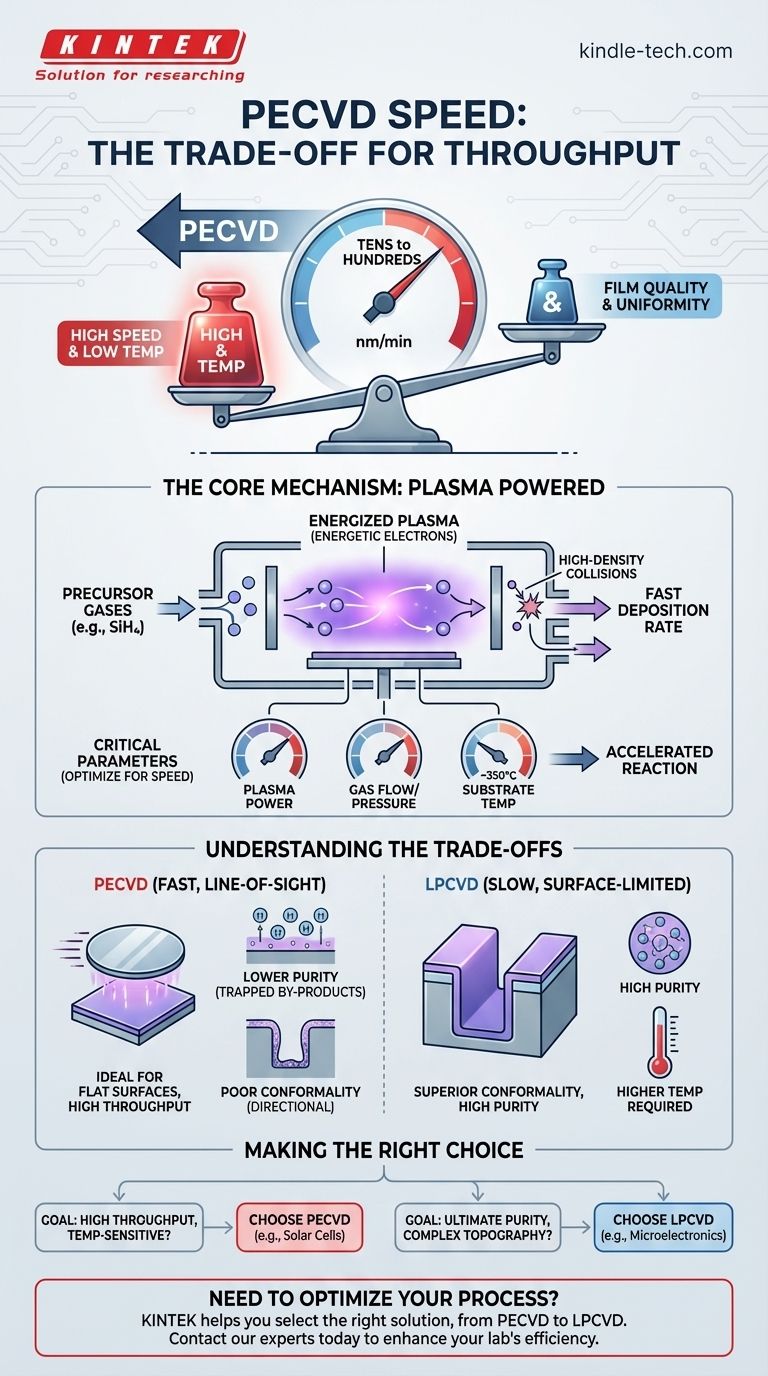
In short, the deposition rate of Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) is not a single number, but it is known for being significantly faster than many alternative methods like Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD). The exact speed is highly variable, ranging from tens to hundreds of nanometers per minute, as it is directly controlled by a set of optimized process parameters including gas pressure, temperature, and plasma power.
The central takeaway is that PECVD intentionally sacrifices some film quality and uniformity in exchange for high deposition speed and, critically, lower operating temperatures. Understanding this trade-off between speed and perfection is the key to deciding if PECVD is the right tool for your specific application.

