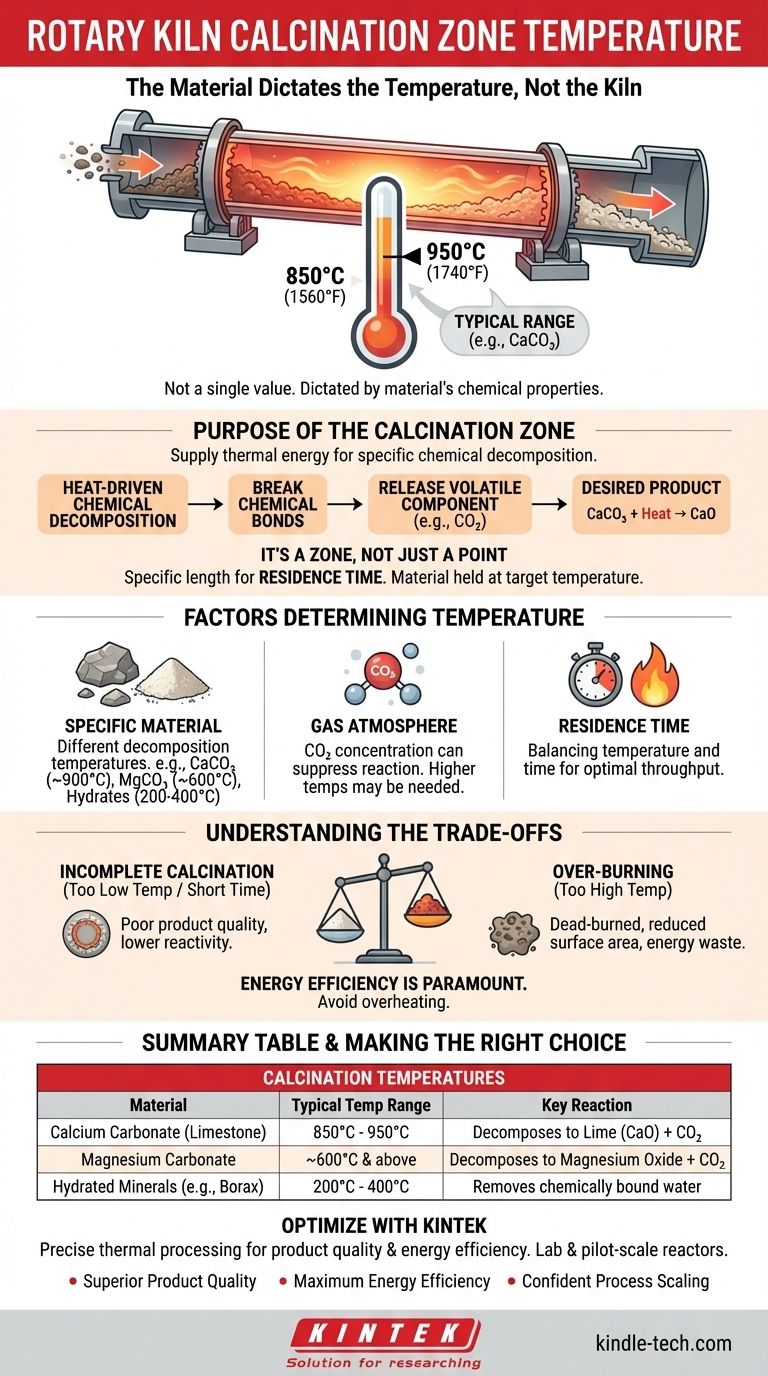
The temperature in the calcination zone of a rotary kiln is not a single value, but is instead dictated entirely by the chemical properties of the material being processed. For the most common application, the calcination of calcium carbonate (CaCO3) in cement and lime production, the material bed temperature is typically maintained between 850°C and 950°C (1560°F to 1740°F) to facilitate the necessary chemical decomposition.
The core principle to understand is that the kiln provides the environment, but the material dictates the temperature. Calcination is a chemical reaction, and the required temperature is the specific point at which the raw material breaks down into its desired components.

What is the Purpose of the Calcination Zone?
The rotary kiln is a carefully controlled environment with distinct thermal zones. The calcination zone's sole purpose is to supply enough thermal energy to trigger a specific chemical decomposition.
Heat-Driven Chemical Decomposition
Calcination is the process of heating a solid material to drive off a volatile component. This is not simply drying; it is a fundamental chemical change.
