Furnace brazing is performed at any temperature above 840°F (450°C), but the precise temperature is dictated entirely by the filler metal used to join the parts. For common industrial applications, this typically ranges from 1100°F (600°C) for aluminum alloys to over 2000°F (1100°C) for steel and high-temperature alloys.
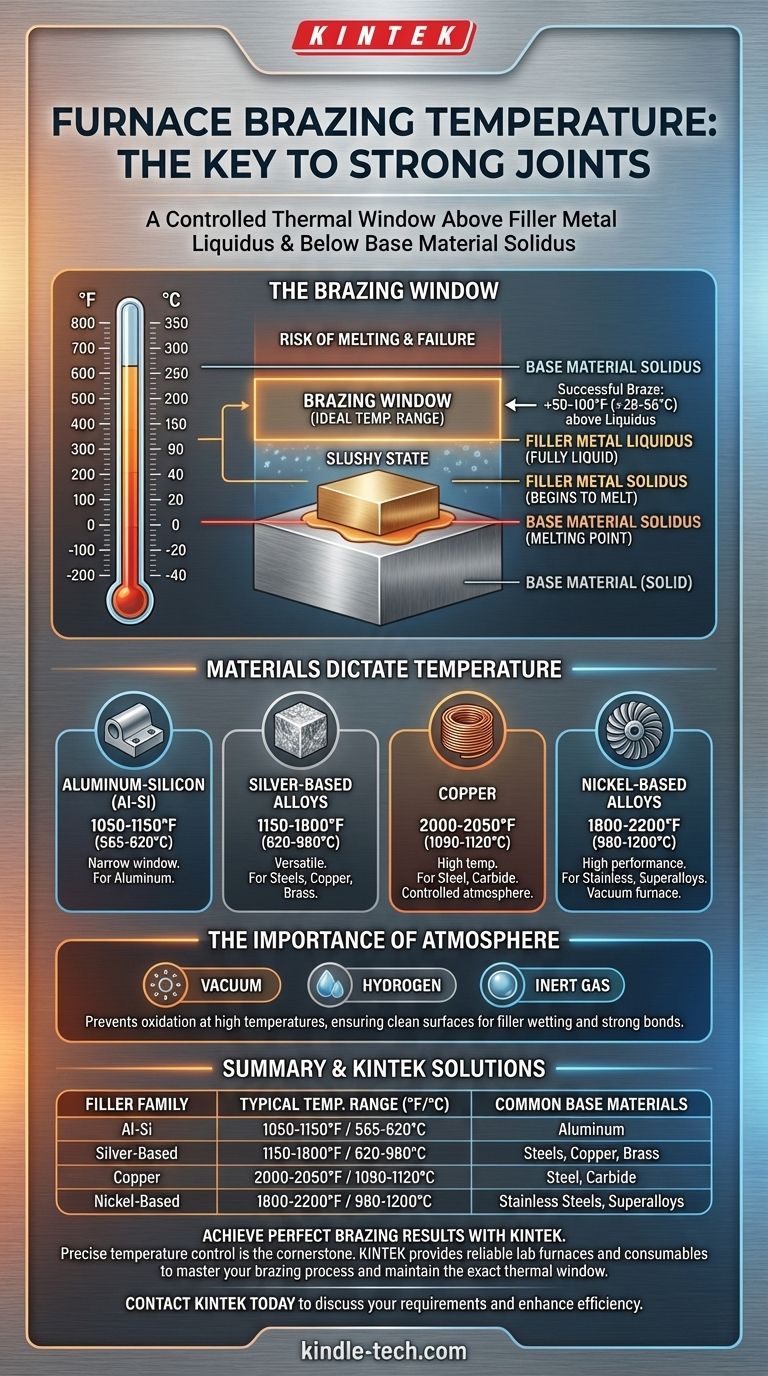
The correct furnace brazing temperature is not a single value but a specific point safely above the melting point of the filler metal and below the melting point of the base materials. This controlled thermal window is the absolute key to creating a strong, metallurgically sound joint.
