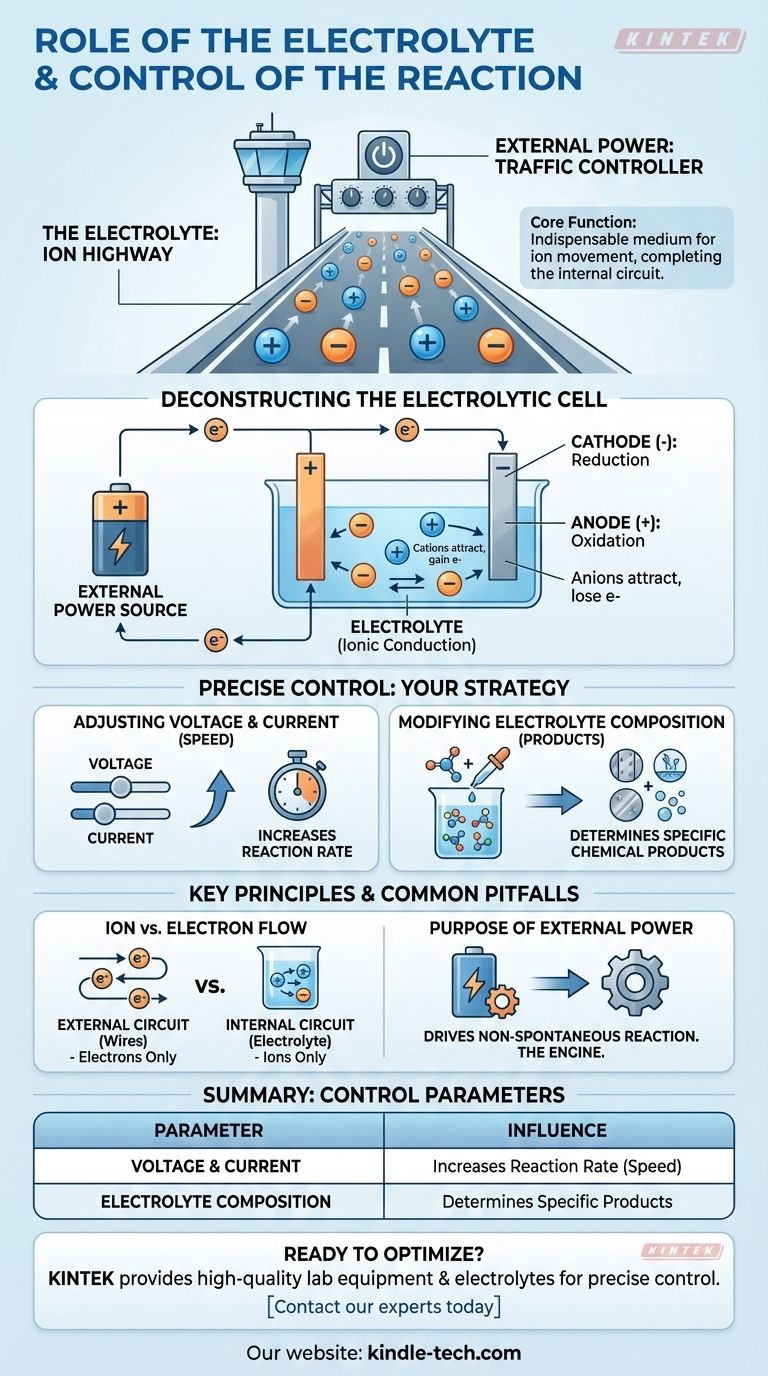
At its core, the electrolyte is the indispensable medium for ion movement within a cell, completing the electrical circuit that allows a chemical reaction to occur. The reaction itself is precisely controlled by manipulating external electrical inputs—specifically the voltage and current—and by changing the chemical makeup of the electrolyte solution.
The electrolyte acts as an "ion highway," allowing charged particles to travel between electrodes inside the cell. The external power supply acts as the "traffic controller," dictating the speed and direction of the chemical reaction by managing the flow of electrons.

The Fundamental Role of the Electrolyte
An electrochemical reaction requires a complete circuit. The electrolyte is responsible for the internal half of that circuit, a role fundamentally different from the wires connected externally.
What is an Electrolyte?
