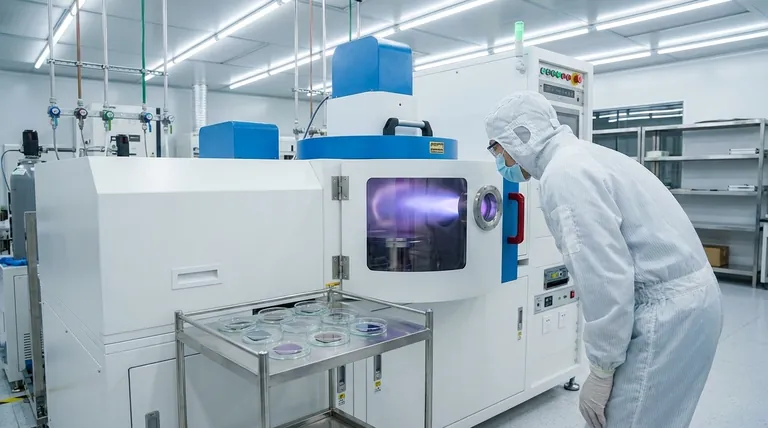
In short, RF plasma is a highly controlled technology used to precisely clean, coat, or chemically alter the surface of materials. It is widely applied across the industrial, semiconductor, and medical device sectors to enhance material properties without affecting the bulk of the object.
The core value of RF plasma is its ability to create a low-temperature, highly energetic gas environment. This allows for powerful surface modifications on a molecular level, even on heat-sensitive materials like plastics, that would be impossible with traditional wet chemical or high-heat methods.

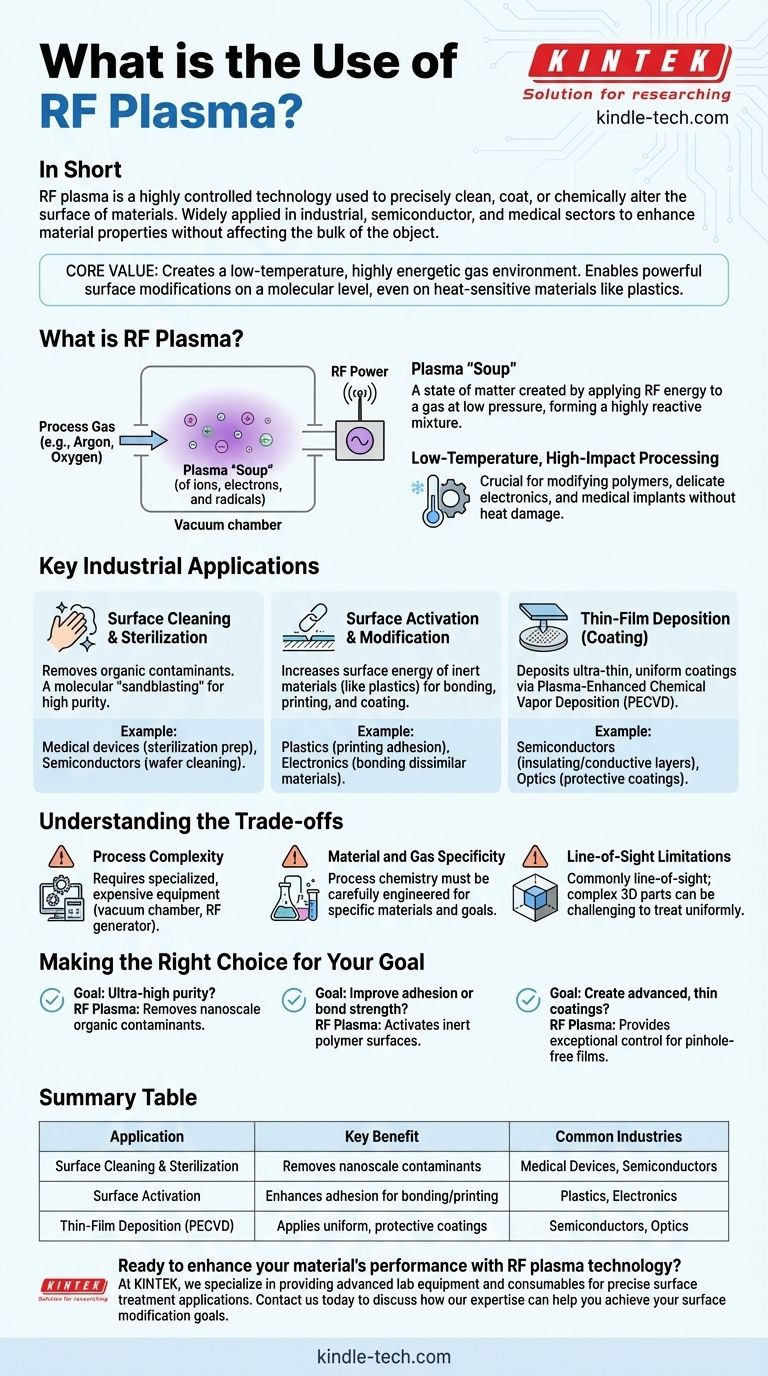
What is RF Plasma and Why is it Useful?
