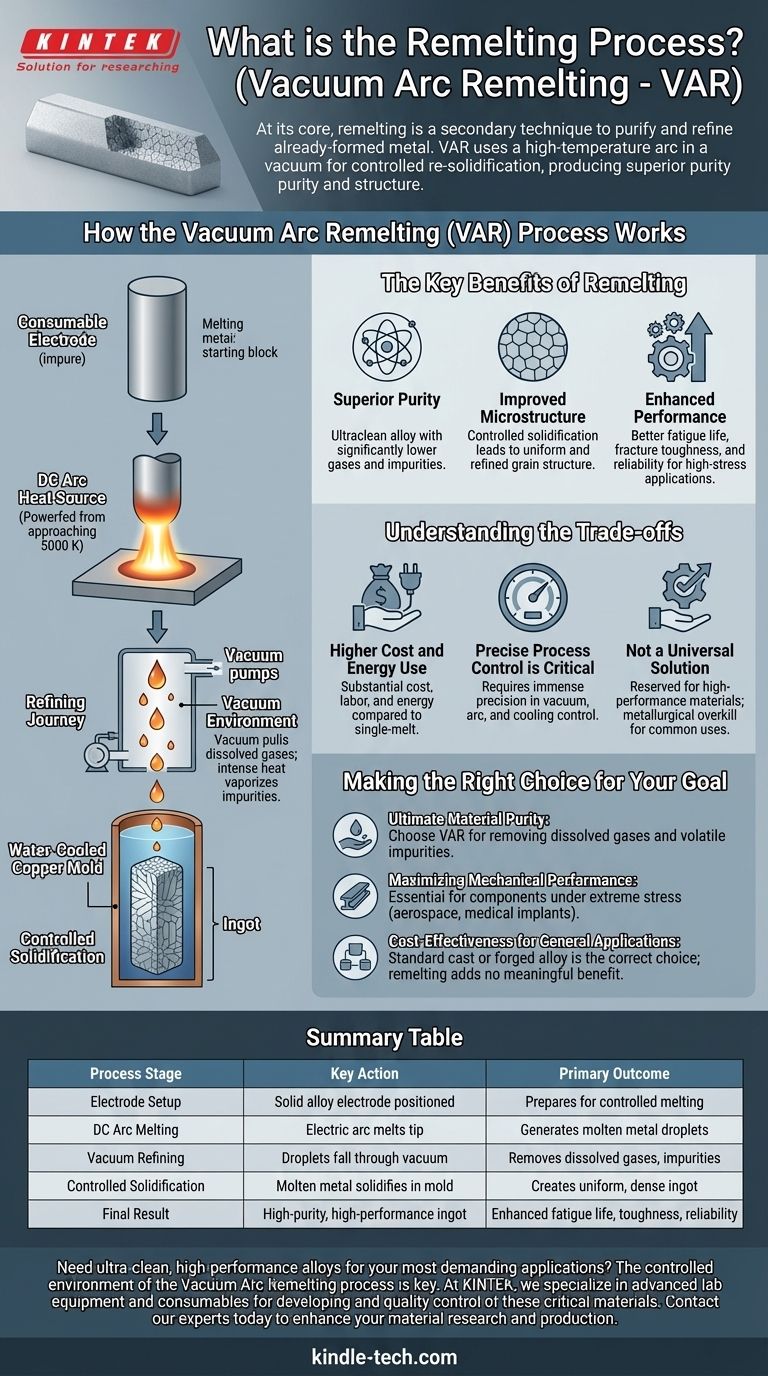
How the Vacuum Arc Remelting (VAR) Process Works
The VAR process is a systematic method for taking a good alloy and making it exceptional. It consists of a few key stages that work together to purify the material.
The Consumable Electrode
The process begins with the material to be refined, which is cast into a solid cylindrical bar known as a consumable electrode. This is essentially the "impure" starting block.
The DC Arc Heat Source
This electrode is placed inside a vacuum chamber and a powerful DC electric arc is struck between the bottom tip of the electrode and a baseplate. This arc generates immense, highly concentrated heat (approaching 5000 K), causing the tip of the electrode to melt rapidly.
