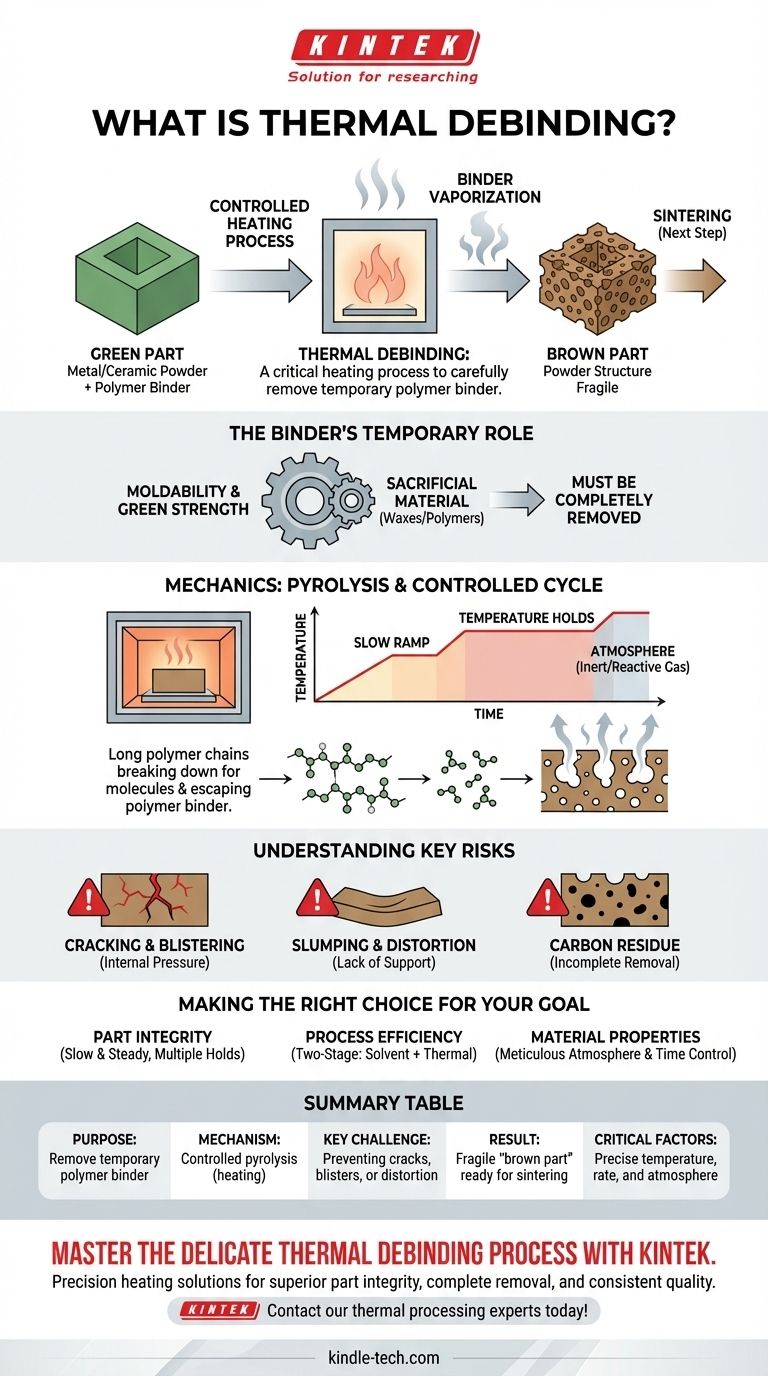
In short, thermal debinding is a critical heating process used in powder metallurgy and ceramic manufacturing to carefully remove a temporary polymer "binder" from a molded component. This controlled burn-off purifies the part, leaving behind a fragile structure of just the primary powder (like metal or ceramic) that is ready for the final high-temperature sintering step.
The core challenge of thermal debinding is not simply applying heat, but precisely controlling the temperature and atmosphere to vaporize the binder without causing the part to crack, bloat, or distort.
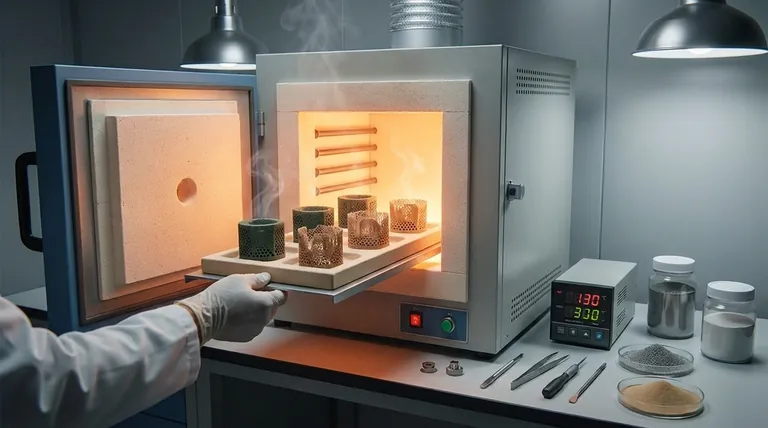

Why Debinding is a Necessary Step
To understand thermal debinding, you must first understand why a binder is used at all. Processes like Metal Injection Molding (MIM) rely on a temporary scaffold to create complex shapes.
