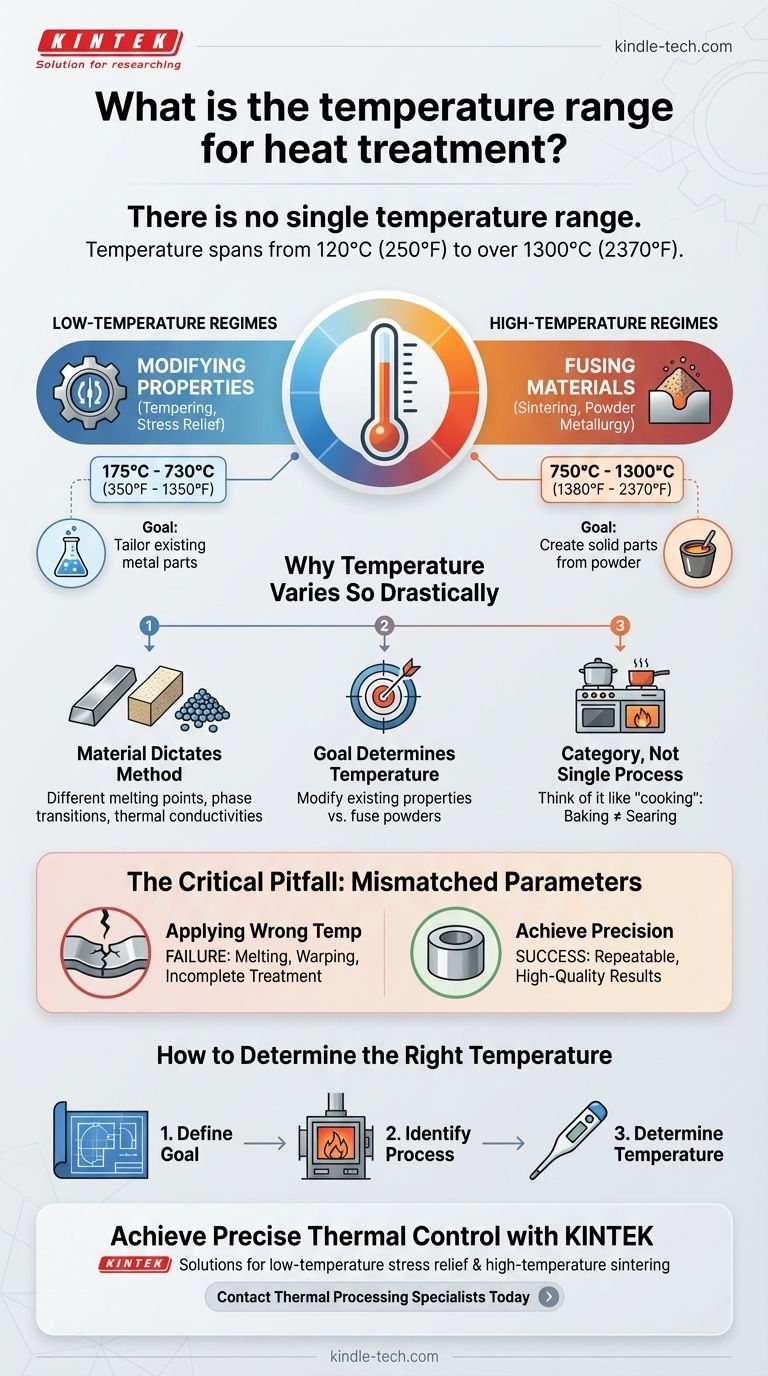
There is no single temperature range for heat treatment. The required temperature is extremely broad, spanning from as low as 120°C (250°F) for specialized applications to over 1300°C (2370°F) for processes like sintering. The correct temperature depends entirely on the specific material being treated and the desired outcome.
The critical takeaway is to view "heat treatment" not as a single procedure, but as a category of highly specific thermal processes. The right temperature is dictated by the engineering goal, whether it's subtly altering a metal's properties or fundamentally fusing powdered materials together.

Why Temperature Varies So Drastically
The term "heat treatment" covers a wide array of metallurgical and materials science processes. Each process uses a precise thermal cycle—heating, holding, and cooling—to achieve a specific change in a material's physical and sometimes chemical properties.
