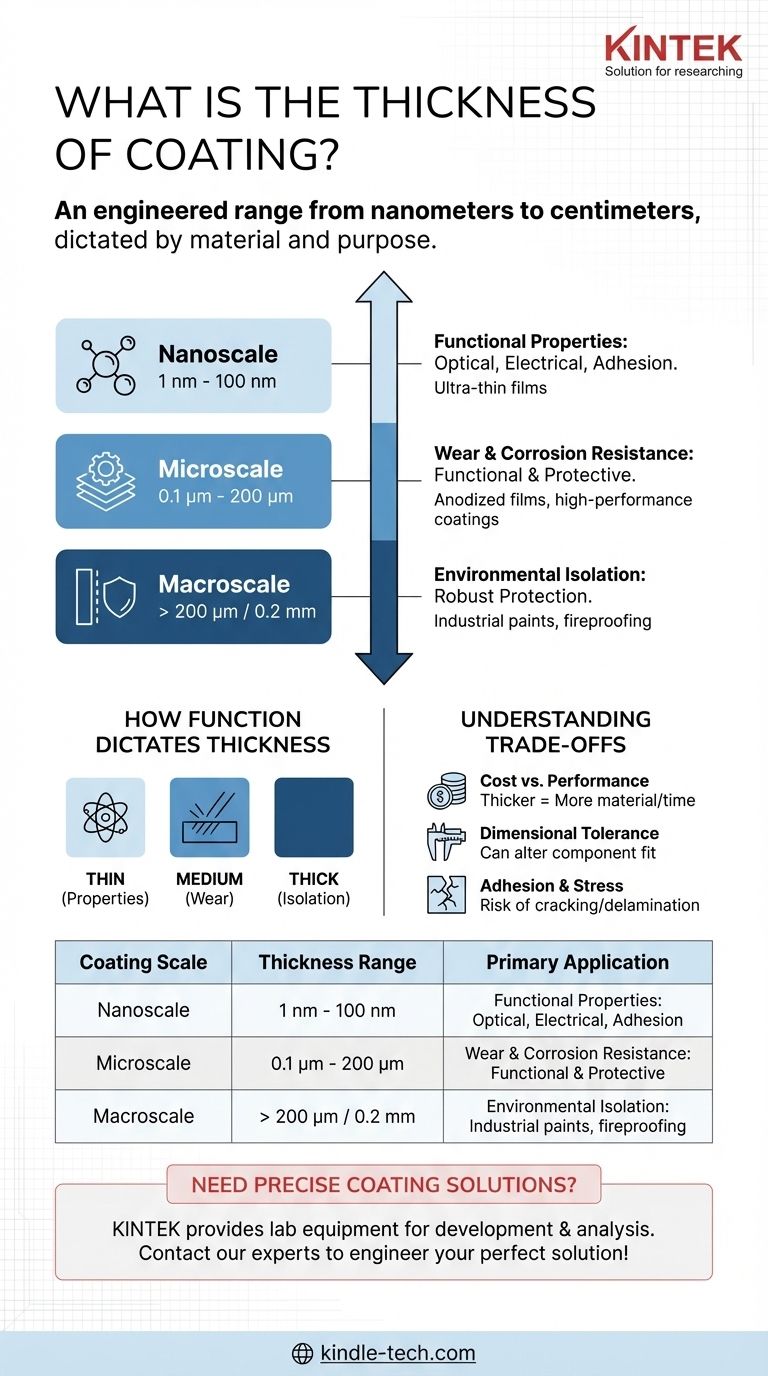
The definitive answer is that coating thickness is not a single value but spans an enormous range, from a few nanometers for advanced functional layers to several centimeters for heavy-duty protective barriers. The specific thickness is entirely dictated by the coating's material and its intended purpose, whether for optical performance, wear resistance, or environmental protection.
The core principle to understand is that coating thickness is a critical design parameter, not a fixed property. It is purposefully engineered to achieve a specific function, balancing performance requirements against factors like cost, dimensional tolerance, and material stress.

The Spectrum of Coating Thickness
To understand thickness, it's best to think in terms of scale. Different applications exist at vastly different orders of magnitude, each serving a unique purpose.
Nanoscale Coatings (1 nm - 100 nm)
These are ultra-thin films where the primary goal is to modify a surface's properties without changing its physical dimensions.
