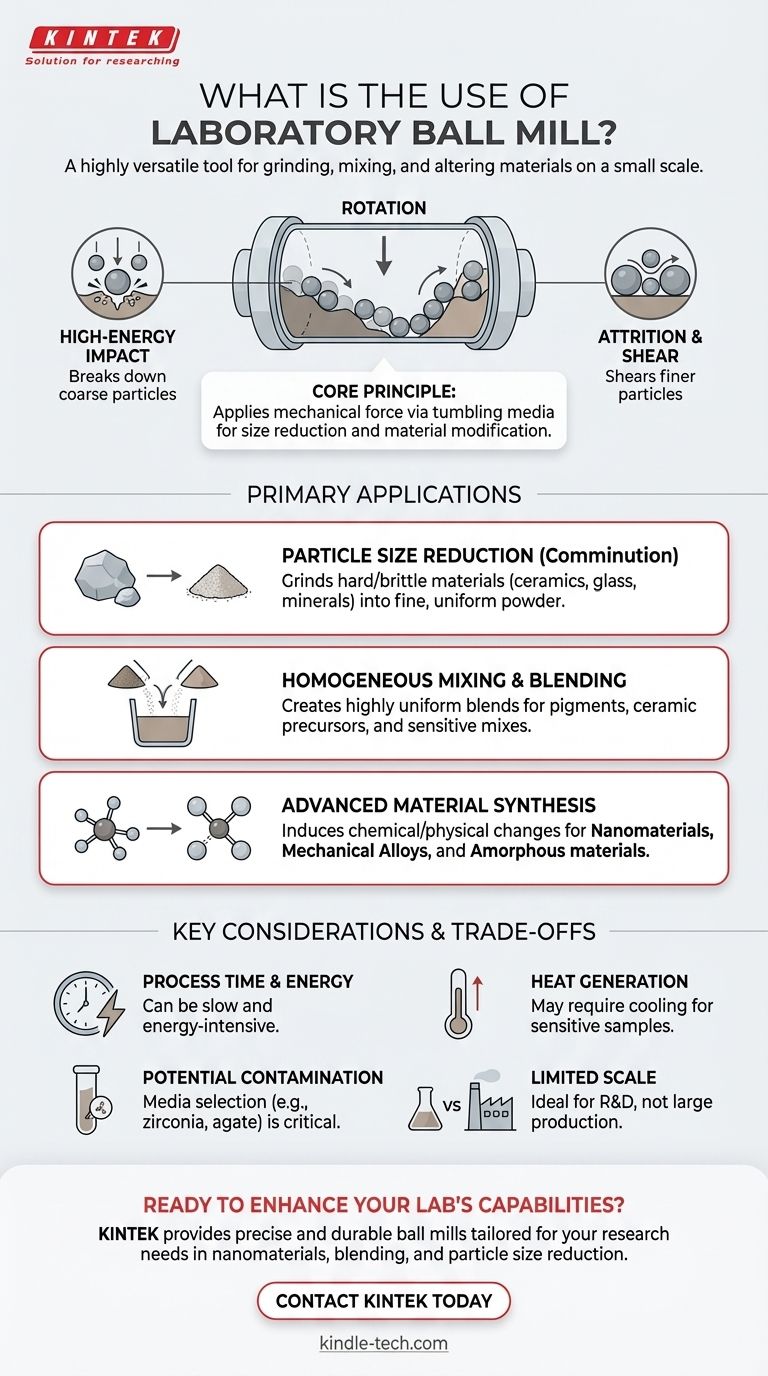
At its core, a laboratory ball mill is a highly versatile tool for grinding, mixing, and even altering materials on a small scale. It is used to reduce the particle size of a wide range of substances, including hard ceramics, chemicals, minerals, and pigments. Its fundamental purpose is to apply high-energy impact and shear forces to a sample, making it indispensable for preparing powders, eliminating agglomeration, and creating uniform blends.
The true value of a laboratory ball mill extends far beyond simple grinding. It is a fundamental instrument in materials science for synthesizing novel materials, such as nanomaterials and mechanical alloys, by using controlled mechanical force to change a substance's physical and chemical properties.

How a Ball Mill Achieves Its Results
A ball mill's effectiveness comes from its simple yet powerful mechanical principle. Understanding this mechanism is key to leveraging its full potential.
The Core Mechanical Principle
A ball mill is a hollow cylinder that rotates on its horizontal axis. This cylinder is partially filled with the material to be processed and a grinding medium—typically hard balls made of steel, ceramic, or another durable material.
As the cylinder rotates, the balls are lifted up the side and then cascade or tumble down, crushing and grinding the sample material through impact and attrition.