It's a Category, Not a Single Process
Think of "heat treatment" like the term "cooking." You wouldn't ask for the single correct temperature for cooking, as baking a cake at 175°C is fundamentally different from searing a steak at 230°C.
Similarly, the temperature for strengthening a steel component is entirely different from the temperature needed to fuse ceramic powders into a solid part.
The Material Dictates the Method
Different materials have vastly different melting points, phase transition temperatures, and thermal conductivities.
The heat treatment process must be tailored to the specific alloy, polymer, or ceramic to achieve the desired result without damaging or destroying the part.
The Goal Determines the Temperature
The intended outcome is the most significant factor. A low-temperature process might aim to relieve internal stresses, while a high-temperature process aims to completely change the material's grain structure or bond separate particles.
Common Heat Treatment Regimes
The references highlight two distinct examples that illustrate this wide thermal spectrum. Each operates in a different temperature regime to accomplish a different goal.
Low-Temperature Vacuum Processes
These treatments typically operate between 175°C and 730°C (350-1350°F).
Their purpose is often to modify existing properties without a complete structural transformation. This includes processes like tempering (reducing brittleness) or stress relieving (removing internal stresses from manufacturing).
High-Temperature Sintering Processes
Sintering operates at much higher temperatures, generally between 750°C and 1300°C (1380-2370°F).
The goal here is not to modify an existing solid part, but to fuse fine powders together into a solid mass. The high heat provides the energy needed for atoms to diffuse across the boundaries of the particles, bonding them together.
The Critical Pitfall to Avoid
The most common mistake is applying a temperature range from one process to another. Using a sintering temperature on a finished steel part intended for tempering would not just be incorrect; it would likely destroy the component entirely.
Mismatched Parameters Lead to Failure
Applying a temperature that is too low for the intended process will result in an incomplete or failed treatment. Conversely, applying a temperature that is too high can cause melting, warping, or the formation of undesirable material properties.
Precision Is Non-Negotiable
In all heat treatment, precision and uniformity are paramount. Even small deviations from the target temperature can have a significant impact on the final properties of the material, affecting its strength, hardness, and durability.
How to Determine the Right Temperature
The correct approach is to define your goal first, then identify the specific process and corresponding temperature required to achieve it.
- If your primary focus is modifying properties of an existing part (e.g., stress relief, tempering): You are likely looking at lower-temperature processes, generally below 730°C.
- If your primary focus is creating a solid part from powder (e.g., powder metallurgy, ceramics): You will require a high-temperature sintering process, often operating above 750°C.
Ultimately, the precise temperature for any heat treatment is a carefully engineered parameter defined by the material's specification and the desired engineering outcome.
Summary Table:
| Process Goal | Typical Temperature Range | Key Application |
|---|---|---|
| Low-Temp Modification (e.g., Tempering, Stress Relief) | 175°C - 730°C (350°F - 1350°F) | Modifying properties of existing metal parts |
| High-Temp Sintering (e.g., Powder Metallurgy) | 750°C - 1300°C (1380°F - 2370°F) | Fusing powdered materials into solid parts |
Achieve Precise Thermal Control for Your Materials
Choosing the wrong heat treatment temperature can lead to failed parts and wasted resources. The exact temperature is critical and depends entirely on your specific material and engineering goal.
KINTEK specializes in precision lab furnaces and thermal processing equipment designed to deliver the exact temperature uniformity and control your application demands, whether you're working with metals, ceramics, or advanced powders.
Let our experts help you select the right equipment for your process. We provide solutions for low-temperature stress relief and high-temperature sintering, ensuring repeatable, high-quality results.
Contact our thermal processing specialists today to discuss your specific heat treatment requirements and find the perfect solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the use of high temperature muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, Contamination-Free Thermal Processing
- How do you cool down a muffle furnace? Ensure Longevity and Safety with the Correct Procedure
- What precautions should you take while using a muffle furnace? Ensure Safe High-Temperature Processing in Your Lab
- What is the working principle of a muffle furnace? Achieve Precise, Contamination-Free Heating
- What is SV and PV in a muffle furnace? Master Temperature Control for Precision Results



