Examples include adhesion promoters like Titanium Zirconium (TiZr) at 1-5 nm, which create a chemical bridge between a substrate and a subsequent layer. Anti-reflective coatings on lenses also fall into this category.
Microscale Coatings (0.1 µm - 200 µm)
This is the most common range for industrial and commercial coatings that provide a combination of functional and protective benefits.
Anodized films on aluminum, for example, can range from 0.5 µm for a decorative finish to 150 µm for a hard, corrosion-resistant architectural layer. Many high-performance thin films for wear resistance sit in the 0.5 µm to 10 µm range.
Macroscale Coatings (>200 µm or 0.2 mm)
These are thick-film coatings designed primarily for robust protection against harsh environments. Here, bulk material is essential to performance.
Industrial paints and primers can easily be a few millimeters thick to provide long-term weather and corrosion resistance. Specialized coatings like fireproofing or thick thermal spray coatings can even be measured in centimeters.
How Function Dictates Thickness
The required thickness is a direct consequence of the problem you are trying to solve. Thinner is not always cheaper, and thicker is not always better.
For Functional Properties (Thin)
When the goal is to alter a surface's optical, electrical, or chemical properties, the coating is often atomically thin. Its performance comes from its specific chemistry and structure, not its bulk.
For Wear & Corrosion Resistance (Medium)
For protection against mechanical wear or chemical attack, the coating needs enough substance to resist erosion and act as a durable barrier. However, it must be thin enough to not interfere with the part's dimensional tolerances.
For Environmental Isolation (Thick)
When shielding a substrate from factors like intense heat, fire, or severe physical impact, the coating's thickness itself provides the protection. It acts as a sacrificial or insulating barrier that is meant to degrade over time to protect what is underneath.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a coating thickness involves balancing competing factors. An incorrect choice can be more detrimental than no coating at all.
Cost vs. Performance
Generally, thicker coatings require more material and longer processing times, increasing cost. Applying a 100 µm coating when only 10 µm is needed is wasteful and inefficient.
Dimensional Tolerance
For precision-engineered parts, a thick coating can fundamentally alter how components fit and function. A 50 µm coating can easily throw off the tolerance of a bearing or threaded part, causing it to fail.
Adhesion and Internal Stress
As coatings get thicker, they can develop higher levels of internal stress. This stress can lead to cracking, flaking, or delamination, especially if the substrate flexes or experiences thermal cycles.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine the appropriate thickness, start with your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is optical, catalytic, or electrical performance: You are almost certainly working with nanoscale to thin-microscale coatings (1 nm to 2 µm).
- If your primary focus is general wear, friction, or corrosion resistance: You should investigate coatings in the microscale range (2 µm to 150 µm).
- If your primary focus is heavy-duty environmental or impact protection: Your solution lies in macroscale coatings measured in millimeters (0.2 mm) or more.
Ultimately, choosing a coating thickness is an engineering decision critical to the success of your final product.
Summary Table:
| Coating Scale | Thickness Range | Primary Application |
|---|---|---|
| Nanoscale | 1 nm - 100 nm | Optical, Electrical, Adhesion Promotion |
| Microscale | 0.1 µm - 200 µm | Wear Resistance, Corrosion Protection |
| Macroscale | > 200 µm (0.2 mm) | Heavy-Duty Environmental & Impact Protection |
Struggling to determine the optimal coating thickness for your specific application? The right choice is critical for performance, cost, and avoiding issues like poor adhesion or dimensional failure. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for coating development and analysis. Our experts can help you select the right tools to achieve your goals, whether you're working with ultra-thin functional films or thick protective barriers. Let's engineer the perfect solution for your project—contact our team today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- RRDE rotating disk (ring disk) electrode / compatible with PINE, Japanese ALS, Swiss Metrohm glassy carbon platinum
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is a laboratory hot press necessary for the production of plastic crystal polymer electrolyte reinforced membranes?
- What are the advantages of using a hot press for Li7P2S8I0.5Cl0.5? Boost Conductivity with Precision Densification
- How is pressure generated and applied in a hot press? Master High-Intensity Hydraulic & Pneumatic Systems
- What are the advantages of hot pressing for PEO electrolytes? Achieve superior density and solvent-free performance.
- What role does a laboratory plate hot press play in the vulcanization and molding of fluorosilicone rubber (F-LSR)?





