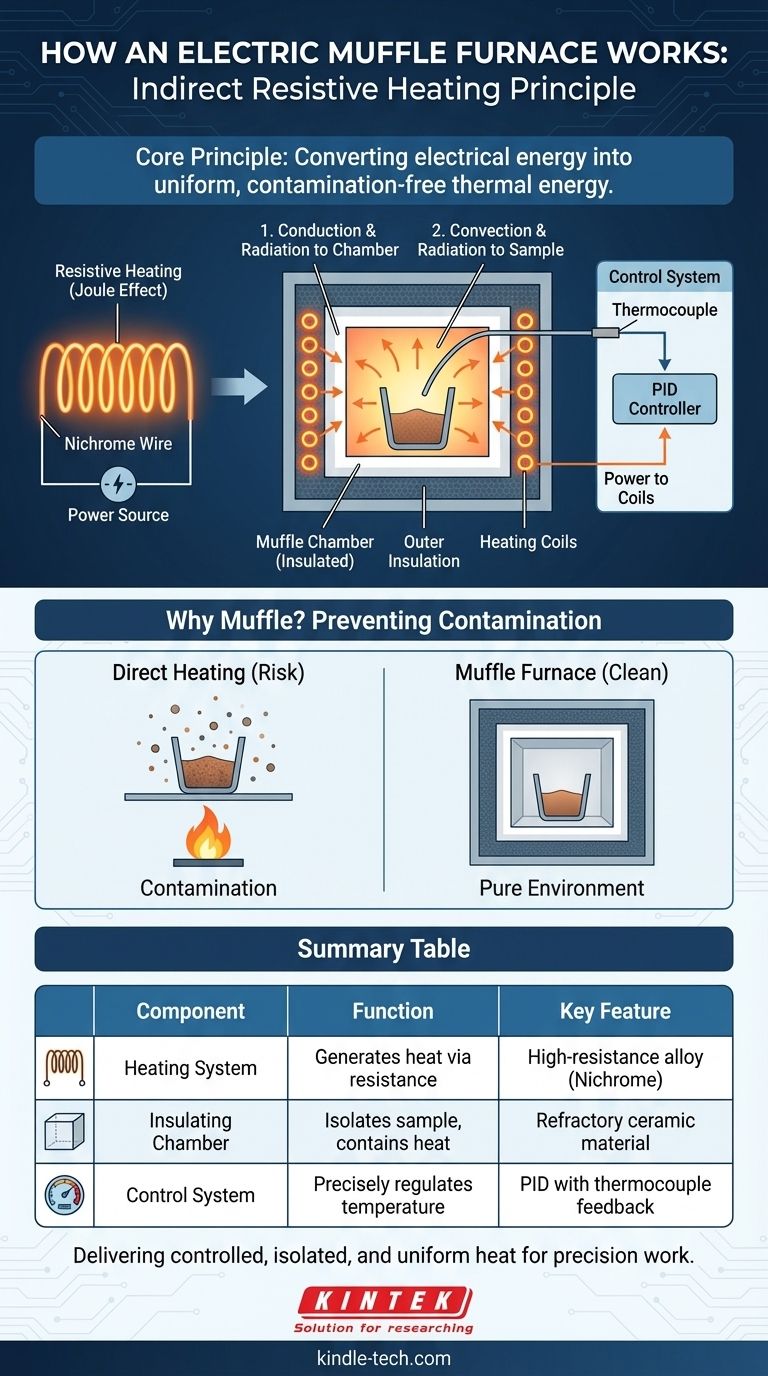
At its core, an electric muffle furnace operates on the principle of indirect resistive heating. It converts electrical energy into thermal energy using heating coils. This heat is then transferred through convection and radiation to a sample held within a self-contained, insulated chamber—the "muffle"—which isolates the sample from the heating elements themselves.
The central challenge in many high-temperature applications is achieving intense, uniform heat without contaminating the material being tested. The muffle furnace solves this by using an insulated chamber to separate the sample from the electrical heating elements, ensuring a clean and precisely controlled environment.

The Core Components and Their Roles
A muffle furnace's function is best understood by examining its three primary systems: the heating system, the insulating chamber, and the control system. Each plays a distinct role in the process.
The Heating System: Generating the Heat
The process begins with resistive heating, also known as Joule heating. High-resistance wire coils, often made of a nickel-chromium alloy (Nichrome), are mounted around the chamber.
