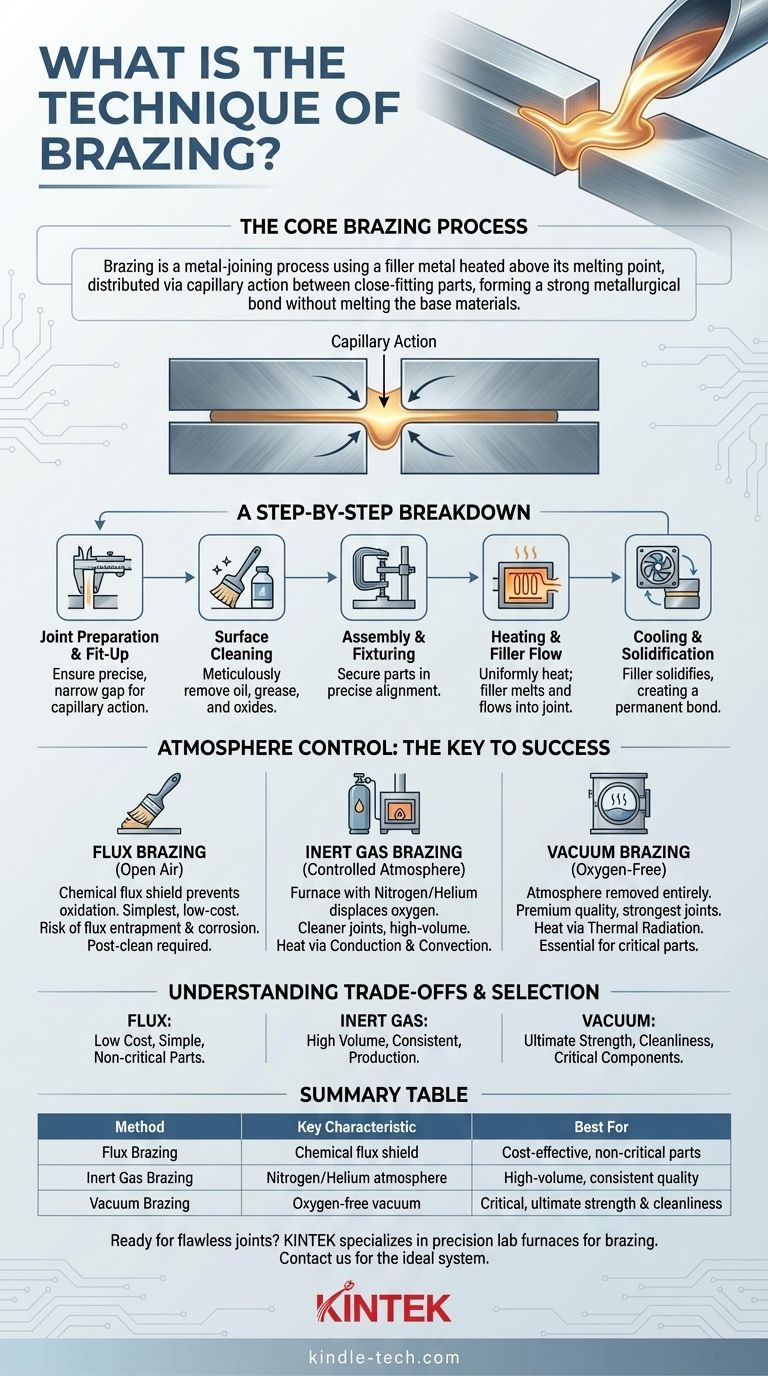
In technical terms, brazing is a metal-joining process where a filler metal is heated above its melting point and distributed between two or more close-fitting parts. The filler metal, which has a lower melting point than the base metals, is drawn into the gap via capillary action. Upon cooling, it solidifies to form a strong, permanent metallurgical bond without melting the base materials themselves.
The central principle of brazing is not to melt the parent materials, but to use a specialized filler alloy that melts at a lower temperature. This alloy flows into a precisely fitted joint within a controlled, oxygen-free environment, creating a clean and powerful bond upon cooling.

The Core Brazing Process: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
Successful brazing is a systematic process that relies on careful preparation and execution. Each step is critical to achieving a sound and reliable joint.
Step 1: Joint Preparation and Fit-Up
The gap between the parts to be joined is a critical parameter. It must be narrow enough to allow capillary action to draw the molten filler metal into the joint, yet wide enough to allow the filler to penetrate completely.
