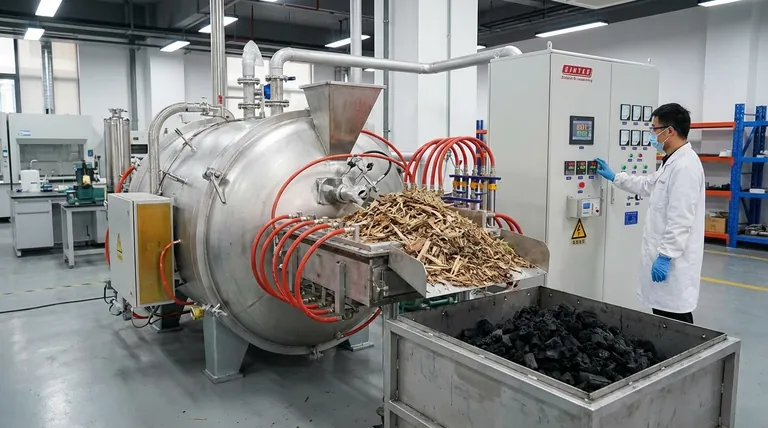
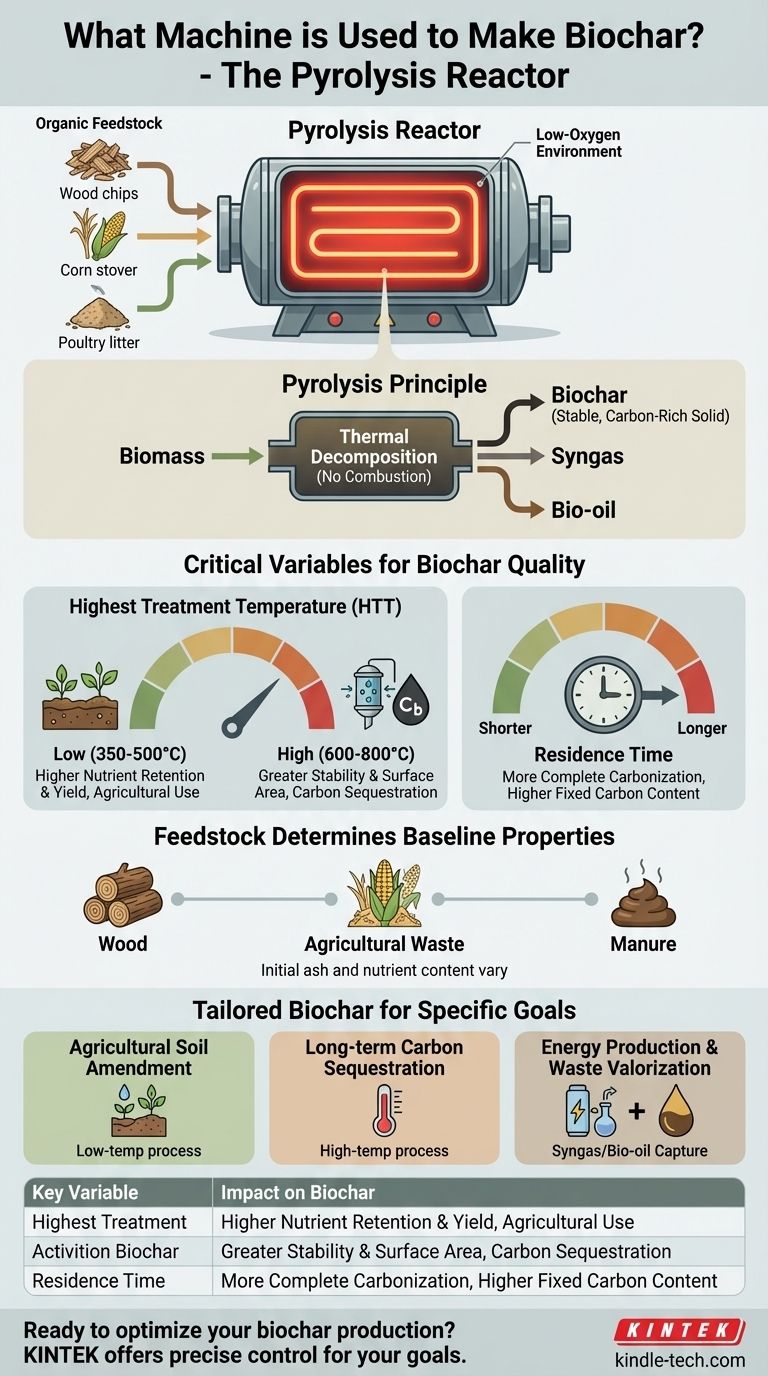
The primary machine used to make biochar is a pyrolysis reactor, sometimes referred to as a pyrolysis kiln or gasifier. This equipment is specifically designed to heat organic materials, such as wood, agricultural waste, or manure, in a controlled, low-oxygen environment. This process, called pyrolysis, thermally decomposes the material without letting it combust, converting it into a stable, carbon-rich solid (biochar).
