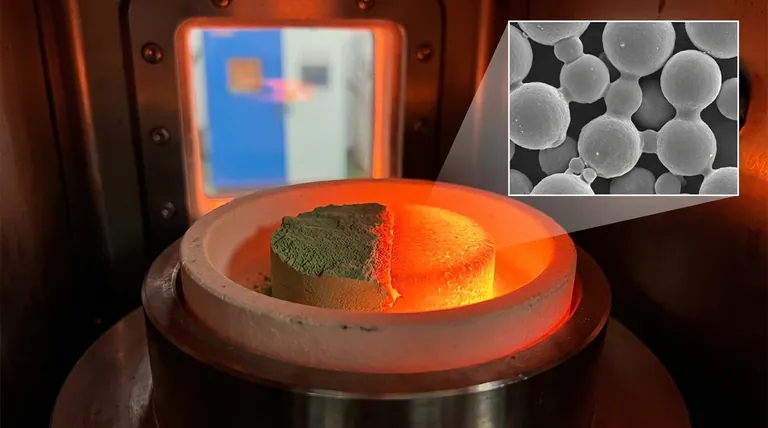
Sintering is a thermal manufacturing process that transforms a compact of loose powder into a dense, solid mass using heat. Crucially, this is accomplished at a temperature below the material's melting point, relying on atomic diffusion rather than liquefaction to bond the particles together.
The core principle of sintering is not to melt a material, but to heat it just enough to excite its atoms. This atomic movement allows adjacent particles to fuse at their contact points, gradually eliminating the pores between them and creating a strong, unified component.
The Goal of Sintering: From Powder to Solid
Sintering is a fundamental process in powder metallurgy and ceramics manufacturing. It solves the problem of how to create a dense, functional part from a collection of fine particles.
Creating the "Green" Part
The process begins with a "green" part. This is a loosely-bound compact of the primary material powder, formed into the desired preliminary shape.
This initial shape is often created by pressing the powder in a die or mixing it with a temporary binding agent, such as wax or a polymer, to hold the particles together. The green part is fragile and highly porous.
The Problem of Porosity
The empty spaces, or pores, between the particles in the green part make it mechanically weak. The primary purpose of the sintering process is to systematically remove this porosity, which dramatically increases the part's density, strength, and other mechanical properties.
The Three Core Stages of the Sintering Process
The transformation from a fragile green part to a durable final product occurs over three distinct thermal stages inside a controlled-atmosphere furnace.
Stage 1: Binder Burn-off
As the green part is initially heated to a relatively low temperature, the temporary binding agent holding the powder together begins to evaporate or burn away.
This step must be controlled carefully to prevent defects in the final part. Once complete, all that remains is the loosely connected network of primary material particles.
Stage 2: Atomic Diffusion and Densification
This is the heart of the sintering process. The temperature is raised significantly, to just below the melting point of the primary material.
At this elevated temperature, the atoms at the surface of the powder particles become highly mobile. They begin to diffuse across the boundaries where particles touch, creating "necks" or bridges between them.
As these necks grow, they pull the particle centers closer together. This action systematically closes the pores, causing the entire part to shrink and become significantly denser.
Stage 3: Controlled Cooling
Once the desired density is achieved, the part is cooled. The rate of cooling can be precisely managed to influence the final microstructure of the material.
This control allows for fine-tuning of properties like hardness and ductility, locking in the final characteristics of the sintered component.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the sintering process involves critical variables and potential challenges that must be managed to achieve a successful outcome.
Managing Part Shrinkage
The elimination of porosity directly results in part shrinkage. This change in dimension is predictable but must be accurately accounted for in the initial design of the green part's mold or die to ensure the final product meets specifications.
The Need for a Controlled Atmosphere
Sintering is performed in a controlled atmosphere (such as a vacuum or an inert gas environment). This is critical to prevent oxidation and other chemical reactions that could compromise the material properties of the final part.
The Risk of Grain Growth
If the sintering temperature is too high or the heating time is too long, the material's microscopic grains can grow excessively large. This can negatively impact the part's mechanical strength and toughness, so a precise balance of time and temperature is essential.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Sintering is selected for specific reasons, and understanding its strengths will help determine if it is the right process for your application.
- If your primary focus is working with high-melting-point materials (like tungsten or ceramics): Sintering is often the most practical and energy-efficient method for creating dense, solid parts without needing to achieve extreme melting temperatures.
- If your primary focus is mass production of complex metal parts: Powder metallurgy using sintering is a highly cost-effective method that minimizes material waste and reduces the need for secondary machining compared to casting or forging.
- If your primary focus is achieving specific final part properties: The precise control over temperature, time, and atmosphere in the sintering process allows for exceptional fine-tuning of density, hardness, and microstructure.
Ultimately, sintering empowers engineers to create robust components from powder, unlocking manufacturing possibilities that would otherwise be impractical or impossible.
Summary Table:
| Stage | Temperature | Key Process | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Binder Burn-off | Low | Removes temporary binding agents | Leaves a porous network of primary particles |
| 2. Densification | High (Below Melting Point) | Atomic diffusion creates necks between particles | Particles fuse, pores close, part shrinks and strengthens |
| 3. Controlled Cooling | Decreasing | Cools the part at a managed rate | Locks in final microstructure and material properties |
Ready to enhance your manufacturing process with precision sintering?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables for powder metallurgy and ceramics. Our sintering furnaces offer the precise temperature control and managed atmospheres necessary to achieve superior part density, strength, and complex geometries.
Whether you are mass-producing metal components or working with high-melting-point materials, KINTEK has the solutions to meet your laboratory's specific needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our sintering solutions can bring efficiency and quality to your production line!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
People Also Ask
- What is the plasma sintering technique? Achieve Rapid, High-Density Material Fabrication
- What is the difference between hot press and SPS? Choose the Right Sintering Method for Your Lab
- What are the steps in spark plasma sintering? Achieve Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification
- What is the mechanism of SPS process? A Deep Dive into Rapid, Low-Temperature Sintering
- What is the vapor phase material? Unlock Faster, Denser Sintering with SPS Technology



















