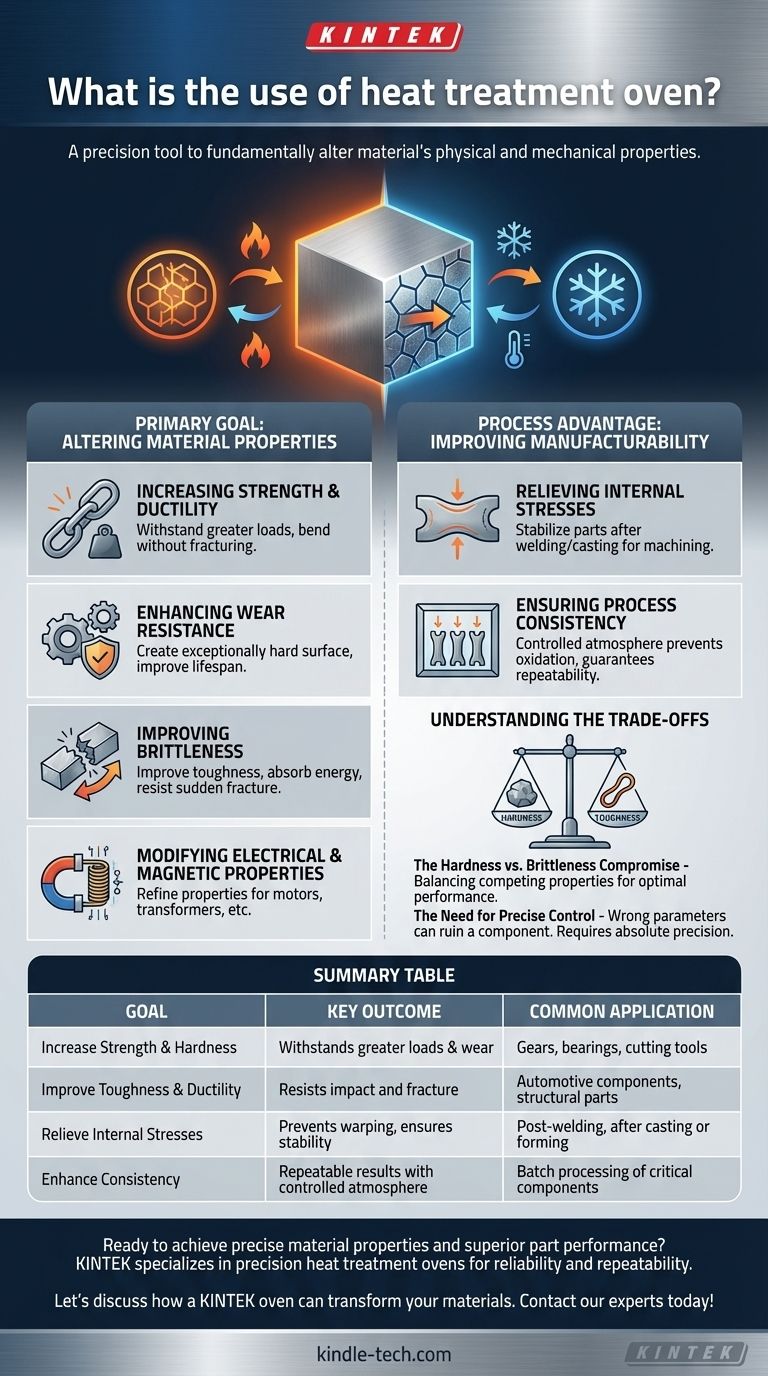
At its core, a heat treatment oven is a precision tool used to fundamentally change a material's physical and mechanical properties. By subjecting a material, most commonly steel, to a controlled cycle of heating and cooling, it is possible to alter its internal structure. This process enhances specific characteristics to improve performance, durability, and manufacturability.
A heat treatment oven is not for simply heating things up. It is an engineering instrument for precisely manipulating a material's microscopic structure to achieve specific outcomes, such as increasing strength, relieving stress, or improving resistance to wear.

The Primary Goal: Altering Material Properties
The main purpose of heat treatment is to transform a material from its base state into one that is optimized for a specific application. This is achieved by modifying its crystalline structure.
Increasing Strength and Ductility
Heat treatment can significantly increase the strength of a material, allowing it to withstand greater loads without deforming. Simultaneously, other processes can improve ductility, which is a material's ability to bend or stretch without fracturing.