Step 2: Surface Cleaning
All surfaces within the joint area must be meticulously cleaned. Any contaminants such as oil, grease, or oxides will prevent the filler metal from wetting the surfaces and creating a strong bond.
Step 3: Assembly and Fixturing
The parts are assembled into their final configuration. They are held in precise alignment using clamps, jigs, or other support fixtures to ensure they do not move during the heating and cooling cycle.
Step 4: Heating and Filler Flow
The entire assembly is heated uniformly in a furnace. When the brazing temperature is reached, the filler metal melts and flows into the joint, displacing the flux or protected by the controlled atmosphere.
Step 5: Cooling and Solidification
After the filler has fully penetrated the joint, the assembly is cooled. The filler metal solidifies, creating a permanent, high-strength connection between the components. The finished part may then require final cleaning.
The Critical Role of Atmosphere Control
Heating metals to brazing temperatures makes them highly reactive with oxygen in the air, which forms oxides that inhibit the joining process. Therefore, protecting the joint is non-negotiable.
The Problem: Oxidation
At red heat, most metals will rapidly oxidize. This oxide layer acts as a barrier, preventing the molten filler alloy from bonding with the parent materials and resulting in a failed joint.
Solution 1: Flux
For brazing in open air, a chemical flux is applied to the joint. When heated, the flux melts and creates a protective shield over the joint area, preventing oxidation and cleaning the surfaces to promote filler flow.
Solution 2: Controlled Atmosphere (Inert Gas)
In more advanced applications, the entire process is performed inside a furnace filled with a controlled, oxygen-free atmosphere. Inert gases like nitrogen or helium are commonly used to displace all oxygen, protecting the assembly. In these furnaces, heat is transferred primarily through conduction and convection.
Solution 3: Vacuum Brazing
For the highest-quality joints, especially with reactive metals, the process is done in a vacuum furnace. By removing the atmosphere entirely, the possibility of oxidation is eliminated. In a vacuum, heat transfer occurs exclusively through thermal radiation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice of brazing environment directly impacts cost, quality, and material compatibility. There is no single "best" method; the correct choice depends entirely on the application's requirements.
Flux Brazing
This is the simplest and often lowest-cost method. However, it carries the risk of flux becoming trapped within the joint, which can lead to corrosion or create a weak point. Post-braze cleaning is almost always required.
Inert Gas Brazing
This method produces cleaner joints than flux brazing and is well-suited for high-volume production in continuous furnaces. The primary costs are the specialized furnace and the consumption of inert gas.
Vacuum Brazing
This is the premium brazing process, producing the cleanest, strongest, and most reliable joints. It is essential for aerospace, medical, and other critical applications. The trade-offs are significantly higher equipment costs and generally longer cycle times.
How to Select the Right Brazing Method
Your application's specific goals will determine the most appropriate brazing technique.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for non-critical parts: Flux brazing in an open-air or simple batch furnace is the most direct approach.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production with consistent quality: Continuous furnace brazing with an inert gas atmosphere provides an excellent balance of throughput and reliability.
- If your primary focus is ultimate strength and cleanliness for critical components: Vacuum brazing is the definitive choice, eliminating any risk of atmospheric contamination.
Understanding these core principles—joint design, cleanliness, and atmosphere control—is the key to leveraging brazing to create exceptionally strong and reliable assemblies.
Summary Table:
| Brazing Method | Key Characteristic | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Flux Brazing | Uses chemical flux to prevent oxidation | Cost-effective, non-critical parts |
| Inert Gas Brazing | Uses nitrogen/helium atmosphere | High-volume production, consistent quality |
| Vacuum Brazing | Occurs in oxygen-free vacuum | Critical components, ultimate strength & cleanliness |
Ready to achieve flawless, high-strength metal joints? The right brazing equipment is critical for your success. At KINTEK, we specialize in precision lab furnaces for brazing, including advanced controlled atmosphere and vacuum models. Our solutions ensure optimal temperature control and atmosphere purity for perfect results every time.
Let our experts help you select the ideal brazing system for your specific materials and application requirements.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and discover how our reliable lab equipment can enhance your metal-joining processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the sintering time? A Critical Process Variable for Material Density and Strength
- Does sintering use diffusion? The Atomic Mechanism for Building Stronger Materials
- Why is environmental control within a vacuum furnace important for diffusion bonding? Master Titanium Alloy Laminates
- What are the methods of brazing heating? Choose the Right Method for Your Production Needs
- What is the operating temperature of a furnace? From Home Heating to Industrial Processing



















