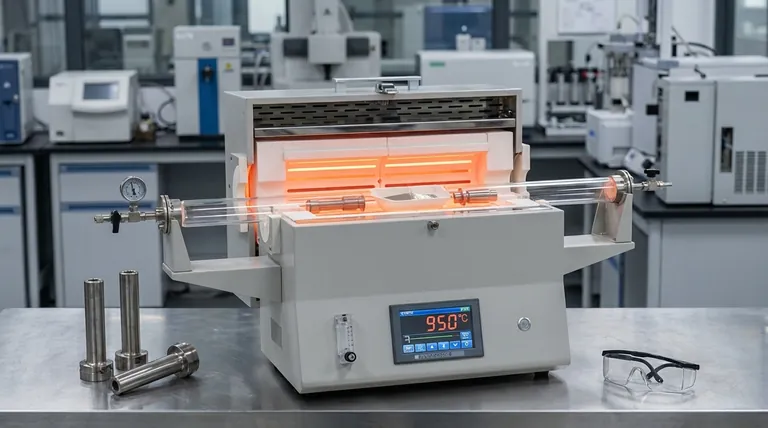
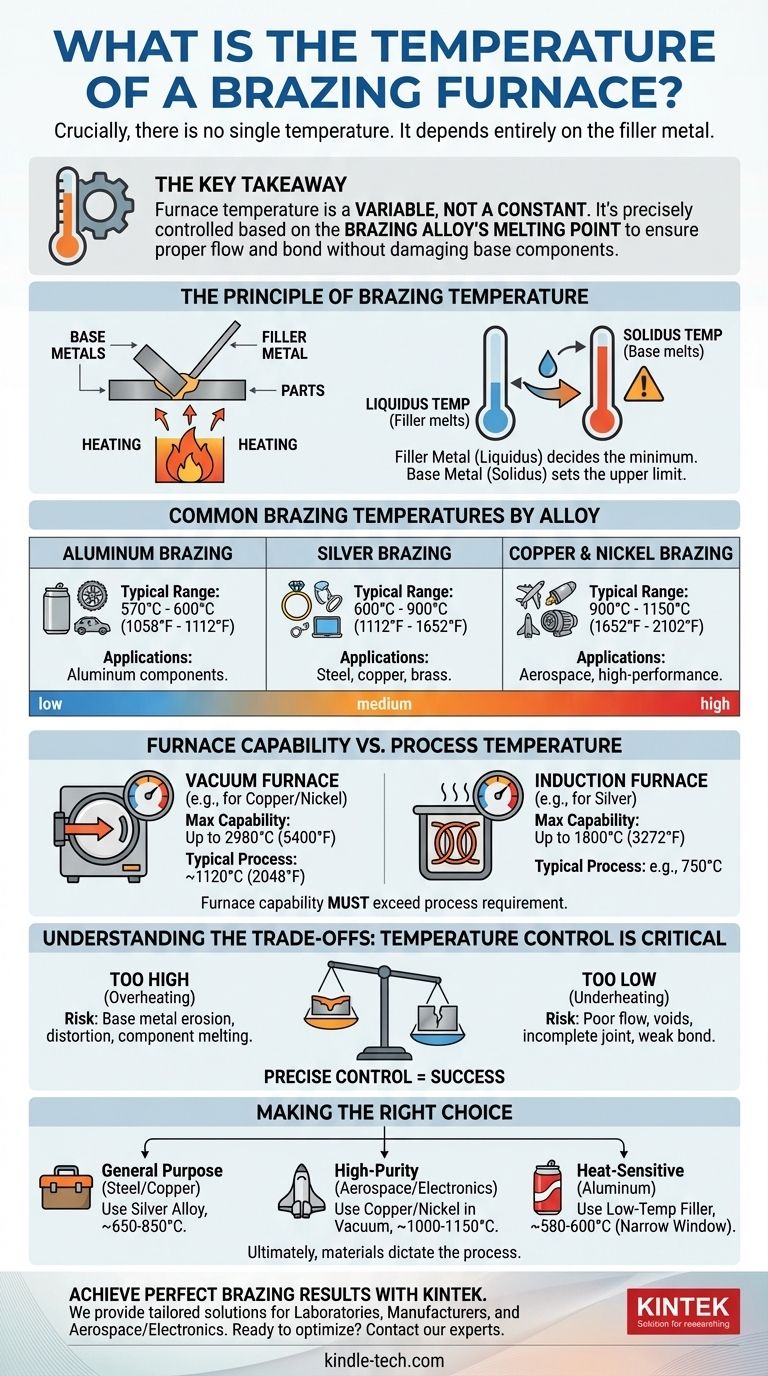
Crucially, there is no single temperature for a brazing furnace. The correct operating temperature is determined entirely by the specific filler metal being used to join the parts. This temperature must be high enough to melt the filler metal but below the melting point of the base metals, typically falling within a wide range of 450°C to over 1100°C (842°F to 2012°F).
The key takeaway is that furnace temperature is a variable, not a constant. It is precisely controlled based on the brazing alloy's melting point to ensure the filler flows correctly and forms a strong bond without damaging the components being joined.

