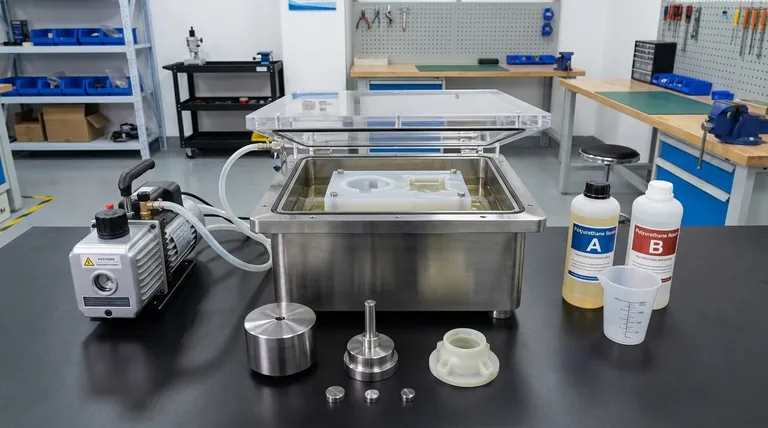
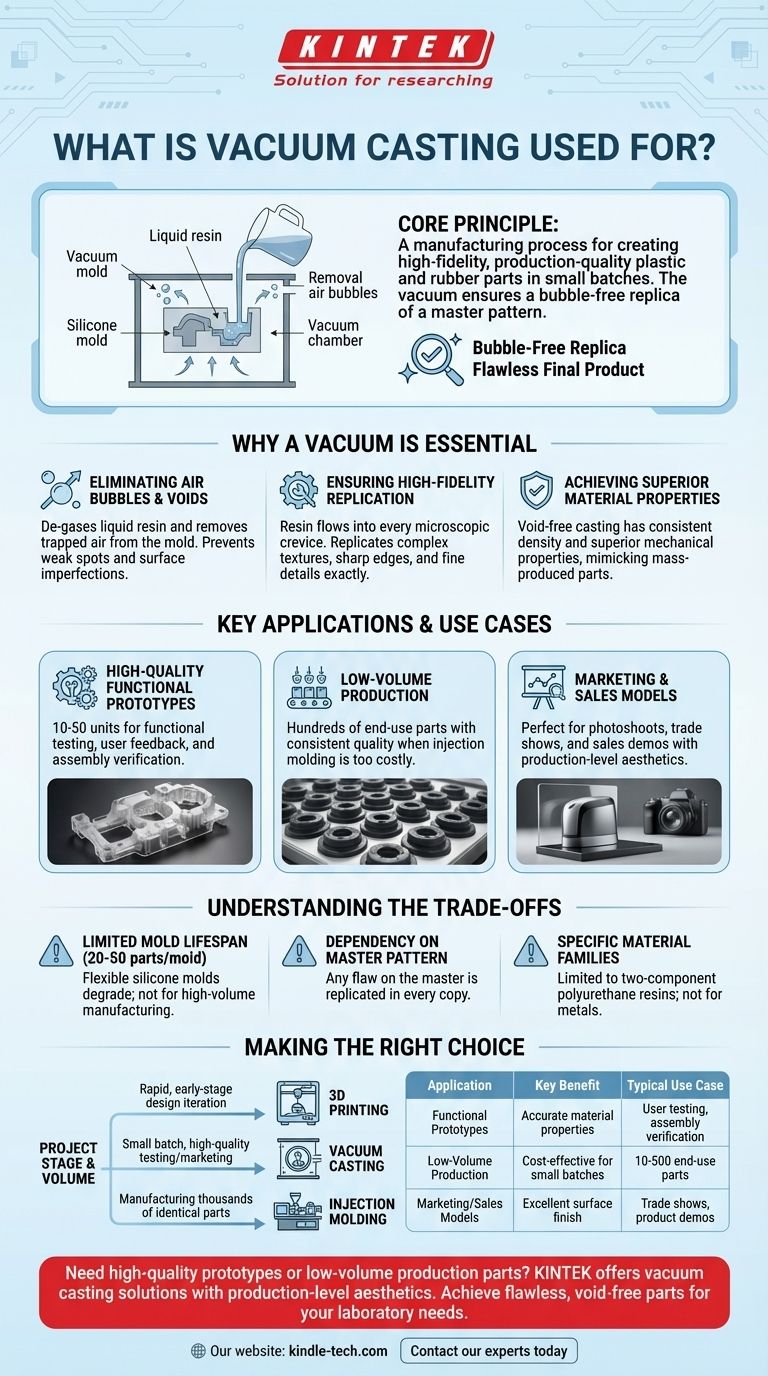
At its core, vacuum casting is a manufacturing process used to create high-fidelity, production-quality plastic and rubber parts in small batches. It excels at producing complex geometries with excellent surface detail, making it an ideal method for creating functional prototypes, marketing models, and low-volume production runs without the high cost of steel tooling.
