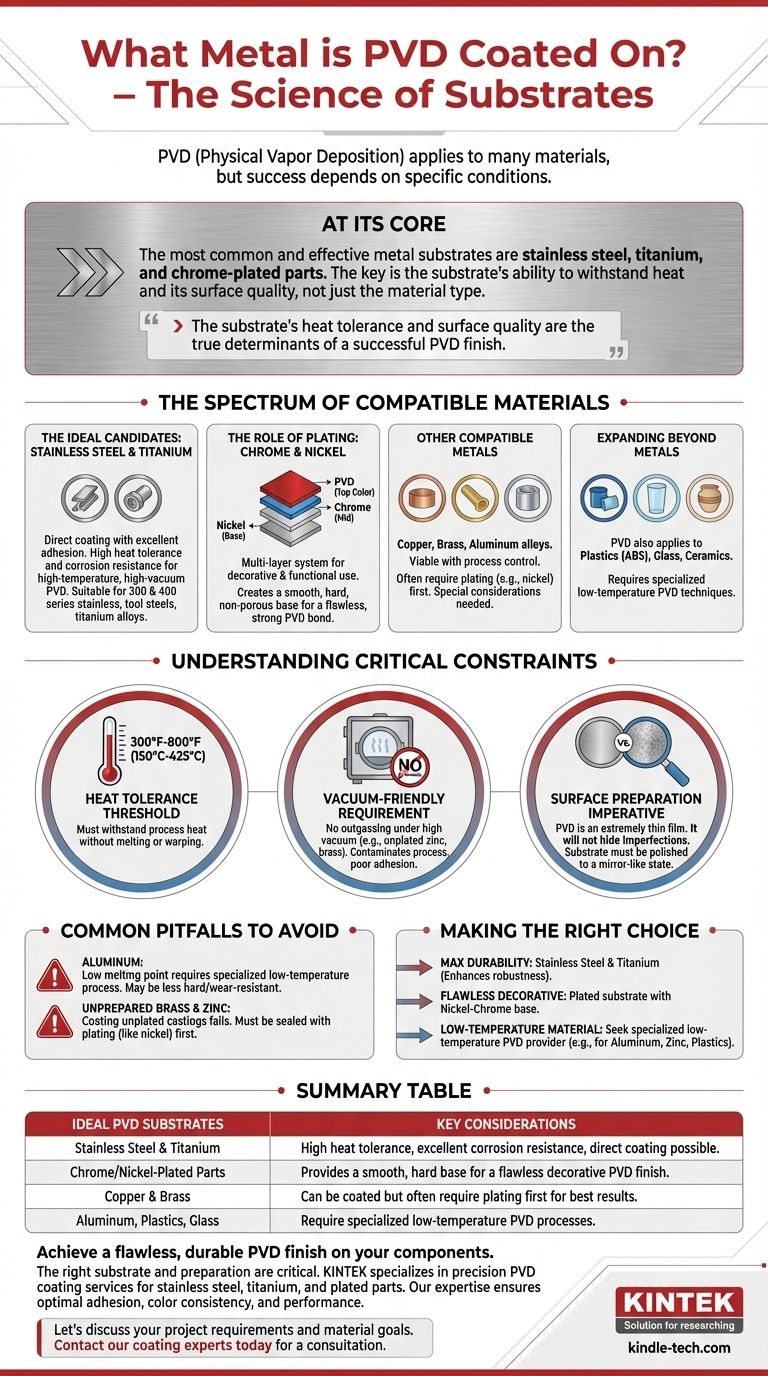
At its core, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) can be applied to an exceptionally wide range of materials, but the most common and effective metal substrates are stainless steel, titanium, and chrome-plated parts. The success of the coating is less about the specific metal and more about its ability to withstand the process conditions, particularly heat, and its surface preparation.
While the list of possible materials is long, the critical factor is not just what can be coated, but how it must be prepared. The substrate's heat tolerance and surface quality are the true determinants of a successful PVD finish.
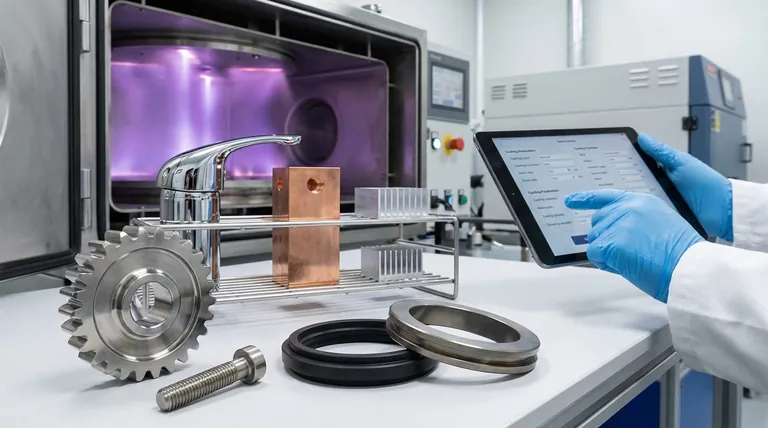

The Spectrum of Compatible Materials
PVD is a versatile technology that is not limited to a single class of material. However, certain metals and surfaces provide an ideal foundation for a durable and aesthetically pleasing coating.