An electrolyte is a solution, typically aqueous or organic, that contains dissociated ions.
These free-floating positive and negative ions are what make the solution electrically conductive.
Enabling Ionic Conduction
The primary function of the electrolyte is ionic conduction.
While electrons flow through the external wires, ions must flow through the solution between the two electrodes. This movement of charged ions completes the circuit, allowing the reaction to be sustained.
Deconstructing the Electrolytic Cell
In an electrolytic cell, an external power source drives a chemical reaction that would not otherwise happen on its own. Here is how the components work together.
The External Power Source
The process begins with an external power source, like a battery or power supply.
This source actively pumps electrons, creating a charge difference between the two electrodes that forces the reaction to proceed.
The Cathode (The Site of Reduction)
The external source pushes electrons to the cathode, giving it a negative charge.
This negative charge attracts the positively charged ions (cations) from the electrolyte. When these ions reach the cathode, they gain electrons in a process called reduction.
The Anode (The Site of Oxidation)
Simultaneously, the external source pulls electrons away from the anode, giving it a positive charge.
This positive charge attracts the negatively charged ions (anions) from the electrolyte. At the anode, these ions lose electrons in a process known as oxidation.
How the Reaction is Precisely Controlled
You have direct control over the outcome and rate of the electrochemical reaction by adjusting three key parameters.
Adjusting Voltage and Current
Voltage can be thought of as the electrical "pressure" driving the reaction, while current is the rate of electron flow.
Increasing the voltage and current will generally increase the rate at which the chemical reaction occurs. This gives you direct, real-time control over the process speed.
Modifying Electrolyte Composition
The specific chemical reaction that takes place is determined by the ions available in the electrolyte.
By changing the composition of the electrolyte—for example, by using a different salt or solvent—you can change the products that are formed at the anode and cathode.
Common Pitfalls and Key Principles
To truly understand the system, it's critical to distinguish between the two halves of the circuit and the nature of the cell.
Ion Movement vs. Electron Flow
A common point of confusion is the difference between what happens inside and outside the cell.
Electrons flow only through the external circuit (the wires). Ions flow only through the internal circuit (the electrolyte). The reaction at the electrode surfaces is what connects these two distinct pathways.
The Purpose of the External Power
It is crucial to remember that this process describes an electrolytic cell.
In these cells, electrical energy is used to drive a non-spontaneous chemical reaction. The external power source is not optional; it is the engine making the entire process possible.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your control strategy depends entirely on what you want to achieve with the reaction.
- If your primary focus is to speed up the reaction rate: Increase the applied voltage and current to drive the flow of electrons and ions more quickly.
- If your primary focus is to create a specific chemical product: Carefully select and control the composition of the electrolyte to ensure the desired ions are available for reaction.
- If your primary focus is to understand the system's efficiency: You must monitor both the electron flow (current) in the external circuit and the resulting chemical change (ion conversion) at the electrodes.
Ultimately, mastering an electrochemical process means understanding that the electrolyte and the external circuit are two halves of a single, controllable system.
Summary Table:
| Control Parameter | How It Influences the Reaction |
|---|---|
| Voltage & Current | Increases the rate (speed) of the chemical reaction. |
| Electrolyte Composition | Determines the specific chemical products formed. |
Ready to Optimize Your Electrochemical Process?
Whether you are developing new materials, performing electroplating, or conducting precise analytical tests, controlling your electrochemical reaction is critical. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your laboratory needs, including reliable power supplies and pure electrolytes.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you achieve precise control and superior results in your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- H Type Electrolytic Cell Triple Electrochemical Cell
- Double Layer Five-Port Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- Quartz Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Electrochemical Experiments
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
People Also Ask
- What are the typical volumes and aperture configurations for a double-layer water-bath electrolytic cell? Optimize Your Electrochemical Setup
- What are the standard opening specifications for an H-type exchangeable membrane electrolytic cell? Asymmetrical Ports for Precise Electrochemistry
- What is the purpose of the double-layer structure in the H-type electrolytic cell? Achieve Precise Thermal Control
- What optical features does the H-type electrolytic cell have? Precision Quartz Windows for Photoelectrochemistry
- What is the typical experimental system used with a double-layer water-bath electrolytic cell? Achieve Precise Electrochemical Control



















