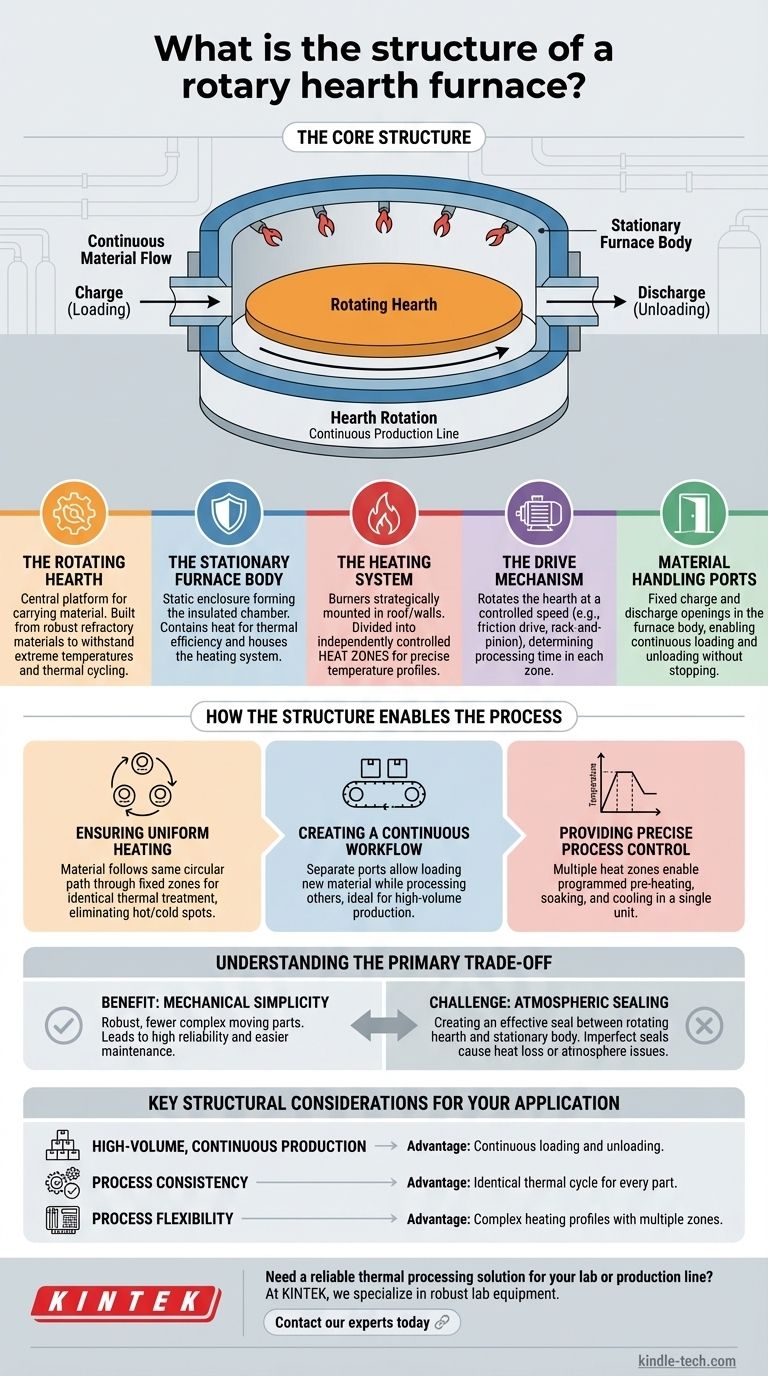
At its core, the structure of a rotary hearth furnace is remarkably straightforward. It consists of a large, circular, rotating platform—the hearth—enclosed within a stationary, insulated furnace body. This design allows materials to be continuously loaded at one point, carried through different heating zones as the hearth rotates, and then unloaded at another point.
The fundamental purpose of this structure is to create a continuous production line within a single furnace. By moving the material on a rotating platform through fixed temperature zones, it guarantees that every single part receives an identical and highly uniform thermal treatment.
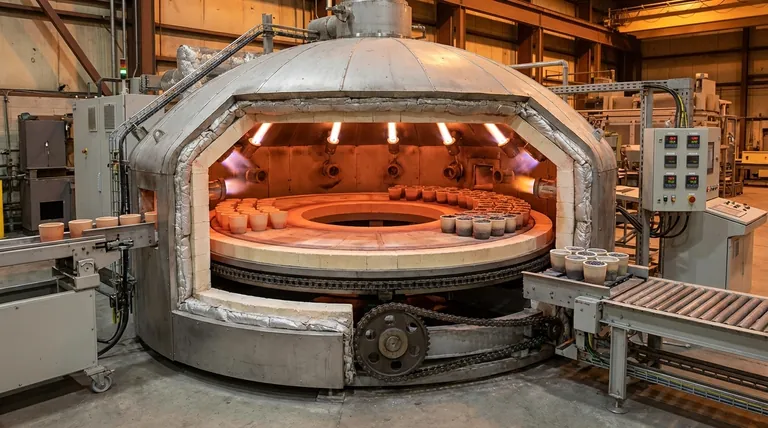

Deconstructing the Key Structural Components
To understand how a rotary hearth furnace operates, it's essential to examine its main structural elements and the role each one plays.
