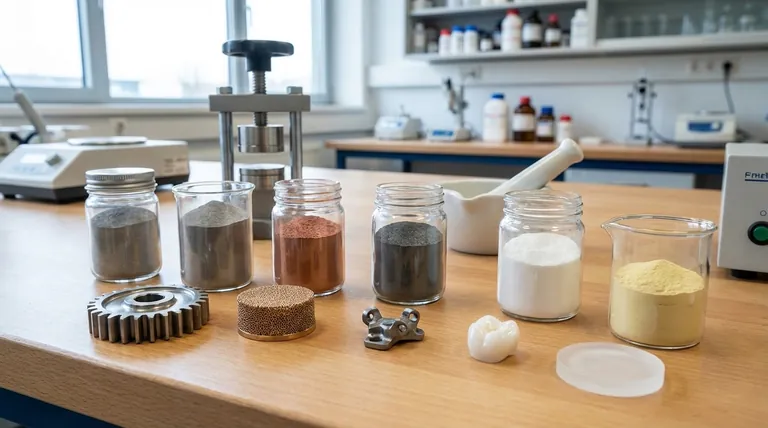
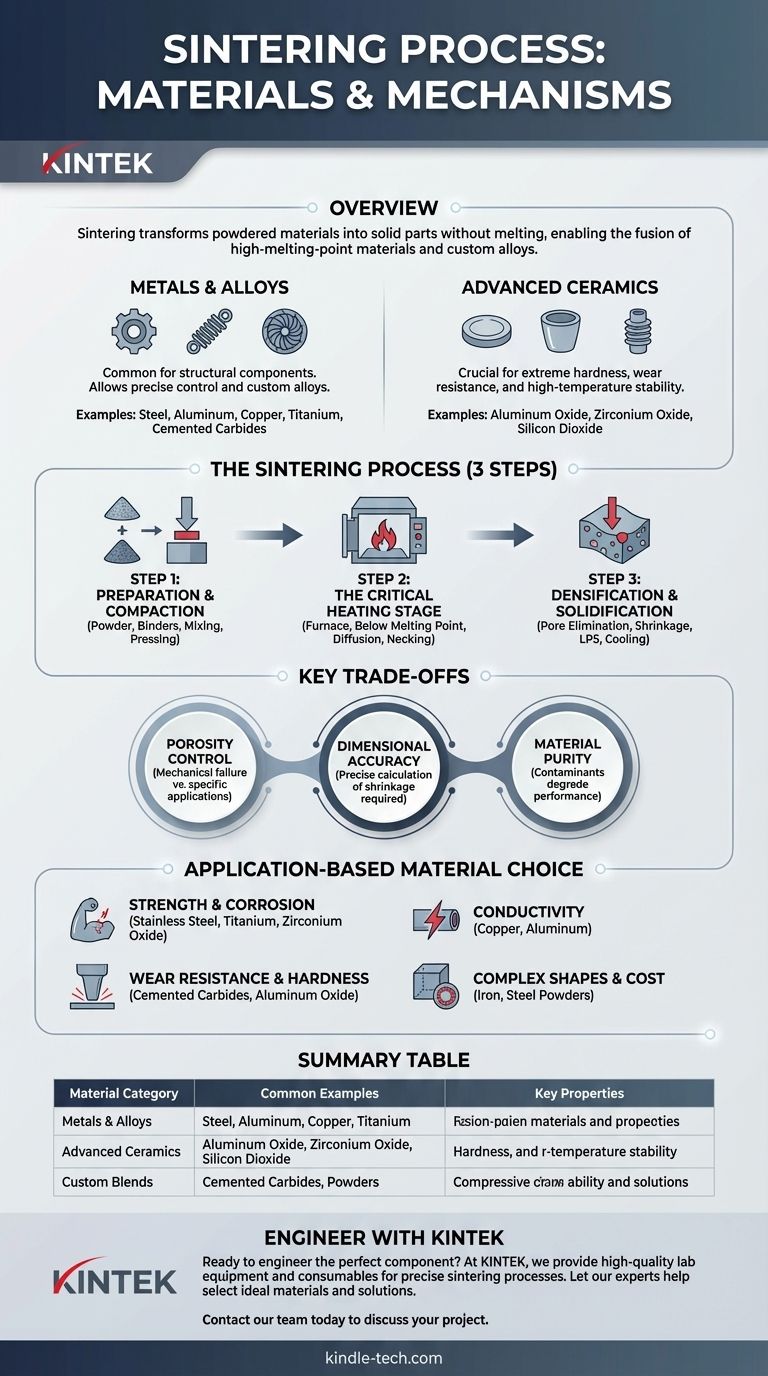
To be precise, the sintering process is exceptionally versatile, using a wide range of materials in powdered form. The two primary categories are metals—including stainless steel, copper, titanium, and aluminum—and advanced ceramics, such as aluminum oxide and zirconium oxide. Critically, these powders can also be mixed to form unique alloys tailored to specific performance requirements.
