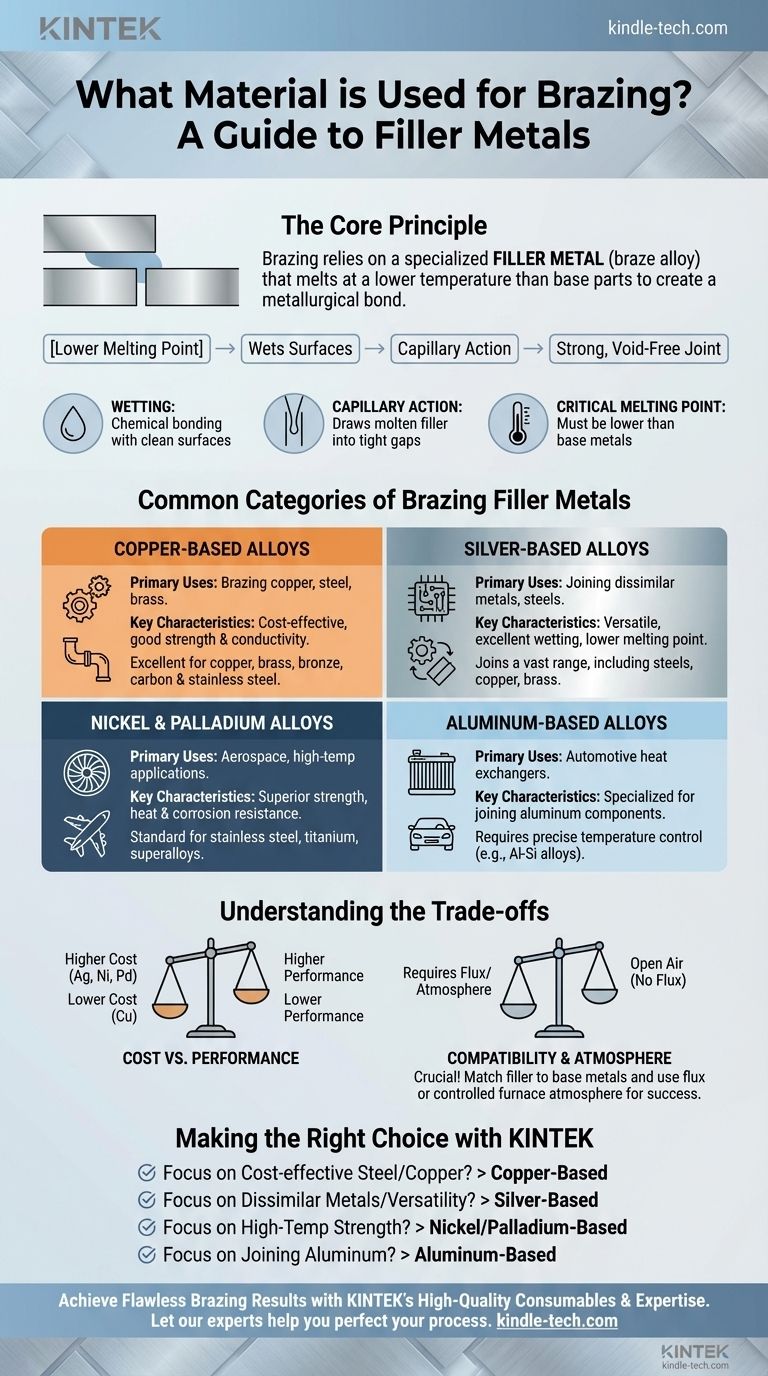
Brazing relies on a specialized filler metal, often called a braze alloy, which is melted and drawn into the gap between two closely fitted parts. Common filler metals include alloys based on silver, copper, nickel, and palladium. The specific material is chosen based on its melting point and its chemical compatibility with the base metals being joined.
The core principle of brazing is not simply filling a gap, but selecting a filler metal that melts at a lower temperature than the parts being joined and is capable of "wetting" their surfaces to create a permanent, metallurgical bond.

The Role of the Filler Metal: More Than Just Glue
Choosing a brazing filler is a technical decision that dictates the strength, conductivity, and durability of the final assembly. The filler metal's properties must be carefully matched to both the base materials and the intended service conditions.
The Principle of Wetting
For a braze to be successful, the molten filler metal must wet and spread across the surfaces of the base metals. This is a chemical interaction where the filler alloy forms an intimate bond with the parts being joined.
This wetting action can only occur if the surfaces are completely clean and free of oxides. This is why brazing is always performed using either a chemical flux or a controlled, oxygen-free furnace atmosphere.
Capillary Action Draws in the Filler
Once the filler metal wets the surfaces, capillary action automatically draws the molten alloy into the tight space between the workpieces. This ensures the joint is completely filled, creating a solid, void-free connection upon cooling.
The Critical Melting Point
A fundamental requirement of any brazing filler metal is that its melting point must be lower than the melting points of the base metals being joined. However, it must also be high enough to withstand the operating temperatures of the finished product.