The primary purpose of vacuum casting is not simply to make a part, but to create a bubble-free replica of a master pattern. The vacuum environment is the critical element that ensures the liquid polyurethane resin perfectly fills every detail of a silicone mold, resulting in a flawless, void-free final product.

The Core Principle: Why a Vacuum is Essential
The term "vacuum casting" directly describes its key advantage. The process takes place inside a vacuum chamber to remove all air from the process, solving problems that plague other casting methods.
Eliminating Air Bubbles and Voids
The most critical function of the vacuum is to de-gas the liquid resin before it is poured and to remove any trapped air from within the silicone mold. Without a vacuum, microscopic air bubbles would be trapped in the cured part, creating weak spots and surface imperfections.
Ensuring High-Fidelity Replication
By removing all air, the liquid resin can flow into every microscopic crevice and feature of the master pattern's mold. This allows for the exact replication of complex textures, sharp edges, and fine details that would otherwise be lost.
Achieving Superior Material Properties
Air bubbles are impurities that compromise the structural integrity of a cast part. A void-free casting produced under vacuum has consistent density and superior mechanical properties, closely mimicking the performance of a final, mass-produced part.
Key Applications and Use Cases
Vacuum casting serves as a crucial bridge between initial 3D printing and full-scale injection molding. It is chosen when quality and material accuracy are more important than the speed of a single prototype.
High-Quality Functional Prototypes
This is the most common application. Teams use vacuum casting to produce a small series (typically 10-50 units) of realistic prototypes for functional testing, user feedback sessions, and pre-production assembly verification.
Low-Volume Production
When the required quantity of parts is too low to justify the massive expense of injection molding tooling, vacuum casting is the ideal solution. It allows for the creation of hundreds of end-use parts with consistent quality.
Marketing and Sales Models
The exceptional surface finish and ability to mimic final production materials make vacuum-cast parts perfect for marketing photoshoots, trade show displays, and sales demonstration units that need to look and feel like the real product.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, vacuum casting is a specific tool for a specific job. It is not a universal solution, and understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
The Mold Has a Limited Lifespan
The flexible silicone molds used in vacuum casting degrade over time. A single mold can typically produce only 20 to 50 parts before it loses detail and needs to be replaced, making the process unsuitable for high-volume manufacturing.
Dependency on the Master Pattern
The quality of the final cast parts is entirely dependent on the quality of the master pattern. Any flaw, layer line, or imperfection on the master (often made via high-resolution 3D printing or CNC machining) will be perfectly replicated in every single copy.
Specific Material Families
The process is designed for a specific range of two-component polyurethane resins. While these materials can be formulated to have a wide variety of properties (from rigid and clear to soft and rubber-like), you are limited to this material family. It is not used for casting metals.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Choosing a manufacturing process depends entirely on your project's stage, volume requirements, and quality criteria.
- If your primary focus is rapid, early-stage design iteration: A 3D printer is likely faster and more cost-effective for creating single, non-cosmetic prototypes.
- If your primary focus is a small batch of high-quality parts for testing or marketing: Vacuum casting is the ideal choice to achieve production-level aesthetics and material feel.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing thousands of identical parts: Investing in injection molding tooling is the only scalable and cost-effective path forward.
Ultimately, vacuum casting empowers you to create parts with the quality of mass production at the scale of prototyping.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefit | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Functional Prototypes | Accurate material properties | User testing, assembly verification |
| Low-Volume Production | Cost-effective for small batches | 10-500 end-use parts |
| Marketing/Sales Models | Excellent surface finish | Trade shows, product demos |
Need high-quality prototypes or low-volume production parts? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering vacuum casting solutions that deliver production-level aesthetics and material accuracy for your laboratory needs. Achieve flawless, void-free parts perfect for functional testing and presentations. Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using high-strength graphite molds in the hot press sintering of Ti6Al4V-based composites?
- What role does a high-purity graphite mold play during hot pressing? Optimize Boron Carbide Sintering at 1850°C
- Why is hot press molding preferred over traditional solution casting? Expert Comparison for Polymer Electrolytes
- What role do high-temperature pressure molds play in SiCp/Al fabrication? Enhancing Densification and Thermal Uniformity
- What technical requirements must specialized pressure-bearing molds meet? Optimize Sulfide Electrolyte Densification



