The Principle of Brazing Temperature
To understand why the temperature varies, you must first understand the core principle of brazing. It is a joining process defined by heating a filler metal above its melting point and distributing it between two or more close-fitting parts by capillary action.
The Filler Metal Is the Deciding Factor
The most critical factor is the liquidus temperature of the brazing filler metal—the temperature at which it becomes fully liquid. The furnace must be set to a temperature slightly above this point to ensure the alloy is fluid enough to flow completely into the joint.
The Base Metal Sets the Upper Limit
The brazing temperature must always be safely below the solidus temperature of the base metals being joined. If the furnace is too hot, it will begin to melt the parts themselves, causing distortion, erosion, or complete failure of the assembly.
Common Brazing Temperatures by Alloy
The required temperature is dictated by the composition of the filler metal alloy. Different alloys are chosen for their compatibility with the base metals, strength, and cost.
Aluminum Brazing
Used for joining aluminum components, these filler metals have the lowest melting points. The process requires very precise temperature control.
- Typical Range: 570°C to 600°C (1058°F to 1112°F)
Silver Brazing
Silver alloys are versatile and widely used for joining steels, copper, and brass. They offer a good balance of strength and a relatively low, manageable melting range.
- Typical Range: 600°C to 900°C (1112°F to 1652°F)
Copper and Nickel Brazing
These high-strength alloys are common in aerospace and high-performance applications. Copper brazing, especially of steel parts in a vacuum furnace, is a very common industrial process.
- Typical Range: 900°C to 1150°C (1652°F to 2102°F)
Furnace Capability vs. Process Temperature
It is important not to confuse the maximum temperature a furnace can achieve with the temperature at which a process is run. The furnace is simply a tool whose capability must exceed the process requirement.
Vacuum Furnaces
Many brazing operations, especially with copper and nickel alloys, are performed in a vacuum to prevent oxidation. While a vacuum furnace might be rated to operate up to 2980°C (5400°F), a typical copper brazing cycle will run at a much lower temperature, around 1120°C (2048°F).
Induction Furnaces
Induction heating uses an electromagnetic coil to rapidly heat the part. An induction system may be able to reach 1800°C (3272°F), but for brazing, its power output is carefully controlled to achieve and hold the specific temperature required by the filler alloy, such as 750°C for a silver alloy.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Temperature Control is Critical
Achieving a successful brazed joint depends on precise thermal management. Deviating from the target temperature, even slightly, can lead to failure.
The Risk of Overheating
Setting the temperature too high can cause the filler metal to react aggressively with the base metal, eroding the joint surfaces. At extreme temperatures, you risk melting the components themselves.
The Risk of Underheating
If the furnace temperature is too low, the filler metal will not become fully liquid. It will not flow properly via capillary action, resulting in voids, incomplete joint fill, and a weak, unreliable bond.
The Importance of Atmosphere
Temperature is only one part of the equation. Most brazing processes require a controlled atmosphere (such as a vacuum or an inert gas like argon) to prevent the formation of oxides on the metal surfaces, which would block the flow of filler metal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The correct temperature setting is a direct function of your materials and your objective.
- If your primary focus is joining steel or copper parts with a general-purpose filler: You will likely use a silver alloy and set your furnace for a temperature in the 650°C to 850°C range.
- If your primary focus is high-purity joints for aerospace or electronics: You are likely using a vacuum furnace with a copper or nickel alloy, requiring precise control around 1000°C to 1150°C.
- If your primary focus is joining heat-sensitive aluminum components: You must use a special low-temperature filler and operate in a very narrow window around 580°C to 600°C.
Ultimately, successful brazing relies on understanding that the materials dictate the process, not the other way around.
Summary Table:
| Brazing Alloy Type | Typical Temperature Range (°C) | Typical Temperature Range (°F) | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Brazing | 570°C - 600°C | 1058°F - 1112°F | Aluminum components |
| Silver Brazing | 600°C - 900°C | 1112°F - 1652°F | Steel, copper, brass |
| Copper & Nickel Brazing | 900°C - 1150°C | 1652°F - 2102°F | Aerospace, high-performance parts |
Achieve Perfect Brazing Results with KINTEK
Precise temperature control is critical for strong, reliable brazed joints. Whether you're working with aluminum, silver, or high-temperature copper and nickel alloys, KINTEK's advanced brazing furnaces deliver the accuracy and consistency your laboratory or production line demands.
We provide tailored solutions for:
- Laboratories requiring precise thermal cycles for R&D and prototyping
- Manufacturers needing high-volume, repeatable brazing processes
- Aerospace and electronics applications demanding vacuum furnace technology
Our equipment ensures optimal filler metal flow and joint integrity while protecting your base materials from thermal damage.
Ready to optimize your brazing process? Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application requirements and discover how KINTEK's lab equipment can enhance your joining capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- How does a tubular furnace work? A Guide to Controlled High-Temperature Processing
- What is the high temperature of a tube furnace? Unlock the Right Model for Your Application
- What material are furnace tubes? Choosing the Right Material for High-Temperature Success
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process



















