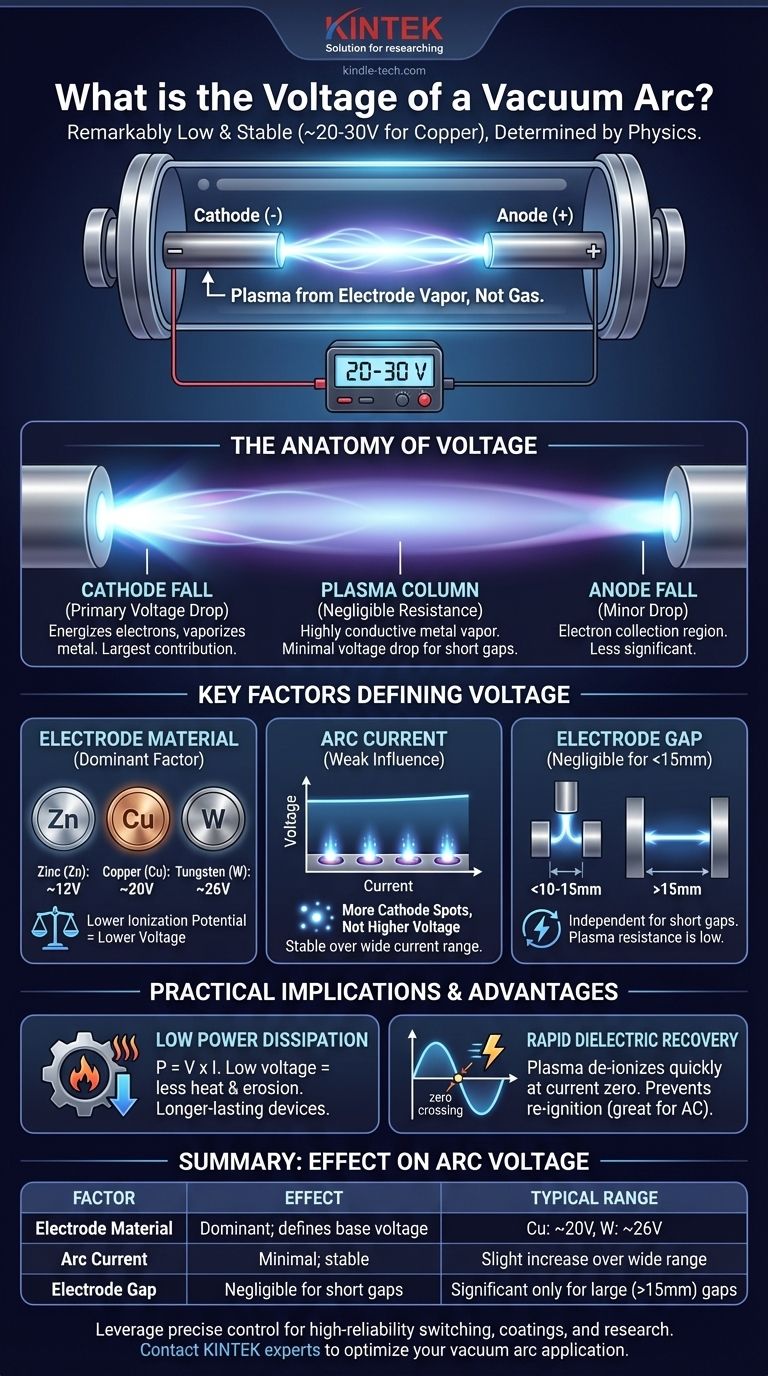
In short, the voltage of a stable vacuum arc is remarkably low. For common electrode materials like copper, this voltage is typically in the range of 20 to 30 volts. This value is relatively constant across a wide range of currents and is primarily determined by the physics of the electrode material itself, not the distance between the electrodes.
A vacuum arc's voltage is fundamentally different from an arc in air. It's not governed by the resistance of a long plasma column but by the energy required to vaporize and ionize atoms from the metal cathode, resulting in a low, stable voltage drop concentrated near the electrode surface.
The Anatomy of a Vacuum Arc Voltage
To understand why the voltage is so low, you must first understand how a vacuum arc is formed. Unlike a familiar arc in air, there is no surrounding gas to ionize. The plasma is created entirely from the electrode material.
The Source of the Plasma
An arc in a vacuum is a plasma discharge sustained by metal vapor that has been evaporated and ionized from the electrodes. This process originates at intensely hot, microscopic regions on the negative electrode known as cathode spots.
The Cathode Fall: The Primary Component
The largest portion of the arc voltage occurs in an extremely thin region directly in front of the cathode surface. This is the cathode fall voltage. This voltage drop provides the energy required to liberate electrons from the cathode and accelerate them, causing the intense localized heating that vaporizes the metal and ionizes the resulting vapor.