The heat energy supplied in this zone must be sufficient to break the chemical bonds within the material. A classic example is heating limestone (calcium carbonate, CaCO3) until it breaks down, releasing carbon dioxide (CO2) gas and leaving behind lime (calcium oxide, CaO).
It's a Zone, Not Just a Point
The calcination zone is a specific length of the kiln where the material is held within the target temperature range. The material moves through this zone as the kiln rotates, providing the necessary residence time for the reaction to complete.
Factors That Determine the Calcination Temperature
The exact temperature is a function of chemistry and physics. Several variables must be managed to ensure an efficient and complete reaction.
The Specific Material Being Processed
This is the single most important factor. Different materials decompose at vastly different temperatures.
- Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3): Requires a material temperature of around 900°C for the decomposition to proceed at an effective rate.
- Hydrated Minerals (e.g., Borax): Removing chemically bound water occurs at much lower temperatures, often in the 200°C to 400°C range.
- Magnesium Carbonate (MgCO3): Decomposes at a lower temperature than calcium carbonate, typically starting around 600°C.
The Kiln's Gas Atmosphere
The composition of the hot gas flowing through the kiln also plays a role. In the case of limestone calcination, the reaction is reversible.
A high concentration of CO2 in the kiln atmosphere can suppress or slow down the reaction, requiring slightly higher temperatures to overcome the partial pressure of the gas.
Residence Time
Temperature and time are interconnected. A lower temperature may suffice if the material is held in the zone for a longer period. Conversely, a higher temperature can speed up the reaction. Operators balance these two factors for optimal throughput and energy efficiency.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Achieving the correct calcination is a balancing act. Mismanaging the process leads to poor product quality and wasted energy.
The Risk of Incomplete Calcination
If the temperature is too low or the residence time is too short, the material will not fully decompose. This results in a final product with an unreacted core, reducing its purity and reactivity. For cement, this means lower quality; for lime, it means poor performance in chemical applications.
The Risk of Over-Burning
If the temperature is too high, the material can become "dead-burned" or sintered. This process reduces the surface area and reactivity of the final product. Over-burned lime, for example, is slow to slake (react with water) and is less effective.
Energy Efficiency is Paramount
Operating a rotary kiln is extremely energy-intensive. Running the calcination zone even slightly hotter than necessary results in a significant waste of fuel, driving up operational costs and environmental impact without any benefit to the product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The correct temperature setting is a direct consequence of your processing objective. You must optimize the kiln's operation to match the specific needs of your material.
- If your primary focus is producing lime or cement: Your goal is to hold the material bed near 900°C to fully decompose the calcium carbonate without over-burning the resulting lime.
- If your primary focus is removing bound water from a hydrate: You must use a much lower temperature specific to that mineral to drive off the water without melting or otherwise degrading the material.
- If your primary focus is general process efficiency: You need to find the lowest possible temperature and shortest residence time that still achieves complete calcination to minimize fuel consumption.
Ultimately, precise temperature control is the key to ensuring both product quality and operational profitability.
Summary Table:
| Material | Typical Calcination Zone Temperature Range | Key Reaction |
|---|---|---|
| Calcium Carbonate (Limestone) | 850°C - 950°C (1560°F - 1740°F) | Decomposes to Lime (CaO) + CO₂ |
| Magnesium Carbonate | ~600°C and above | Decomposes to Magnesium Oxide + CO₂ |
| Hydrated Minerals (e.g., Borax) | 200°C - 400°C | Removes chemically bound water |
Optimize Your Calcination Process with KINTEK
Precise thermal processing is critical for product quality and energy efficiency. Whether you are processing minerals, chemicals, or advanced materials, selecting the right equipment is the first step.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab and pilot-scale reactors and furnaces, perfect for determining the exact calcination parameters your material requires before scaling up to industrial production.
Let us help you achieve:
- Superior Product Quality: Avoid incomplete calcination or over-burning.
- Maximum Energy Efficiency: Identify the optimal temperature and residence time for your specific material.
- Confident Process Scaling: Use reliable data from our equipment to design your full-scale operation.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your thermal processing needs. Our experts are ready to provide solutions that ensure your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of an industrial rotary tube furnace? Master Tungsten Powder Hydrogen Reduction
- What is the purpose of pre-treating coal samples? Ensure Accurate Pyrolysis with Nitrogen Drying
- What are the advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for MoVOx catalysts? Elevate Uniformity and Crystallinity
- What is modified chemical vapour deposition method? The Inside-Out Process for Ultra-Pure Optical Fibers
- What are the advantages of a rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Homogeneity & Efficiency for Powders & Granules



