Enhancing Wear Resistance
For components that experience friction, such as gears or bearings, heat treatment can create an exceptionally hard surface. This "case hardening" dramatically improves the part's lifespan by making it more resistant to abrasion and wear.
Improving Brittleness
Some materials, while strong, can be brittle and prone to shattering under impact. Specific heat treatment cycles can improve toughness, making the material better able to absorb energy and resist sudden fractures.
Modifying Electrical and Magnetic Properties
Beyond just mechanical traits, heat treatment is also used to refine a material's electrical and magnetic properties. This is critical for components used in electric motors, transformers, and other electromagnetic applications.
The Process Advantage: Improving Manufacturability
Heat treatment is not only for enhancing the final product; it is also a crucial intermediate step that makes manufacturing processes more efficient and reliable.
Relieving Internal Stresses
Processes like welding, casting, and hot forming introduce significant internal stresses into a material. If left unaddressed, these stresses can cause parts to warp, crack, or fail prematurely, and they make precise machining difficult. A heat treatment cycle can relieve these stresses, stabilizing the part for subsequent operations.
Ensuring Process Consistency
Modern heat treatment ovens provide a controlled atmosphere. This prevents the material from reacting with oxygen in the air during heating, which would otherwise cause scaling and degradation of the surface. This control ensures that every part in a batch receives the exact same treatment, leading to high levels of quality and consistency.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Heat treatment is a process of balancing competing properties. Optimizing for one characteristic often means compromising on another, which is a fundamental principle in materials engineering.
The Hardness vs. Brittleness Compromise
A classic trade-off is between hardness and toughness. Making a steel component extremely hard will almost always make it more brittle and susceptible to shattering from impact. The goal of the engineer is to find the optimal heat treatment that provides sufficient hardness without introducing unacceptable brittleness.
The Need for Precise Control
Heat treatment is not a forgiving process. Using the wrong temperature, holding time, or cooling rate can permanently ruin a component, making it weaker or more brittle than it was before. The process requires absolute precision and a deep understanding of metallurgy to achieve the desired outcome.
How to Apply This to Your Project
The specific heat treatment process you need depends entirely on your end goal. The oven is the tool; the metallurgical recipe is the key.
- If your primary focus is final part performance: Prioritize treatments that create hardness and wear resistance for durability, or toughness for impact resistance.
- If your primary focus is manufacturability: Use stress-relieving heat treatments after welding or forming to ensure dimensional stability for later machining.
- If your primary focus is product consistency: Insist on using a controlled atmosphere oven to prevent surface oxidation and guarantee repeatable results across every part.
Ultimately, mastering heat treatment allows you to dictate a material's behavior to meet the exact demands of your design.
Summary Table:
| Goal | Key Outcome | Common Application |
|---|---|---|
| Increase Strength & Hardness | Withstands greater loads and wear | Gears, bearings, cutting tools |
| Improve Toughness & Ductility | Resists impact and fracture | Automotive components, structural parts |
| Relieve Internal Stresses | Prevents warping, ensures stability | Post-welding, after casting or forming |
| Enhance Consistency | Repeatable results with controlled atmosphere | Batch processing of critical components |
Ready to achieve precise material properties and superior part performance?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-performance lab equipment, including precision heat treatment ovens designed for reliability and repeatability. Whether you're focused on enhancing final part durability, improving manufacturability, or ensuring batch-to-batch consistency, our solutions are engineered to meet your specific metallurgical needs.
Let's discuss how a KINTEK oven can transform your materials and optimize your process. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Scientific Electric Heating Blast Drying Oven
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- 50L Heating Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Bath Circulator for High and Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction
People Also Ask
- How does a controlled drying process ensure the quality of radiochromic films? Achieve Precise Dosimetric Results
- What role does a laboratory drying oven play in the processing and chemical analysis of aluminum dross?
- What is the role of a blast drying oven in COF synthesis? Driving High-Crystallinity Solvothermal Reactions
- What is the primary purpose of using an electric drying oven for dense refractory bricks? Optimize Raw Material Prep
- What is the function of a laboratory drying oven in Zr2.5Nb alloy pretreatment? Ensure Precise Corrosion Test Results



