Common Categories of Brazing Filler Metals
Filler metals are typically categorized by their primary elemental component. Each category offers a different balance of performance, cost, and application suitability.
Copper-Based Alloys
Copper alloys, such as copper-zinc and copper-phosphorus, are widely used due to their excellent strength, corrosion resistance, and good electrical and thermal conductivity.
They are the go-to choice for brazing copper, brass, bronze, carbon steel, and stainless steel. Copper-phosphorus alloys are particularly useful for joining copper to copper without needing flux.
Silver-Based Alloys
Silver-based alloys are extremely popular because of their versatility and relatively low melting temperatures. They can join a vast range of metals, including steels, stainless steels, copper, and brass.
The addition of silver improves the alloy's ability to wet different base metals, making it an excellent choice for joining dissimilar materials.
Nickel and Palladium Alloys
For high-performance applications, nickel and palladium alloys are the standard. These fillers provide superior strength, heat resistance, and corrosion resistance at elevated temperatures.
They are primarily used for brazing stainless steel, titanium, and other high-temperature "superalloys" found in aerospace and industrial turbine applications.
Aluminum-Based Alloys
Brazing aluminum requires a specialized filler metal, typically an aluminum-silicon alloy. These fillers have a melting point just below that of the aluminum base metal, requiring precise temperature control. This process is common in manufacturing automotive heat exchangers, like radiators and condensers.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a brazing filler is always a balance of engineering requirements and practical constraints.
Cost vs. Performance
There is a direct correlation between cost and performance. Copper-based alloys are generally the most economical, while fillers containing significant amounts of silver, nickel, or palladium are substantially more expensive. The choice depends on whether the application justifies the higher material cost.
Base Material Compatibility
Not every filler works with every base metal. For example, phosphorus-bearing fillers should not be used on ferrous or nickel-based alloys as they can form brittle compounds, leading to joint failure. Always verify the compatibility between your filler and base materials.
The Need for Flux or Atmosphere
You cannot achieve a proper braze joint in open air without a flux. The flux shields the joint from oxygen during heating, dissolves oxides, and promotes wetting. Alternatively, furnace brazing in a vacuum or a controlled atmosphere (like hydrogen or nitrogen) eliminates the need for flux, resulting in cleaner joints.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Your selection should be guided by the materials you are joining and the performance you need from the final assembly.
- If your primary focus is joining steel or copper alloys cost-effectively: A copper-based filler metal like copper-zinc or copper-phosphorus is your most reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar metals or requires a lower brazing temperature: A silver-based alloy offers excellent versatility and wetting characteristics across a wide range of materials.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature strength and corrosion resistance: Nickel or palladium-based alloys are the required standard for demanding applications involving stainless steel or superalloys.
- If your primary focus is joining aluminum components: You must use a specialized aluminum-silicon filler alloy and a precisely controlled process.
Ultimately, a successful braze joint is the result of a deliberate match between the base metals, the filler material, and the process environment.
Summary Table:
| Filler Metal Category | Primary Uses | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Copper-Based Alloys | Brazing copper, steel, brass | Cost-effective, good strength & conductivity |
| Silver-Based Alloys | Joining dissimilar metals, steels | Versatile, excellent wetting, lower melting point |
| Nickel/Palladium Alloys | Aerospace, high-temp applications | Superior strength & heat resistance |
| Aluminum-Based Alloys | Automotive heat exchangers | For joining aluminum components |
Achieve Flawless Brazing Results with KINTEK
Choosing the correct brazing filler metal is critical for the integrity and performance of your assembly. The right selection ensures joint strength, thermal conductivity, and durability under service conditions.
KINTEK specializes in supplying high-quality lab equipment and consumables for precise thermal processing applications, including brazing. We provide the materials and expertise to help you:
- Select the optimal filler metal for your specific base materials and performance requirements.
- Ensure process reliability with consistent, high-quality consumables.
- Improve your brazing outcomes and enhance product quality.
Let our experts help you perfect your brazing process. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your laboratory needs and how our solutions can bring value to your operations.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 100L Chilling Circulator Cooling Water Circulator for Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath Water Bath Cooling
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
- Laboratory High Pressure Horizontal Autoclave Steam Sterilizer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Non-Standard Insulator Customization
People Also Ask
- What critical experimental conditions do high-temperature furnaces provide for FeCrAl coatings? Expert Testing Guide
- What are the three main heat treatments? Mastering Annealing, Hardening & Tempering
- What role does an industrial thermochemical treatment furnace with a resistive heating anode play in boriding?
- What is the application of vacuum technology in industries? Enabling Precision Manufacturing and Purity
- What is powder sintering? A Guide to Efficient High-Performance Part Manufacturing
- What is the primary function of a small vertical vacuum furnace in magnesium refining? Maximize Purity & Recovery
- What are the applications of hardening of steel? A Guide to Hardness, Wear Resistance, and Performance
- What keeps the mould together in vacuum casting? Harness Atmospheric Pressure for Perfect Casts