What Determines PECVD Deposition Rate?
The high speed of PECVD is not accidental; it is a direct result of its core mechanism. Unlike processes that rely solely on thermal energy, PECVD uses an energized plasma to drive the chemical reaction, dramatically accelerating the entire process.
The Role of Plasma
The defining feature of PECVD is the use of a plasma, or a glow discharge, between two electrodes. This plasma creates a high-density field of energetic electrons that collide with the reactant gas molecules.
These collisions break down the precursor gases (like silane, SiH4) far more efficiently than heat alone. This creates a high concentration of reactive chemical species, leading directly to a faster deposition rate on the substrate surface.
Critical Process Parameters
The speed is not fixed but is actively tuned by the operator. The key controllable parameters that influence the deposition rate include:
- Gas Flow and Pressure: Higher reactant gas flow can increase the rate, but pressure must be optimized to control the plasma and reaction environment.
- Plasma Power and Frequency: Increasing the discharge voltage or current density increases the plasma's energy, which can accelerate the breakdown of precursor gases and boost the deposition rate.
- Substrate Temperature: While PECVD is a "low-temperature" process (often around 350°C), temperature still influences surface reactions and the quality of the deposited film.
Gas Chemistry and Precursors
The choice of reactant gases is fundamental. For example, in the creation of a silicon nitride (SiNx) anti-reflection layer for solar cells, ammonia (NH3) and silane (SiH4) are used. The specific reaction kinetics of these chosen precursors sets the baseline for the potential deposition speed.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Speed vs. Quality
PECVD's speed comes with inherent compromises. The rapid, plasma-driven deposition process creates films with different characteristics than slower, thermally-driven methods.
Film Purity and Density
Because the deposition is so fast, there is a higher chance of trapping by-products, such as hydrogen from the precursor gases, within the film. This can lead to a less dense and less pure film compared to the output of a slower process like LPCVD. This can affect the film's electrical properties and mechanical stability.
Step Coverage (Conformality)
Step coverage, or conformality, is the ability of a film to evenly coat a surface with complex 3D topography. PECVD is generally a more directional, line-of-sight process due to the nature of the plasma.
This makes it less effective at uniformly coating the sidewalls of deep trenches or complex structures. Slower, surface-reaction-limited processes like LPCVD excel at this, providing superior conformality.
Application-Specific Advantages
These trade-offs are often acceptable depending on the goal. For depositing a silicon nitride anti-reflection coating on a relatively flat silicon wafer, perfect conformality is not the primary concern.
In this context, PECVD is the ideal choice. Its high speed allows for greater manufacturing throughput, and its low temperature prevents damage to the underlying structures of the solar cell, ultimately improving its efficiency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a deposition technology is about matching the process characteristics to your application's most critical requirements.
- If your primary focus is high throughput and temperature-sensitive substrates: PECVD is almost always the superior choice for coating large, relatively flat surfaces quickly and without high heat.
- If your primary focus is ultimate film purity and coating complex topography: A slower, high-temperature method like LPCVD is often required to achieve the necessary conformality and material quality for demanding microelectronic components.
Choosing the right method requires a clear understanding of whether your priority is manufacturing speed or film perfection.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on PECVD Speed |
|---|---|
| Plasma Power | Higher power increases the deposition rate by energizing the reaction. |
| Gas Flow/Pressure | Optimized flow and pressure are key to maximizing the rate. |
| Precursor Gases | The specific chemistry sets the baseline potential speed. |
| Trade-off | Higher speed often comes with lower film purity and conformality compared to LPCVD. |
Need to optimize your thin-film deposition process?
KINTEK specializes in providing lab equipment and consumables for advanced materials research. Whether your priority is the high-speed, low-temperature capabilities of PECVD or the superior film quality of LPCVD, our experts can help you select the right solution for your specific application, from solar cells to microelectronics.
Contact our team today to discuss your project requirements and enhance your lab's efficiency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate


















