In graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry (GFAAS), there is no single operating temperature. Instead, the instrument executes a precise, multi-stage temperature program that can range from approximately 100 °C for initial drying to as high as 3000 °C for atomization and cleaning, depending on the specific element and sample matrix being analyzed.
The core principle of GFAAS is not to use one high temperature, but to leverage a sequence of carefully controlled temperature steps. This program is designed to systematically remove the sample's solvent and matrix before a final, rapid heating phase isolates and measures the target analyte.
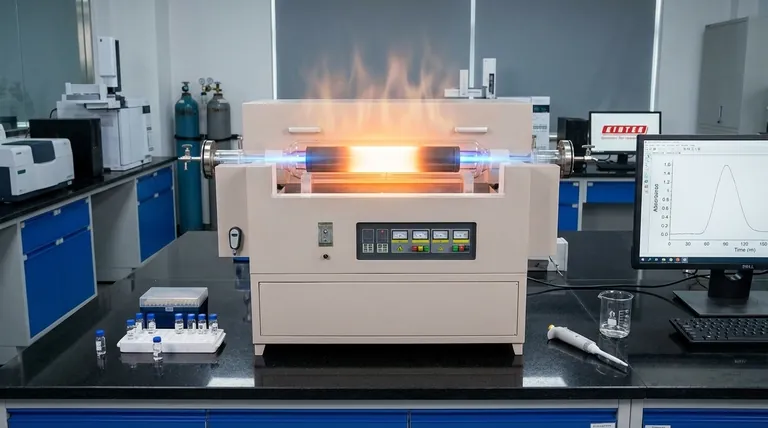

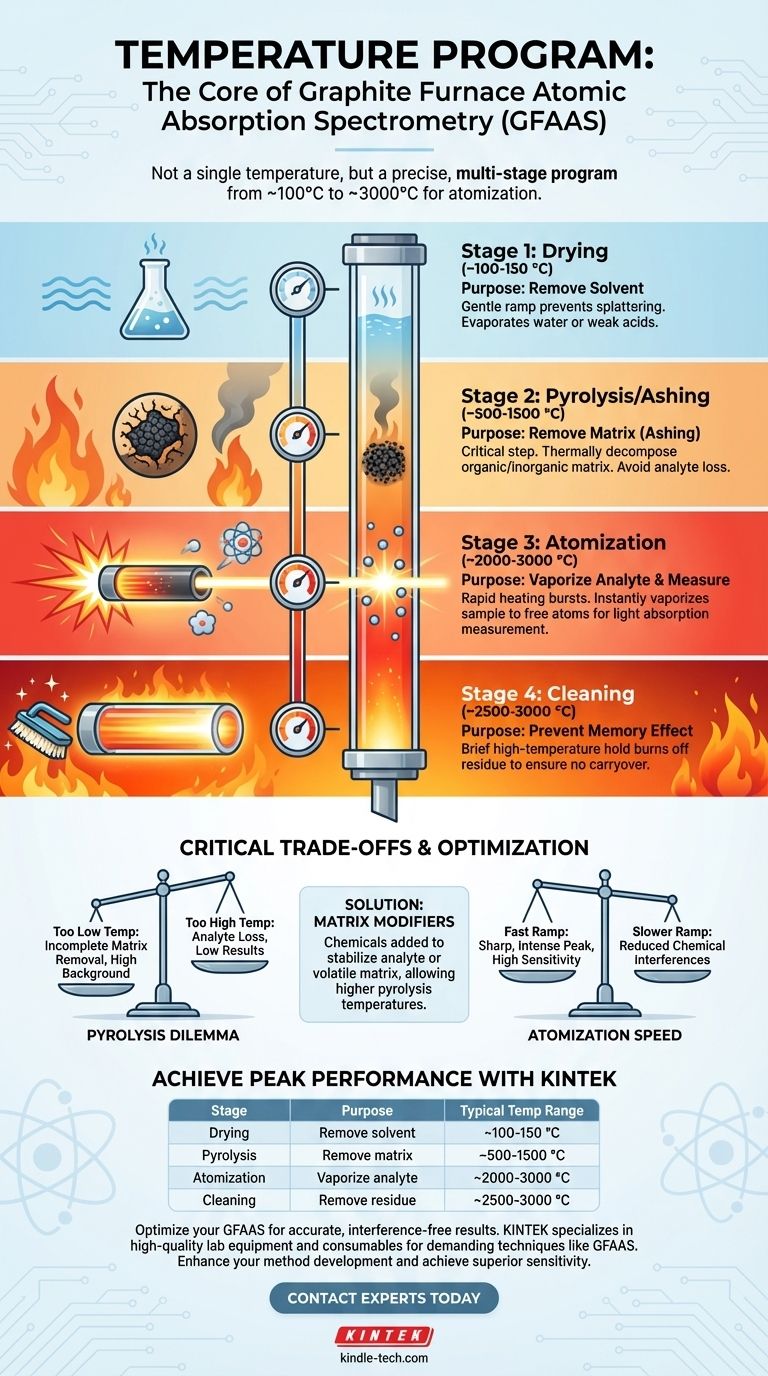
The Purpose of the Temperature Program
GFAAS achieves its exceptional sensitivity by performing sample preparation directly inside the graphite tube. This in-situ preparation is accomplished through a timed and controlled heating program, which consists of several distinct stages. Each stage has a specific purpose, collectively ensuring that the final measurement is of the analyte alone, free from interferences.
