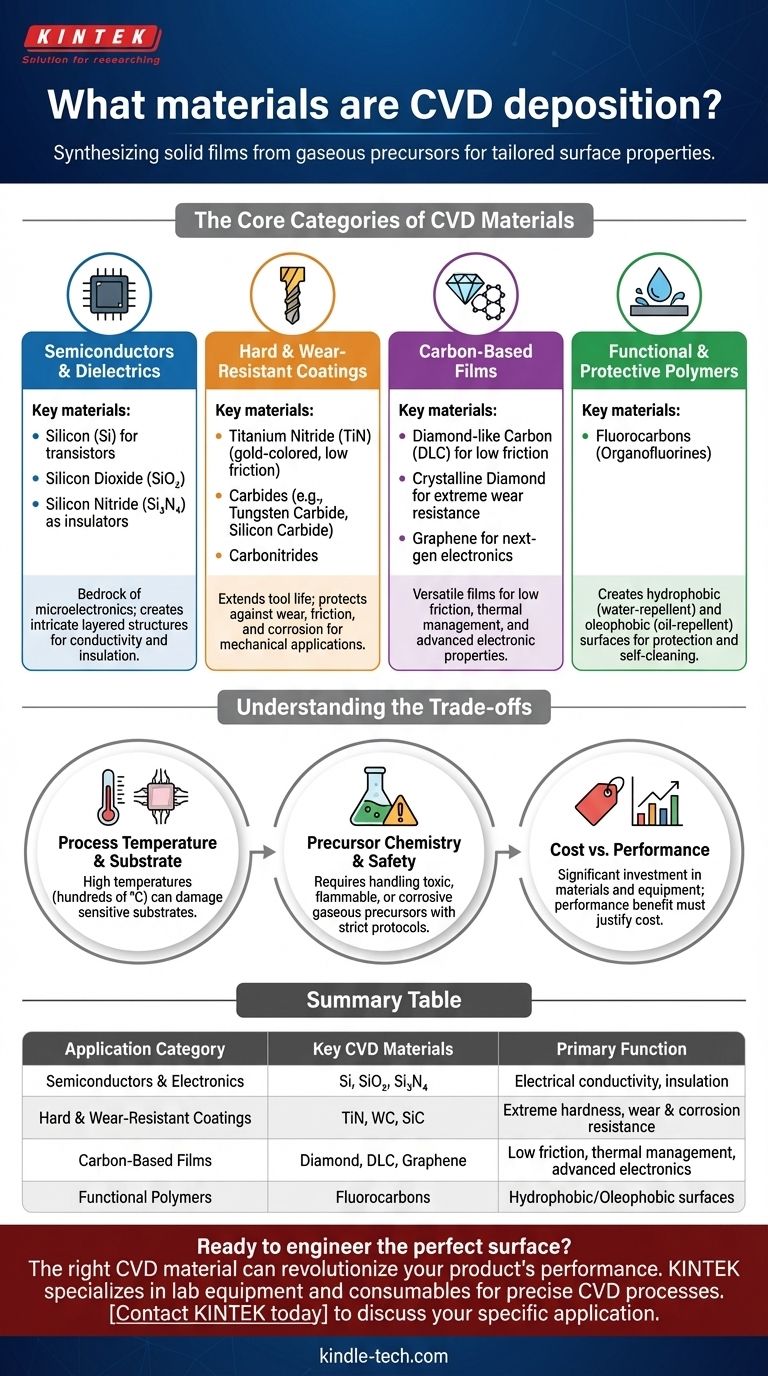
In essence, a vast range of materials can be deposited using Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). This process is used to create thin films of semiconductors like silicon, hard coatings such as titanium nitride, various forms of carbon including diamond and graphene, and functional polymers like fluorocarbons. The choice of material is dictated by the specific properties required for the final application, from electrical conductivity to mechanical hardness.
The core principle of CVD is its versatility. Rather than thinking of a fixed list of materials, it's better to understand that CVD is a technique for synthesizing solid films from gaseous precursors. The real question isn't what can be deposited, but what functional property you need to create on a surface.

The Core Categories of CVD Materials
The material you deposit with CVD is fundamentally tied to the function you want the surface to perform. These materials generally fall into a few key categories based on their primary application.
Semiconductors and Dielectrics
This is the bedrock of the microelectronics industry. CVD is essential for building the intricate layered structures of integrated circuits.