The Refining Journey
As the electrode melts, it forms small droplets of liquid metal. These droplets detach and fall downward through the vacuum environment. This stage is where the primary purification happens.
The vacuum pulls dissolved gases (like hydrogen and nitrogen) out of the molten droplets, while the intense heat can vaporize other low-boiling-point impurities, effectively cleaning the metal in transit.
Controlled Solidification
The purified droplets collect in a water-cooled copper mold at the base of the chamber. Because the mold is actively cooled, the molten metal re-solidifies in a highly controlled, directional manner. This process creates a dense, uniform internal crystal structure, known as an ingot.
The Key Benefits of Remelting
This complex process is undertaken for very specific and critical reasons, primarily centered on achieving the highest possible material quality.
Superior Purity
The combination of high heat and vacuum is exceptionally effective at removing unwanted elements. The result is an ultraclean alloy with significantly lower levels of dissolved gases and trace element impurities.
Improved Microstructure
Standard cooling processes can introduce defects and inconsistencies into a metal's crystal structure. The controlled, directional solidification in the VAR process minimizes these issues, leading to a more uniform and refined grain structure.
Enhanced Performance
The direct result of high purity and a superior microstructure is enhanced material performance. Remelted alloys exhibit significantly better fatigue life, fracture toughness, and overall reliability, making them essential for high-stress applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the benefits are significant, the VAR process is a specialized tool with inherent trade-offs that limit its use to specific applications.
Higher Cost and Energy Use
Remelting is a secondary process performed on an already-made alloy. This additional manufacturing step adds substantial cost, labor, and energy consumption compared to a single-melt material.
Precise Process Control is Critical
Although the principles are straightforward, execution requires immense precision. Maintaining the correct vacuum level, controlling the arc stability, and managing the cooling rate are all critical. Any deviation can compromise the quality of the entire ingot.
Not a Universal Solution
Due to the expense and complexity, remelting is reserved for high-performance materials. It is metallurgical overkill for common structural steels or standard aluminum alloys where the added cost provides no practical benefit.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding whether to specify a remelted material depends entirely on the non-negotiable requirements of your application.
- If your primary focus is ultimate material purity and cleanliness: VAR is the definitive choice for removing dissolved gases and volatile impurities that are impossible to eliminate in a standard air-melt process.
- If your primary focus is maximizing mechanical performance and reliability: The refined, uniform grain structure from the VAR process is essential for components subjected to extreme stress or cyclical fatigue, such as in aerospace or medical implants.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for general applications: A standard cast or forged alloy is almost always the correct choice, as the significant added expense of remelting will not deliver a meaningful performance benefit.
Ultimately, specifying a remelted material is a strategic decision to invest in metallurgical perfection for the most demanding applications.
Summary Table:
| Process Stage | Key Action | Primary Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Electrode Setup | Solid alloy electrode is positioned in a vacuum chamber. | Prepares the starting material for controlled melting. |
| DC Arc Melting | An electric arc melts the electrode tip. | Generates molten metal droplets for purification. |
| Vacuum Refining | Droplets fall through a vacuum. | Removes dissolved gases and volatile impurities. |
| Controlled Solidification | Molten metal solidifies in a water-cooled mold. | Creates a uniform, dense ingot with a refined grain structure. |
| Final Result | A high-purity, high-performance ingot is produced. | Delivers enhanced fatigue life, toughness, and reliability. |
Need ultra-clean, high-performance alloys for your most demanding applications? The controlled environment of the Vacuum Arc Remelting process is key to achieving the material purity and structural integrity required for aerospace, medical, and energy components. At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment and consumables that support the development and quality control of these critical materials. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your material research and production capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the overview of vacuum arc remelting? Achieve Ultra-Clean, High-Performance Alloys
- What is a remelting process? A Guide to High-Purity Metal Refinement
- What is the process of vacuum arc remelting? Achieve Ultimate Purity for High-Performance Alloys
- What is VAR in metallurgy? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Performance
- What is the benefit of vacuum arc remelting? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Structural Integrity



