Energy Transfer and Particle Reduction
The process relies on two primary forces. Impact occurs when the balls fall from the top of the cylinder onto the material below, breaking down coarse particles. Attrition happens as the balls slide and roll against each other and the cylinder wall, shearing finer particles.
The size of the grinding media is critical. Large balls are effective at breaking down coarse feed, while smaller balls fill the void spaces and are essential for producing a very fine, uniform final powder.
Primary Applications in a Laboratory Setting
While often seen as just a "grinder," the lab ball mill serves several distinct and critical functions in research and development.
Particle Size Reduction (Comminution)
This is the most common application. A ball mill is ideal for reducing hard or brittle materials like ceramics, glass, and minerals into a fine powder. It excels where other methods fail to achieve the desired fineness or consistency.
Homogeneous Mixing and Blending
The constant tumbling motion makes the ball mill an excellent device for mixing powders. It ensures a highly uniform, homogeneous blend, which is critical in applications like creating pigments, ceramic precursors, or even blending sensitive materials like explosives.
Advanced Material Synthesis
This is where the ball mill transitions from a preparation tool to a synthesis reactor. The high-energy impacts can induce chemical and physical changes in materials.
Key examples include mechanical alloying, where powders of different metals are milled together to form a true alloy without melting, and the production of amorphous materials by breaking down a substance's crystalline structure. It is also a classic and effective method for preparing nanomaterials.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, the ball milling process has inherent characteristics that you must manage for successful outcomes.
Process Time and Energy
Ball milling can be a slow process, often requiring hours to achieve the desired particle size or material phase. It is an energy-intensive method, and this energy input can sometimes generate significant heat.
Potential for Contamination
The grinding media and the cylinder walls can wear down during operation, potentially introducing small amounts of contamination into your sample. Choosing the right material for the balls and jar (e.g., hardened steel, zirconia, agate) is critical to minimize this effect.
Heat Generation
For heat-sensitive materials, the energy imparted during milling can raise the sample's temperature. This may be undesirable and can alter the material's properties or cause degradation. In some cases, cooling systems or intermittent operation may be necessary.
Limited to Small Quantities
By definition, laboratory ball mills are designed for small-scale work. They are ideal for research, development, and quality control but are not suited for large-scale production, which requires much larger industrial mills.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To use a ball mill effectively, you must align its capabilities with your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is creating a uniform fine powder: The ball mill is an excellent choice for hard materials where consistent, micron-level particle sizes are required.
- If your primary focus is mixing small batches of powders: The thorough tumbling action provides superior homogenization compared to simpler mixing methods.
- If your primary focus is materials research and development: The ball mill is an indispensable tool for exploring mechanical alloying, amorphization, and producing novel nanomaterials.
By viewing it as a controlled high-energy processor, you can leverage the laboratory ball mill far beyond simple grinding to achieve truly innovative results.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Function | Common Materials |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Size Reduction | Grinds hard, brittle materials into fine powders | Ceramics, Minerals, Chemicals |
| Homogeneous Mixing | Creates uniform blends of different powders | Pigments, Ceramic Precursors |
| Material Synthesis | Induces chemical/physical changes via mechanical force | Nanomaterials, Mechanical Alloys |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a high-performance ball mill?
KINTEK specializes in providing precise and durable laboratory ball mills and grinding media tailored to your research needs. Whether you are developing novel nanomaterials, ensuring perfect powder blends, or achieving consistent particle size reduction, our equipment delivers the controlled energy and reliability you require.
Contact us today to discuss your application and find the perfect solution for your laboratory. Let KINTEK be your partner in innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Planetary Ball Mill Rotating Ball Milling Machine
- Laboratory Planetary Ball Mill Cabinet Planetary Ball Milling Machine
- Stainless Steel Laboratory Ball Mill for Dry Powder and Liquid with Ceramic Polyurethane Lining
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are two advantages of ball mill? Achieve Ultra-Fine Grinding and Versatile Material Processing
- What are the elements of a ball mill? A Guide to Its Core Components and Grinding Efficiency
- Are roller mills more energy efficient? The truth about particle size and performance.
- What are the parameters of the ball mill process? Optimize Grinding for Efficiency and Particle Size
- How to increase the efficiency of a ball mill? Optimize Speed, Feed, and Grinding Media for Peak Performance
- How does a laboratory ball mill contribute to the processing of solid polysilanes into coating powders?
- What is the particle size for XRF? Achieve Accurate and Reliable Elemental Analysis
- What is the role of a V-type mixer in the preparation of Ti-Cr3C2 composite powders? Ensuring Macroscopic Uniformity



