The specific name of the machine is less important than understanding the process it facilitates: pyrolysis. The quality and characteristics of the final biochar are determined not by the machine itself, but by how precisely it controls the key variables of temperature and time in an oxygen-starved environment.

How Biochar Production Works: The Principle of Pyrolysis
The creation of biochar relies on a simple but powerful thermochemical process. The machine's entire purpose is to manage this reaction with precision.
What is Pyrolysis?
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of materials at elevated temperatures in an inert atmosphere. Think of it as baking biomass in the absence of air, rather than burning it.
When biomass is burned with oxygen, the carbon combines with oxygen to form carbon dioxide. In pyrolysis, the lack of oxygen prevents this, forcing the carbon to re-form into stable, porous charcoal-like structures.
The Critical Role of a Low-Oxygen Environment
The defining feature of a pyrolysis reactor is its ability to heat feedstock without introducing significant oxygen. This is the key that unlocks biochar production.
By starving the reaction of oxygen, the machine ensures the biomass carbonizes instead of turning to ash. This process also produces valuable co-products like syngas (synthetic gas) and bio-oil, which can be captured and used as energy.
Controlling the Key Variables
As noted in process analysis, the two most critical parameters a biochar machine must control are Highest Treatment Temperature (HTT) and residence time.
The control system of the reactor manages the heating elements and the feedstock flow rate to precisely dictate how hot the material gets and how long it stays at that temperature.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Not All Biochar is Equal
The specific settings used during pyrolysis fundamentally change the final product. A "one-size-fits-all" approach does not exist, and the machine's operator must make deliberate choices.
The Impact of Temperature
The temperature at which biochar is produced has the single greatest impact on its properties.
-
Low-Temperature Biochar (350–500°C): This process yields more biochar by mass and retains more volatile organic compounds and nutrients. This char is often preferred for agricultural soil amendment where nutrient addition is a goal.
-
High-Temperature Biochar (600–800°C): This produces a highly stable, porous biochar with a greater surface area and higher fixed carbon content. This type of char is ideal for carbon sequestration, water filtration, or as an additive for environmental remediation.
The Role of Residence Time
Residence time is the duration the biomass is held at the peak temperature. A longer residence time generally leads to a more complete carbonization process, increasing the fixed carbon content and stability of the biochar.
However, a longer time also reduces the final yield and requires more energy, presenting a classic engineering trade-off between quality and efficiency.
Feedstock Determines the Starting Point
The type of organic material used as feedstock—whether wood chips, corn stover, or poultry litter—establishes the baseline chemistry of the biochar. For example, biochar made from manure will have a much higher initial ash and nutrient content than one made from clean wood. The machine's process then refines these properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The best biochar production strategy depends entirely on your intended application. You must align the process variables with your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is agricultural soil amendment: Aim for a lower-temperature (~450°C) pyrolysis to produce a char that retains more nutrients.
- If your primary focus is long-term carbon sequestration: Use a higher-temperature process (>600°C) to create a more stable, high-carbon biochar with maximum permanence.
- If your primary focus is energy production and waste valorization: Choose a system designed to efficiently capture and utilize the syngas and bio-oil co-products to offset energy costs.
By understanding the principles behind the process, you can leverage any pyrolysis machine to create a biochar tailored to its specific purpose.
Summary Table:
| Key Variable | Impact on Biochar |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Low temp (350–500°C): Higher nutrient retention. High temp (600–800°C): Greater stability & surface area. |
| Residence Time | Longer time: More complete carbonization, higher fixed carbon content. |
| Feedstock Type | Determines baseline properties (e.g., wood vs. manure). |
Ready to produce high-quality biochar tailored to your needs? Whether for soil amendment, carbon sequestration, or energy recovery, KINTEK's advanced pyrolysis reactors offer precise control over temperature and residence time to achieve your specific goals. Our lab equipment and consumables are designed to help you optimize your biochar production process efficiently. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's biochar research and development!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a constant temperature laboratory reactor in AEM preparation? Optimize Polymer Synthesis.
- How many types of glass lined reactor are there? Choose the Right Thermal Control for Your Process
- Which physical conditions are simulated by high-pressure autoclaves? Precise SCWR Environment Replication
- How does rapid decompression in AFEX affect biomass quality? Unlock Maximum Surface Area for Enzymatic Hydrolysis
- Why must hydrothermal pretreatment of sulfonated activated carbon use a PTFE-lined reactor? Ensure Catalyst Purity
- What are the unique capabilities of specialized supercritical reaction systems in the hydrogenation of fatty alcohols?
- What are the reactors used in chemical engineering? A Guide to Batch, CSTR, and PFR Systems
- What are the advantages of using a high-pressure reactor like an autoclave? Maximize Liquefaction Speed & Yield



