The Rotating Hearth
The hearth is the central, defining component. It is a large, flat, donut-shaped platform that rotates slowly within the furnace.
This platform is built from robust refractory materials, chosen for their ability to withstand extreme temperatures and thermal cycling without degrading. It essentially acts as the conveyor system for the material being processed.
The Stationary Furnace Body
The furnace body, or chamber, is the static enclosure that surrounds the rotating hearth. It forms the roof and walls of the heating environment.
This structure is heavily insulated to contain the immense heat, ensuring thermal efficiency and maintaining a stable internal temperature. It houses the heating system and has fixed ports for loading and unloading material.
The Heating System
Heat is typically generated by a series of burners fired by gas or oil. These burners are strategically mounted in the roof or walls of the stationary furnace body.
Crucially, the furnace is often divided into multiple, independently controlled heat zones. This structural feature allows for precise temperature profiles, enabling processes like pre-heating, soaking, and controlled cooling to occur sequentially as the hearth rotates.
The Drive Mechanism
The hearth itself is rotated by a powerful drive system. This is typically a friction drive wheel system or a more positive rack-and-pinion or chain drive, depending on the size of the furnace.
This mechanism controls the rotational speed of the hearth, which directly determines the amount of time the material spends in each heating zone—a critical process variable.
Material Handling Ports
Fixed openings in the stationary furnace body serve as the charge (loading) and discharge (unloading) ports. As the hearth rotates, it brings a new section of the platform past the charge port to receive material and simultaneously moves a fully processed section to the discharge port for removal.
How the Structure Enables the Process
The interaction between these static and dynamic components is what makes the furnace so effective for high-volume, precision heating applications.
Ensuring Uniform Heating
Because every piece of material placed on the hearth follows the exact same circular path through the same fixed temperature zones, heating is exceptionally uniform. This design eliminates the common issues of hot and cold spots found in batch furnaces.
Creating a Continuous Workflow
The separation of charge and discharge ports allows the furnace to operate continuously. New, cold material can be loaded without interrupting the processing of materials already inside, making it ideal for integration into a larger production line.
Providing Precise Process Control
The use of multiple heat zones gives operators precise control over the entire thermal cycle. A product can be brought up to temperature slowly, held at a peak temperature for a specific duration, and then cooled at a controlled rate, all within one machine.
Understanding the Primary Trade-off
While highly effective, the design of a rotary hearth furnace presents a core engineering challenge that defines its primary trade-off.
The Benefit: Mechanical Simplicity
The core concept is mechanically robust and relatively simple. A rotating table inside a heated box has fewer complex moving parts than many alternative continuous systems, leading to high reliability and easier maintenance.
The Challenge: Atmospheric Sealing
The most significant challenge is creating and maintaining an effective seal between the edge of the rotating hearth and the floor of the stationary furnace body. Imperfect seals can lead to heat loss, reducing efficiency, or allow atmosphere to enter or exit the furnace, which is a critical issue when a specific controlled atmosphere is required.
Key Structural Considerations for Your Application
The structure of a rotary hearth furnace is designed for specific industrial goals.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, continuous production: The structure's ability to be constantly loaded and unloaded without stopping is its defining advantage.
- If your primary focus is process consistency: The hearth's rotational movement through fixed zones ensures every part receives an identical thermal cycle, guaranteeing uniformity.
- If your primary focus is process flexibility: The division into multiple, independently controlled heating zones allows you to program complex and precise heating profiles within a single unit.
Ultimately, the furnace's structure is a direct and elegant solution to the challenge of performing consistent, high-volume thermal processing.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Rotating Hearth | Carries material through the furnace | Robust refractory platform |
| Stationary Furnace Body | Encloses the heating environment | Heavily insulated chamber |
| Heating System | Provides heat in controlled zones | Multiple, independently controlled burners |
| Drive Mechanism | Rotates the hearth at a controlled speed | Friction drive or rack-and-pinion system |
| Material Handling Ports | Allow for continuous loading and unloading | Fixed charge and discharge openings |
Need a reliable thermal processing solution for your lab or production line?
The precise, continuous operation of a rotary hearth furnace is ideal for achieving uniform results in high-volume applications. At KINTEK, we specialize in supplying robust lab equipment, including furnaces, to meet your specific thermal processing needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your efficiency and consistency.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a rotary retort furnace? Achieve Superior Uniformity in Continuous Heat Treatment
- How do tube furnaces or muffle furnaces ensure stoichiometric accuracy during synthesis? Mastering Li4GeO4 & Li4VO4
- What is the process of zirconium production? From Ore to High-Performance Metal & Ceramic
- What is the function of a high-temperature furnace during burnout? Master Aluminum Foam Production with Precision
- Why is a high-temperature furnace with multi-probe testing used for ABO3 perovskite? Get Precise Conductivity Data



