When a high electrical current is passed through these coils, their resistance causes them to become extremely hot, converting electrical energy directly into thermal energy. This is the fundamental source of heat for the entire furnace.
The Insulating Chamber: The "Muffle"
The term "muffle" refers to the insulated inner chamber that holds the sample. This component is the defining feature of the furnace.
It is typically constructed from high-temperature refractory ceramic materials. The muffle serves two critical functions:
- Isolation: It creates a physical barrier between the glowing-hot heating elements and the sample.
- Insulation: It works with the outer insulation box to prevent heat from escaping, which ensures energy efficiency and allows the furnace to reach very high temperatures rapidly.
The Control System: Ensuring Precision
Modern furnaces rely on a sophisticated feedback loop for precise temperature management.
A thermocouple, a temperature-sensing probe inside the chamber, continuously measures the internal temperature. This reading is sent to a PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller, which is the "brain" of the furnace. The controller compares the actual temperature to the user's setpoint and precisely adjusts the power sent to the heating elements to maintain the target temperature with minimal fluctuation.
How Heat Reaches the Sample
Because the heating elements do not directly touch the sample, the heat must be transferred indirectly. This happens in two main ways.
Step 1: Conduction and Radiation to the Chamber
First, the heating elements radiate heat and conduct it to the walls of the muffle chamber, causing the entire interior surface to heat up uniformly.
Step 2: Convection and Radiation to the Sample
Once the chamber walls are hot, they transfer thermal energy to the sample inside. This occurs primarily through:
- Radiation: The hot inner walls of the chamber radiate thermal energy directly to the surface of the sample.
- Convection: The air (or gas) inside the chamber is heated by the walls, and these circulating currents of hot air transfer heat to the sample.
This two-step, indirect process is what ensures the sample is heated evenly from all sides without any "hot spots."
Understanding the Key Advantage: Preventing Contamination
The primary reason for this muffle design is to guarantee a clean heating environment.
The Problem with Direct Heating
In many scientific and industrial processes, such as ashing, heat treating, or materials research, it is crucial that the sample remains pure. If a sample were heated by direct combustion (like a gas flame) or direct contact with electric coils, byproducts or flaking from the heat source could contaminate it, invalidating the results.
The Muffle Furnace Solution
By separating the sample in its own chamber, the muffle furnace ensures that the only thing interacting with the sample is heat and the controlled atmosphere inside the chamber. This isolation is the furnace's most important design principle.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the working principle helps you leverage the furnace for specific outcomes.
- If your primary focus is sample purity: The isolation provided by the muffle chamber is the most critical feature, preventing any contamination from the heating elements.
- If your primary focus is process repeatability: The PID controller and thermocouple system are key, providing the precise temperature regulation needed for consistent, reliable results across multiple tests.
- If your primary focus is efficiency: The high-grade insulation and indirect heating design allow for rapid, uniform heating cycles while conserving energy.
Ultimately, a muffle furnace is engineered to deliver controlled, isolated, and uniform heat, making it an indispensable instrument for precision work.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Heating System | Generates heat via electrical resistance in coils | High-resistance alloy wires (e.g., Nichrome) |
| Insulating Chamber (Muffle) | Isolates sample and contains heat | High-temperature refractory ceramic material |
| Control System | Precisely regulates temperature | PID controller with thermocouple feedback |
Ready to achieve contamination-free heating and precise temperature control in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance muffle furnaces designed for reliability and accuracy in applications like ashing, heat treatment, and materials research. Our equipment ensures your samples remain pure and your processes are repeatable.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect muffle furnace for your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a high-temperature furnace in dolomite catalyst preparation? Achieve 850°C Thermal Activation
- How do you run a muffle furnace? Master the Step-by-Step Process for Safe, Precise Results
- Why must coated titanium dioxide and silica undergo a final heat treatment at 600°C? Unlock Material Performance.
- How is a muffle furnace utilized to evaluate titanium-based composite materials? Master Oxidation Resistance Testing
- How does a high-temperature sintering furnace influence NASICON-type LAGP pellets? Optimize Your Solid Electrolyte
- What is the sintering method of ceramics? A Guide to Creating Strong, Dense Components
- Why is it important to know moisture and ash content? Essential Metrics for Material Quality and Value
- What are the primary functions of using a high-temperature laboratory furnace for the calcination of zirconium dioxide products?



