The Plasma Column
Once the metal vapor is ionized, it forms a highly conductive plasma bridge between the electrodes. Because the vacuum offers no other gas molecules to obstruct the flow of charge, this plasma column has very low resistance. For the short gaps found in most applications (e.g., a few millimeters), the voltage drop across this column is often negligible.
The Anode Fall
A smaller voltage drop, the anode fall, occurs at the positive electrode where electrons are collected. Its contribution to the total arc voltage is typically less significant than the cathode fall.
Key Factors That Define the Voltage
The stability and low value of the vacuum arc voltage are a direct result of the physics at the cathode. Only a few key parameters have a significant influence.
Electrode Material (The Dominant Factor)
The single most important factor is the cathode material. The arc voltage is strongly correlated with the energy required to create ions from the specific metal. Materials with lower ionization potentials and work functions tend to produce lower arc voltages.
- Zinc (Zn): ~12 V
- Copper (Cu): ~20 V
- Tungsten (W): ~26 V
This direct link between material and voltage is a defining characteristic of the vacuum arc.
Arc Current (A Surprisingly Weak Influence)
For a diffuse arc, the voltage is remarkably independent of the current over a very wide range. Increasing the current from tens to thousands of amperes may only raise the voltage by a few volts. This is because a higher current is accommodated by forming more cathode spots, not by increasing the voltage of each spot.
Electrode Gap (Only Matters When It's Large)
For short electrode gaps (up to ~10-15 mm), the arc voltage is nearly independent of the gap length. The low resistance of the plasma column means that making it slightly longer has a minimal effect on the total voltage. Only at much larger gaps does the plasma column's resistance become a significant factor.
Practical Implications and Trade-offs
The unique properties of the vacuum arc voltage have critical consequences for its application, particularly in high-power electrical switching.
Low Voltage Means Low Power Dissipation
The low sustaining voltage is a significant advantage. Since power is the product of voltage and current (P = V × I), a low arc voltage means less energy is dissipated as heat in the device for a given current. This results in reduced contact erosion and less thermal stress, enabling the design of compact, long-lasting vacuum interrupters.
The Challenge of Ignition
While the sustaining voltage is low, initiating the arc requires different conditions. Breakdown in a vacuum requires either a very high electric field to pull electrons from the cathode or the physical separation of current-carrying contacts to draw the arc out.
The Advantage in AC Interruption
The plasma in a vacuum arc is very tenuous. When the AC current naturally approaches a zero crossing, the creation of new plasma at the cathode spots ceases. The existing low-density plasma diffuses and de-ionizes with extreme speed, allowing the vacuum gap to rapidly recover its dielectric strength and prevent the arc from re-igniting.
How This Applies to Your Application
Understanding the nature of the vacuum arc voltage allows you to leverage its properties for specific goals.
- If your primary focus is electrical switching (e.g., circuit breakers): The key takeaway is that the low voltage minimizes contact erosion and energy stress during operation, enabling the creation of highly reliable and maintenance-free devices.
- If your primary focus is materials science (e.g., thin-film deposition): The arc voltage is a direct indicator of the ion energy produced by the cathode, which can be controlled by material selection to tailor the properties of deposited coatings.
- If your primary focus is plasma physics research: The vacuum arc voltage serves as a fundamental diagnostic, providing critical insight into the complex energy balance and particle generation mechanisms at the cathode surface.
Ultimately, the low and stable voltage of a vacuum arc is the direct signature of its fundamental operating principle: creating a conductive path from solid metal in an empty void.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Effect on Arc Voltage | Typical Range |
|---|---|---|
| Electrode Material | Dominant factor; defines base voltage | Copper: ~20V, Tungsten: ~26V |
| Arc Current | Minimal effect; voltage is stable | Increases only slightly over wide current ranges |
| Electrode Gap | Negligible for short gaps (<10-15mm) | Becomes significant only for large gaps |
Leverage the precise control of vacuum arc technology for your application.
Whether you are developing high-reliability electrical switches, advanced thin-film coatings, or conducting plasma research, understanding and controlling the arc voltage is critical to your success.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our expertise can help you select the right electrode materials and system configurations to optimize performance, minimize erosion, and achieve consistent results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific vacuum arc requirements and enhance your project's efficiency and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CF KF Flange Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Lead Sealing Assembly for Vacuum Systems
- 304 316 Stainless Steel Vacuum Ball Valve Stop Valve for High Vacuum Systems
- KF ISO Stainless Steel Vacuum Flange Blind Plate for High Vacuum Systems
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
- Oil Free Diaphragm Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- How do you maintain vacuum pressure? Master the balance between gas removal and gas load for stable performance.
- What is the calibration of a vacuum? Ensuring Accurate Pressure Measurement for Your Process
- What are the different types of ovens in the lab? A Guide to Choosing the Right Heating Equipment
- What can carbon nanotubes be used for? Unlock Superior Performance in Batteries & Materials
- What instrument is used to measure vacuum? Selecting the Right Gauge for Your Pressure Range



