The most common material in this category is silicon (Si). It can be deposited as polycrystalline silicon (poly-Si) for gates in transistors or doped with elements like phosphorus or boron to precisely control its electrical properties.
CVD is also used to deposit insulating films, or dielectrics, like silicon dioxide (SiO₂) and silicon nitride (Si₃N₄). These layers isolate conductive components from each other, which is critical for preventing short circuits in a microchip.
Hard and Wear-Resistant Coatings
For mechanical applications, CVD is used to apply exceptionally hard coatings that protect tools and components from wear, friction, and corrosion.
Nitrides, such as titanium nitride (TiN), are a classic example. TiN provides a gold-colored, low-friction, and extremely hard surface, dramatically extending the life of cutting tools, drills, and industrial molds.
Other common hard coatings include carbides (e.g., tungsten carbide, silicon carbide) and carbonitrides (e.g., titanium carbonitride), each offering a unique balance of hardness, toughness, and thermal stability.
Carbon-Based Films
Carbon is an incredibly versatile element, and CVD can produce it in several valuable forms.
Diamond-like carbon (DLC) is an amorphous carbon film that combines high hardness with a very low coefficient of friction, making it an excellent coating for engine parts and medical implants.
At the highest end, CVD can grow films of pure, crystalline diamond for extreme wear resistance or thermal management, as well as single-atom-thick sheets of graphene for next-generation electronics and sensors.
Functional and Protective Polymers
CVD isn't limited to inorganic materials. It can also deposit thin polymer films for specialized surface properties.
Fluorocarbons (or organofluorines) are used to create hydrophobic (water-repellent) and oleophobic (oil-repellent) surfaces. These are the same types of chemistry found in non-stick coatings and are used in CVD to protect electronics or create self-cleaning surfaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the choice of a CVD material is constrained by practical and chemical realities. You must consider the entire process, not just the final film.
Process Temperature and Substrate
Many CVD processes require very high temperatures—often several hundred degrees Celsius—to drive the necessary chemical reactions. This heat can damage or warp temperature-sensitive substrates like plastics or certain metal alloys.
Precursor Chemistry and Safety
CVD relies on volatile chemical precursors in a gaseous state. These precursors can be highly toxic, flammable, or corrosive, requiring sophisticated safety protocols, handling equipment, and exhaust gas treatment.
Cost vs. Performance
The cost of high-purity precursor gases and the capital expense of CVD reactor systems can be significant. The performance benefit of the coating must justify the investment. A titanium nitride coating is invaluable for a high-performance machine tool but would be overkill for a simple household item.
Selecting the Right Material for Your Application
Your final choice depends entirely on your end goal. The versatility of CVD allows for a tailored solution, but you must start with a clear objective.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing semiconductors: Silicon-based materials (polysilicon, SiO₂, Si₃N₄) are the industry standard for creating conductive and insulating layers.
- If your primary focus is enhancing tool life and wear resistance: Nitrides (TiN) and carbides (WC, SiC) provide the extreme hardness and durability required for mechanical applications.
- If your primary focus is creating low-friction or specialized surfaces: Carbon films (like DLC) or functional polymers (like fluorocarbons) are your best options.
Ultimately, the power of CVD lies in its ability to engineer a surface at the molecular level to achieve a specific functional outcome.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key CVD Materials | Primary Function |
|---|---|---|
| Semiconductors & Electronics | Silicon (Si), Silicon Dioxide (SiO₂), Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄) | Electrical conductivity, insulation |
| Hard & Wear-Resistant Coatings | Titanium Nitride (TiN), Tungsten Carbide (WC), Silicon Carbide (SiC) | Extreme hardness, wear and corrosion resistance |
| Carbon-Based Films | Diamond, Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC), Graphene | Low friction, thermal management, advanced electronics |
| Functional Polymers | Fluorocarbons | Hydrophobic/Oleophobic (water/oil-repellent) surfaces |
Ready to engineer the perfect surface for your project?
The right CVD material can revolutionize your product's performance, whether you need a durable coating for industrial tools or a specialized film for advanced electronics. KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and consumables needed for precise CVD processes, serving the exact needs of laboratories and R&D teams.
Let our experts help you select the ideal solution to enhance durability, functionality, and efficiency. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific application and discover the benefits we can bring to your work.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition
- What is the process of PECVD in semiconductor? Enabling Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate



