Stage 1: Drying (~100-150 °C)
The first step is a low-temperature drying phase. A gentle ramp up to just above the boiling point of the solvent (typically water or a weak acid) removes the liquid in a controlled manner, preventing the sample from splattering and ensuring even deposition on the furnace wall.
Stage 2: Pyrolysis or Ashing (~500-1500 °C)
This is arguably the most critical optimization step. The temperature is raised significantly to thermally decompose, or "ash," the organic and inorganic matrix of the sample. The goal is to eliminate these components, which would otherwise interfere with the measurement.
The ideal pyrolysis temperature is the highest possible temperature that can be used without causing any premature loss of the target analyte. This temperature is highly element-dependent.
Stage 3: Atomization (~2000-3000 °C)
During this stage, the furnace is heated as rapidly as possible to the target atomization temperature. This burst of intense thermal energy instantly vaporizes the remaining sample residue, creating a dense cloud of free, ground-state atoms within the graphite tube.
A beam of light specific to the analyte is passed through this atomic cloud, and the amount of light absorbed is directly proportional to the analyte concentration. This is the measurement step.
Stage 4: Cleaning (~2500-3000 °C)
After the measurement is complete, the furnace is held at a very high temperature for a few seconds. This final step serves to burn off any remaining residue from the furnace, preventing sample-to-sample carryover, also known as the "memory effect."
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Optimizing a GFAAS temperature program is a process of balancing competing factors. A poorly chosen program is the most common source of inaccurate results.
The Pyrolysis Temperature Dilemma
The central challenge is finding the optimal pyrolysis temperature.
- Too Low: If the temperature is too low, the sample matrix is not fully removed. This can cause high background signals during atomization, which obscure the analyte signal and lead to inaccurate results.
- Too High: If the temperature is too high, the analyte itself (especially volatile elements like cadmium or lead) will begin to vaporize and be lost along with the matrix. This leads to an artificially low reading.
The Role of Matrix Modifiers
To solve the pyrolysis dilemma, chemists often use matrix modifiers. These are chemicals added to the sample that selectively interact with either the analyte or the matrix.
A common strategy is to add a modifier (like palladium nitrate) that forms a more thermally stable compound with the analyte. This allows for a higher pyrolysis temperature to be used for more effective matrix removal without losing the analyte.
Atomization Speed and Signal Shape
The speed of the temperature ramp during the atomization step also matters. A very fast ramp creates a sharp, narrow, and intense absorption peak, which often yields the best sensitivity. However, for some complex matrices, a slower ramp can help reduce certain chemical interferences.
Optimizing Temperature for Your Analysis
Choosing the correct temperature program is essential for method development. The ideal settings are always a function of your specific element, sample matrix, and analytical goals.
- If your primary focus is analyzing a volatile element (e.g., Cadmium, Lead): You must use relatively low pyrolysis and atomization temperatures and strongly consider a matrix modifier to prevent premature analyte loss.
- If your primary focus is analyzing a refractory element (e.g., Vanadium, Molybdenum): You will require very high atomization temperatures and potentially a longer atomization hold time to ensure complete vaporization.
- If your primary focus is reducing background interference: Invest the majority of your method development time in optimizing the pyrolysis step, experimenting with different temperatures and matrix modifiers to achieve maximum matrix removal.
Mastering the temperature program transforms GFAAS from a complex instrument into an exceptionally powerful and precise analytical tool.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Purpose | Typical Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|
| Drying | Remove solvent | ~100-150 °C |
| Pyrolysis/Ashing | Remove sample matrix | ~500-1500 °C |
| Atomization | Vaporize analyte for measurement | ~2000-3000 °C |
| Cleaning | Remove residue to prevent carryover | ~2500-3000 °C |
Achieve Peak Analytical Performance with KINTEK
Optimizing your GFAAS temperature program is critical for accurate, interference-free results. Whether you're analyzing volatile elements like Cadmium and Lead or refractory elements like Vanadium and Molybdenum, the right equipment and consumables are essential for success.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables designed specifically for demanding analytical techniques like Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Spectrometry. We provide the reliable components you need to ensure precise temperature control and consistent performance in your laboratory.
Ready to enhance your GFAAS method development and achieve superior sensitivity?
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can support your laboratory's specific needs with precision-engineered solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Multi-zone Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Desktop Fast High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 16L 24L for Lab Use
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Customizable Laboratory High Temperature High Pressure Reactors for Diverse Scientific Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the four main types of sensors? A Guide to Power Source and Signal Type
- What are the advantages of using a Multi-zone Tube Furnace? Enhanced Thermal Uniformity for Diffusion Research
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- What is a three zone furnace? Achieve Superior Thermal Control and Uniformity
- What is a multi-position furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Flexible HVAC Installation



