Sintering’s core advantage is its ability to transform powdered materials into a solid, functional part without melting them. This allows for the fusion of materials with high melting points and the creation of custom alloys that would be difficult or impossible to produce through traditional casting.

The Two Pillars of Sintering Materials
The choice of material is dictated entirely by the desired properties of the final component, such as strength, heat resistance, conductivity, or hardness. Sintering accommodates two broad classes of materials.
Metal Powders and Alloys
Metals are the most common materials used in sintering, especially for structural components in the automotive, industrial, and consumer goods sectors.
The process allows for precise control over the final product's properties. Powders of different metals can be mechanically mixed to create custom alloys with specific characteristics before the sintering process even begins.
Common metals include:
- Steel and Stainless Steel
- Aluminum
- Nickel
- Copper
- Titanium Alloys
- Cemented Carbides
Advanced Ceramics
Ceramic sintering is crucial for producing components that require extreme hardness, wear resistance, or stability at high temperatures.
These materials are often brittle and have exceptionally high melting points, making sintering one of the few viable methods for shaping them. Additives, such as organic binders, are sometimes required to aid in the initial forming stage.
Common ceramics include:
- Aluminum Oxide (Alumina)
- Zirconium Oxide (Zirconia)
- Silicon Dioxide
- Magnesium Oxide
- Iron Oxide
How Materials Behave in the Sintering Process
Understanding the material is inseparable from understanding the process. Sintering works by using heat and pressure to encourage atomic diffusion between particle surfaces, bonding them into a single, solid piece.
Step 1: Preparation and Compaction
The process begins with the chosen raw material in a powdered state. If creating an alloy, different metal powders are mixed. Binders or lubricants are also added to improve compaction.
This mixture is then pressed into the desired shape using a die or mold, creating what is known as a "green compact." This part is solid but fragile, holding its shape through the mechanical interlocking of the particles.
Step 2: The Critical Heating Stage
The green compact is placed into a controlled-atmosphere furnace and heated to a temperature below the material's melting point.
This thermal energy activates the atoms, causing them to migrate across the boundaries of the particles. This process, known as diffusion, creates strong metallurgical bonds or "necks" where the particles touch.
Step 3: Densification and Solidification
As the bonds form and strengthen, the particles pull closer together. This eliminates the pores between them, causing the part to densify and shrink.
In some cases, a technique called Liquid Phase Sintering (LPS) is used. A small amount of an additive with a lower melting point is included, which liquefies and flows into the pores, accelerating densification. The part is then cooled, solidifying into a unified mass.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
While powerful, the sintering process has inherent characteristics that must be managed to achieve a successful outcome.
Porosity Control
The primary challenge in sintering is managing porosity. While sometimes desirable for applications like filters or self-lubricating bearings, residual porosity can be a point of mechanical failure in structural parts.
Dimensional Accuracy
The shrinkage that occurs during densification is a natural part of the process. This must be precisely calculated and accounted for in the initial mold design to ensure the final part meets dimensional tolerances.
Material Purity
The final properties of a sintered part are highly sensitive to the purity of the initial powder. Contaminants can interfere with the bonding process and degrade the component's performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice of material is directly linked to the problem you need the final component to solve.
- If your primary focus is strength and corrosion resistance: You should select stainless steel, titanium alloys, or high-performance ceramics like zirconium oxide.
- If your primary focus is high thermal or electrical conductivity: Copper and aluminum-based powders are the most effective choices.
- If your primary focus is wear resistance and hardness: Your best options are cemented carbides and ceramics like aluminum oxide.
- If your primary focus is complex shapes at a low cost for mass production: Iron and steel powders offer an excellent balance of performance and economy.
Ultimately, the power of sintering lies in its ability to engineer materials and shapes for a specific purpose.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Common Examples | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Metals & Alloys | Stainless Steel, Aluminum, Copper, Titanium | Strength, Conductivity, Corrosion Resistance |
| Advanced Ceramics | Aluminum Oxide (Alumina), Zirconium Oxide (Zirconia) | Extreme Hardness, High-Temperature Stability |
| Custom Blends | Mechanically Mixed Powders | Tailored Performance for Specific Applications |
Ready to engineer the perfect component for your application? The right material choice is critical for achieving strength, conductivity, or heat resistance. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables needed for precise sintering processes. Let our experts help you select the ideal materials and solutions for your laboratory's unique needs.
Contact our team today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK can support your innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is a dental oven? The Precision Furnace for Creating Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations
- What is the temperature of sintering zirconia? Mastering the Protocol for Perfect Dental Restorations
- What is the price of zirconia sintering furnace? Invest in Precision, Not Just a Price Tag
- Can you change the color of zirconia crowns? Understanding the Permanent Nature of Zirconia
- What are the white spots on zirconia after sintering? A Guide to Diagnosing and Preventing Defects



















