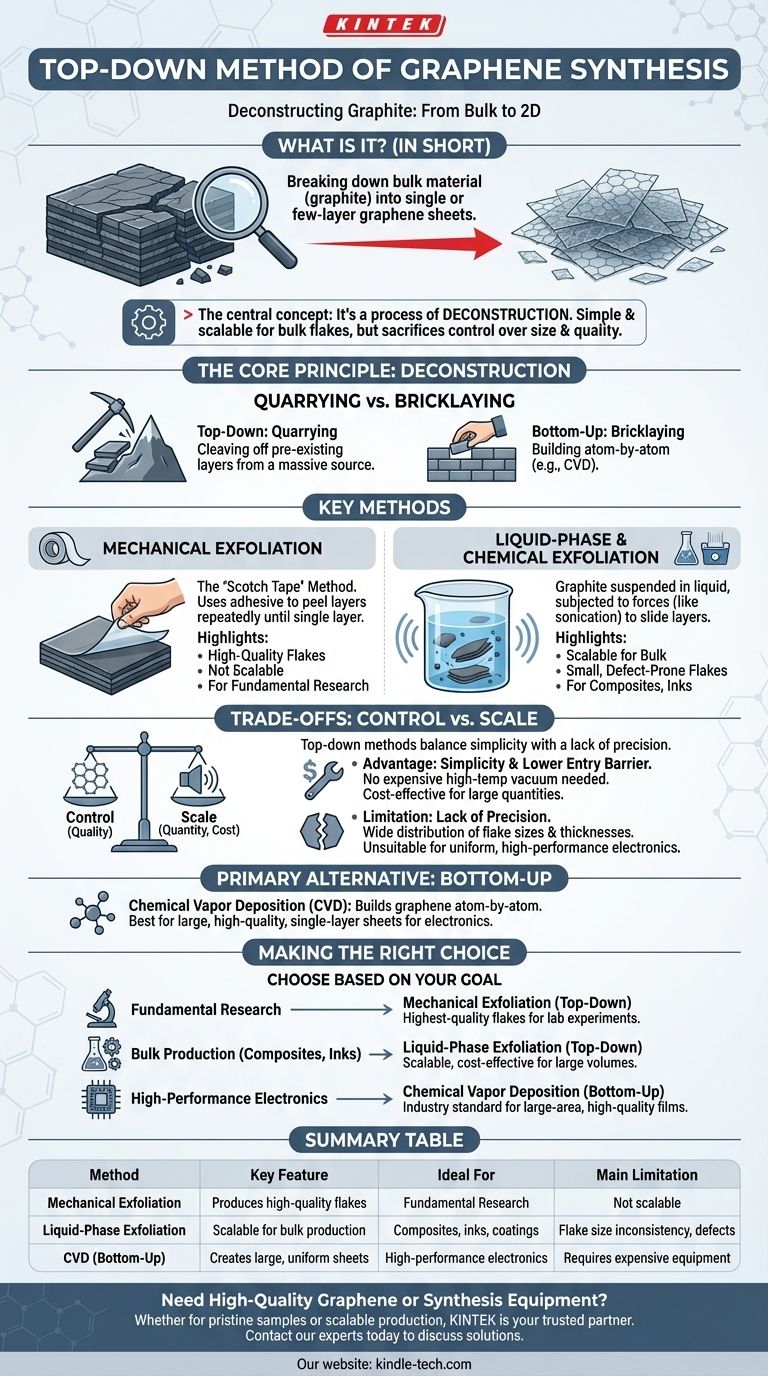
In short, the top-down method of graphene synthesis involves breaking down a bulk source material, like graphite, into single or few-layer graphene sheets. This is achieved through physical or chemical force, using techniques such as mechanical exfoliation (the "Scotch tape" method) or liquid-phase exfoliation in solvents.
The central concept to grasp is that top-down methods are fundamentally a process of deconstruction. While often simpler and more scalable for producing graphene flakes in bulk, they inherently sacrifice control over the size, shape, and electronic quality of the final product compared to more precise, bottom-up techniques.

The Top-Down Philosophy: Deconstructing Graphite
The name "top-down" describes the core strategy: you start with a large, three-dimensional crystal (graphite) and break it down into its two-dimensional building blocks (graphene).
The Core Principle: Quarrying vs. Bricklaying
Think of it like quarrying massive stone slabs from a mountain. You are cleaving off pre-existing layers. This is in direct contrast to the "bottom-up" approach, which is like building a wall brick-by-brick (or in graphene's case, atom-by-atom).
Key Method: Mechanical Exfoliation
This is the original, Nobel Prize-winning method for isolating graphene. It uses an adhesive surface, like tape, to peel layers from a piece of graphite repeatedly until a single layer is achieved.
While it produces exceptionally high-quality graphene flakes, the process is not scalable. It is used almost exclusively for fundamental research where pristine, small-scale samples are required.
Key Method: Liquid-Phase and Chemical Exfoliation
To achieve scale, graphite can be suspended in a liquid. The mixture is then subjected to forces—like sonication—that create shear forces strong enough to slide the layers apart.
This method is suitable for mass-producing graphene flakes for use in composites, inks, and coatings. However, the resulting flakes are typically small and have more defects, leading to lower electrical quality.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Control vs. Scale
No synthesis method is perfect; each represents a compromise between quality, scalability, and cost. The top-down approach has a clear and important place in the field, defined by its specific trade-offs.
The Advantage: Simplicity and Lower Barrier to Entry
Top-down methods like liquid-phase exfoliation do not require the expensive, high-temperature vacuum equipment needed for bottom-up techniques. This makes them more accessible and cost-effective for producing large quantities of graphene material.
The Critical Limitation: Lack of Precision
The main drawback is a lack of control. The exfoliation process produces a wide distribution of flake sizes and thicknesses (number of layers). This inconsistency makes top-down graphene unsuitable for applications that demand uniform, large-area, single-layer sheets, such as high-performance electronics.
The Primary Alternative: The Bottom-Up Approach
In contrast, bottom-up methods like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) build graphene atom-by-atom on a substrate. CVD is considered the most promising technique for industrial applications requiring large, continuous sheets of high-quality, single-layer graphene.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" synthesis method is entirely dependent on the final application.
- If your primary focus is fundamental scientific research: Mechanical exfoliation (top-down) provides the highest-quality flakes for lab-scale experiments.
- If your primary focus is bulk production for composites or inks: Liquid-phase exfoliation (top-down) is a scalable and cost-effective method for producing graphene flakes in large volumes.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electronics or transparent conductors: Chemical Vapor Deposition (bottom-up) is the industry standard for creating the large-area, high-quality films required.
Ultimately, selecting the right method requires aligning the process capabilities with the specific performance demands of your project.
Summary Table:
| Method | Key Feature | Ideal For | Main Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Exfoliation | Produces high-quality flakes | Fundamental research | Not scalable |
| Liquid-Phase Exfoliation | Scalable for bulk production | Composites, inks, coatings | Flake size inconsistency, defects |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (Bottom-Up) | Creates large, uniform sheets | High-performance electronics | Requires expensive equipment |
Need High-Quality Graphene or Synthesis Equipment?
Choosing the right synthesis method is critical for your project's success. Whether you require pristine graphene samples for research or scalable production equipment, KINTEK is your trusted partner. We specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific graphene synthesis needs.
Let us help you achieve your goals. Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and drive your innovations forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques
- What are the steps of the CVD process? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application



