The Ideal Candidates: Stainless Steel and Titanium
Stainless steel and titanium are premier choices for PVD coating. The process can be applied directly to these metals with excellent adhesion and results.
Their high melting points and inherent corrosion resistance make them robust enough to handle the high-temperature, high-vacuum environment of the PVD chamber without issue. Most grades, including 300 and 400 series stainless steels, tool steels, and titanium alloys, are suitable.
The Role of Plating: Chrome and Nickel
For many decorative and functional applications, PVD coatings adhere best to materials that have first been plated with nickel and/or chrome.
This multi-layer system (e.g., Nickel-Chrome-PVD) creates an exceptionally smooth, hard, and non-porous base. This ensures the final PVD color layer is flawless and strongly bonded, which is why it is common for fixtures, automotive parts, and consumer goods.
Other Compatible Metals
A variety of other metals can be successfully coated, though some require more careful process control.
This category includes copper, brass, and aluminum alloys. These non-ferrous metals are viable substrates, but their suitability often depends on the specific PVD process being used and whether they have been plated first.
Expanding Beyond Metals
It's important to recognize that PVD is not exclusively for metals. The process can also be applied to plastics (like ABS), glass, and ceramics. This requires specialized low-temperature PVD techniques but demonstrates the technology's broad applicability.
Understanding the Critical Constraints
Simply choosing a compatible material is not enough. The substrate must meet several key requirements to ensure a high-quality outcome.
The Heat Tolerance Threshold
Most industrial PVD processes involve heating the substrate to temperatures between 300°F and 800°F (150°C to 425°C) to ensure proper coating adhesion and structure.
Any material being coated must be able to withstand this temperature without melting, warping, or degrading. This is the primary reason some materials are more challenging than others.
The "Vacuum-Friendly" Requirement
PVD takes place in a high-vacuum chamber. Materials that "outgas" (release trapped gases or vapors) under vacuum, such as unplated zinc or certain types of brass, are unsuitable.
This outgassing contaminates the vacuum environment and interferes with the deposition process, resulting in a poor-quality, non-adherent coating.
The Surface Preparation Imperative
PVD is an extremely thin film that conforms precisely to the surface it covers. It will not hide or fill in scratches, pores, or other imperfections.
For a smooth, mirror-like PVD finish, the substrate must first be polished to an equally smooth, mirror-like state. The principle is "garbage in, garbage out"—a poor surface will always result in a poor finish.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Understanding the limitations is as important as knowing the capabilities.
The Challenge with Aluminum
While some sources list aluminum as compatible, it requires special consideration. Its low melting point makes it incompatible with standard high-temperature PVD processes.
Coating aluminum is possible but demands a specialized low-temperature PVD process. This may result in a coating that is not as hard or wear-resistant as a high-temperature equivalent.
The Risk of Unprepared Brass and Zinc
As mentioned, attempting to coat unplated or improperly prepared brass and zinc castings is a common failure point. These materials must typically be sealed with a layer of plating (like nickel) to make them vacuum-compatible before PVD can be applied.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of substrate should be guided by your end goal for the product.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and corrosion resistance: Your best options are stainless steel and titanium, as the PVD coating enhances their already robust properties.
- If your primary focus is a flawless decorative finish: Start with a substrate that can be plated, and use a nickel-chrome base layer before applying the PVD topcoat.
- If your primary focus is coating a low-temperature material: You must seek a PVD provider who specializes in low-temperature processes suitable for substrates like aluminum, zinc, or plastics.
Ultimately, a successful PVD outcome begins with an informed decision about the foundation material.
Summary Table:
| Ideal PVD Substrates | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Stainless Steel & Titanium | High heat tolerance, excellent corrosion resistance, direct coating possible. |
| Chrome/Nickel-Plated Parts | Provides a smooth, hard base for a flawless decorative PVD finish. |
| Copper & Brass | Can be coated but often require plating first for best results. |
| Aluminum, Plastics, Glass | Require specialized low-temperature PVD processes. |
Achieve a flawless, durable PVD finish on your components. The right substrate and preparation are critical to your project's success. KINTEK specializes in precision PVD coating services for a wide range of materials, including stainless steel, titanium, and plated parts. Our expertise ensures optimal adhesion, color consistency, and performance for your laboratory equipment, tools, or consumer products.
Let's discuss your project requirements and material goals. Contact our coating experts today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is diamond coating film? A Thin Layer of Diamond for Extreme Performance
- What are diamond coated films? Enhance Materials with Super-Hard, Transparent Layers
- What is CVD diamond coating? Grow a Super-Hard, High-Performance Diamond Layer
- Is diamond coating permanent? The Truth About Its Long-Lasting Durability
- Is diamond coating worth it? Maximize Component Life and Performance



