To understand its applications, we must first understand what RF plasma is. It is a state of matter created by applying radio frequency (RF) energy to a gas at low pressure.
Creating the Plasma "Soup"
Inside a vacuum chamber, a process gas (like argon, oxygen, or nitrogen) is introduced. When RF energy is applied, it strips electrons from the gas atoms, creating a highly reactive mixture of ions, electrons, radicals, and neutral particles often called the fourth state of matter.
The Power of an Energetic Environment
This "energetic environment" is the key to its utility. The reactive particles in the plasma can interact with any material surface placed within it, leading to powerful and precise changes at the nanoscale.
Low-Temperature, High-Impact Processing
Crucially, this entire process can occur at or near room temperature. This makes RF plasma an ideal solution for modifying polymers, delicate electronics, or medical implants that would be damaged by high-heat processes.
Key Industrial Applications Explained
The unique properties of RF plasma unlock three primary categories of surface treatment, each critical to different industries.
Surface Cleaning and Sterilization
The plasma environment is exceptionally effective at removing organic contaminants from surfaces. This process, often called plasma cleaning, is more of a molecular "sandblasting" than a simple wash.
It is indispensable for preparing medical devices for sterilization or ensuring that semiconductor wafers are atomically clean before the next fabrication step.
Surface Activation and Modification
Many materials, especially polymers like plastics, have inert, low-energy surfaces. This makes it difficult for adhesives, inks, or coatings to bond to them.
RF plasma treatment alters the surface chemistry, increasing its surface energy. This process, known as surface activation, makes the material highly receptive to bonding, enabling durable printing on otherwise "unprintable" surfaces or creating powerful bonds between dissimilar materials.
Thin-Film Deposition (Coating)
By introducing specific precursor gases into the chamber, the plasma can break them down and deposit them as an ultra-thin, uniform coating onto a material.
This process, called plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition (PECVD), is fundamental to the semiconductor industry for creating insulating and conductive layers on silicon wafers. It's also used to apply protective, scratch-resistant, or water-repellent coatings in various industries.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, RF plasma technology is not a universal solution and comes with specific considerations.
Process Complexity
Generating a stable, uniform plasma requires specialized and often expensive equipment. This includes a vacuum chamber, precise gas flow controllers, and a sophisticated RF power generator and matching network.
Material and Gas Specificity
An RF plasma process is not "one-size-fits-all." The chemistry must be carefully engineered for the specific material being treated and the desired outcome, requiring significant process development and expertise.
Line-of-Sight Limitations
In its most common configuration, plasma treatment is a line-of-sight process. Complex, three-dimensional parts with deep crevices or internal channels can be challenging to treat uniformly.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if RF plasma is the correct tool, consider your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is ultra-high purity: RF plasma offers a final cleaning step that removes nanoscale organic contaminants that wet chemical processes cannot.
- If your primary focus is improving adhesion or bond strength: RF plasma activation is one of the most effective methods for preparing inert polymer surfaces for printing, coating, or bonding.
- If your primary focus is creating advanced, thin coatings: RF plasma deposition provides an exceptional level of control for creating high-performance, pinhole-free films essential for optics and electronics.
Ultimately, RF plasma provides an unmatched ability to engineer the surface properties of a material independently of its core characteristics.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit | Common Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Surface Cleaning & Sterilization | Removes nanoscale contaminants | Medical Devices, Semiconductors |
| Surface Activation | Enhances adhesion for bonding/printing | Plastics, Electronics |
| Thin-Film Deposition (PECVD) | Applies uniform, protective coatings | Semiconductors, Optics |
Ready to enhance your material's performance with RF plasma technology?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables for precise surface treatment applications. Whether you need to improve adhesion, apply ultra-thin coatings, or achieve superior surface cleanliness, our RF plasma solutions are engineered to meet your specific laboratory requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can help you achieve your surface modification goals with reliable, high-performance equipment tailored to your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Why is PECVD environment friendly? Understanding the Eco-Friendly Benefits of Plasma-Enhanced Coating
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition



