From "Green Part" to "Brown Part"
A newly molded component is called a "green part." It consists of metal or ceramic powder held together by a polymer binder system. It has the correct shape but none of the final material properties.
After the binder is removed through debinding, the component is known as a "brown part." It is now extremely fragile and porous, essentially a loosely held-together powder skeleton of the final object.
The Binder's Temporary Role
The binder is the glue. It's a sacrificial material, typically a mix of waxes and polymers, that provides the flowability needed to inject the powder into a mold and gives the green part its initial handling strength. Once it has served this purpose, it must be completely removed.
The Mechanics of Thermal Debinding
Thermal debinding is a process of controlled decomposition. It is often the most time-consuming and delicate stage of the entire manufacturing process.
The Core Mechanism: Pyrolysis
The fundamental principle is pyrolysis. As the part is slowly heated in a furnace, the long polymer chains of the binder break down into smaller, lighter molecules.
These smaller molecules turn into a gas, which can then permeate through the porous structure of the part and be swept away by the furnace atmosphere.
The Importance of a Controlled Cycle
This process cannot be rushed. The temperature is ramped up very slowly, often with specific "holds" at various temperature plateaus. Each plateau targets the decomposition of a different component within the binder system.
A slow rate ensures the binder vapor is generated gradually, allowing it to escape without building up internal pressure that would damage the part.
The Furnace Atmosphere
The atmosphere inside the furnace is critical. It might be an inert gas (like nitrogen or argon) to prevent the metal powder from oxidizing.
In some cases, as noted in process documentation, a reactive gas is used. This gas can initiate a chemical reaction that helps degrade the binder more efficiently at lower temperatures, converting it into components that are easier to evaporate and remove.
Understanding the Key Risks
Improper thermal debinding is a primary source of defects that cannot be corrected in later stages.
Cracking and Blistering
If heating is too rapid, the binder vaporizes faster than it can escape. This builds immense internal pressure, leading to surface blisters, internal voids, or catastrophic cracking of the part.
Slumping and Distortion
The brown part has very little strength before it is sintered. If the heating cycle is not properly designed or the part is not adequately supported, it can slump, warp, or distort under its own weight.
Carbon Residue
Incomplete binder removal can leave behind a carbon residue. This residual carbon can interfere with the final sintering process, leading to brittleness, poor density, and unacceptable final material properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The design of a thermal debinding cycle is a balance between process speed and part quality.
- If your primary focus is part integrity: Prioritize a slow, conservative heating rate with multiple temperature holds to ensure binder vapor can escape without building damaging internal pressure.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency: Consider a two-stage process, using solvent debinding first to remove a large portion of the binder before a shorter, faster thermal cycle to remove the rest.
- If your primary focus is final material properties: Meticulously control the furnace atmosphere to prevent oxidation and ensure the cycle is long enough for complete binder removal, avoiding residual carbon.
Ultimately, mastering the thermal debinding stage is the key to successfully converting a molded shape into a dense, high-performance final component.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Remove temporary polymer binder from a molded "green part". |
| Mechanism | Controlled pyrolysis (heating) to vaporize the binder. |
| Key Challenge | Removing binder without causing cracks, blisters, or distortion. |
| Result | A fragile "brown part" ready for final sintering. |
| Critical Factors | Precise temperature control, heating rate, and furnace atmosphere. |
Master the delicate thermal debinding process with KINTEK.
Precision heating is critical for successfully converting your molded parts into high-performance components. KINTEK specializes in the lab equipment and consumables needed for controlled thermal processes, serving the exacting needs of laboratories in powder metallurgy and ceramics.
We can provide the reliable solutions you need to:
- Achieve complete binder removal without defects.
- Optimize your cycle for superior part integrity and material properties.
- Ensure consistent, high-quality results batch after batch.
Let's discuss how our expertise can enhance your manufacturing process. Contact our thermal processing experts today!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a continuous furnace? A Guide to High-Volume, Automated Heat Treatment
- What are the disadvantages of annealing? The Critical Trade-offs in Material Strength and Cost
- Why is a Laboratory Vacuum Drying Oven recommended for PBAT microspheres? Protect Sensitive Polymer Integrity
- Which method of heat transfer occur in a vacuum? Unlocking the Power of Thermal Radiation
- What type of brazing works at lower temperature? Silver Alloys for Heat-Sensitive Materials
- Why is a vacuum drying oven essential for lithium-air battery air electrodes? Ensure Peak Stability and Performance
- Is calcination done in a blast furnace? Clarifying the Purpose of Industrial Furnaces
- What are the disadvantages of a continuous furnace? High Costs and Inflexibility Explained



