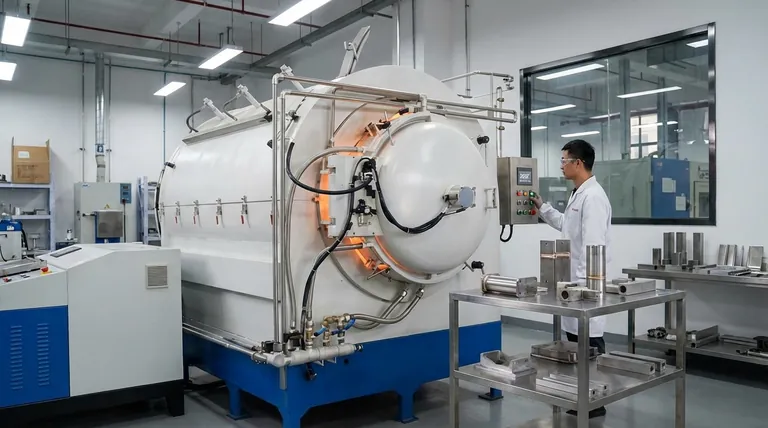

The Core Principle: Liquidus and Solidus
To understand brazing temperature, you must first understand the melting characteristics of the filler metal, which are defined by two critical points: solidus and liquidus.
Defining Solidus and Liquidus
The solidus is the temperature at which the filler metal alloy begins to melt. The liquidus is the temperature at which the filler metal is completely liquid. The range between these two points is a slushy, semi-solid state.
The "Brazing Window"
For a successful braze, the furnace must heat the entire assembly to a temperature slightly above the liquidus point of the filler metal. This ensures the filler is fully molten and has low enough viscosity to be drawn into the joint by capillary action.
A common rule of thumb is to set the furnace temperature 50-100°F (28-56°C) above the filler's liquidus temperature.
Protecting the Base Materials
Simultaneously, the brazing temperature must remain safely below the solidus (melting point) of the base materials being joined. Exceeding this would cause the parts to sag, distort, or melt, resulting in catastrophic failure.
How Materials Dictate Brazing Temperature
The selection of a filler metal is always dependent on the base materials you need to join. This material combination is what sets the required temperature for the process.
Common Filler Metal Families
Different families of filler metals have vastly different brazing temperature ranges.
- Aluminum-Silicon (Al-Si): Used for brazing aluminum. Requires a very narrow temperature window, typically 1050-1150°F (565-620°C).
- Silver-Based Alloys: A versatile category used for joining steels, copper, and brass. Brazing temperatures range widely from 1150-1800°F (620-980°C) depending on the specific alloy composition.
- Copper: Pure copper is a common, cost-effective filler for brazing steel and carbide. It requires a high temperature, typically 2000-2050°F (1090-1120°C), and must be done in a controlled atmosphere to prevent oxidation.
- Nickel-Based Alloys: Used for stainless steels and superalloys in high-performance applications. These require very high temperatures, often from 1800-2200°F (980-1200°C), and are almost always performed in a vacuum furnace.
The Importance of Atmosphere
Furnace brazing is not just about temperature; it's about controlling the environment. At these high temperatures, metals will rapidly oxidize if exposed to air, which prevents the filler metal from wetting and bonding to the surfaces.
Furnaces use controlled atmospheres—such as a vacuum, hydrogen, or inert gas—to protect the parts and ensure a clean, strong joint is formed.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
Setting the wrong temperature is one of the most common failure modes in furnace brazing. Both overheating and underheating have significant consequences.
The Risk of Overheating
Setting the temperature too high, even if it's below the base metal's melting point, can be detrimental. It can cause base metal erosion, where the liquid filler "dissolves" part of the parent material, weakening the joint. It can also lead to the formation of brittle intermetallic compounds, which drastically reduce the joint's strength and ductility.
The Problem with Underheating
If the furnace temperature is too low or the cycle is too short, the filler metal will not become fully liquid. This results in poor capillary action, leading to voids and incomplete joint fill. The resulting bond will be weak and unreliable.
The Need for Thermal Uniformity
It is critical that the entire assembly reaches the target temperature uniformly. Thicker sections heat more slowly than thinner sections. A proper furnace cycle includes "soak" times to allow the temperature to equalize throughout the parts before the filler metal melts, ensuring consistent flow and a complete bond.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice of temperature is a direct consequence of your materials and your performance requirements. Use the filler metal manufacturer's data sheet as your primary guide.
- If your primary focus is joining steel with a copper filler: You will operate in a high-temperature, oxygen-free atmosphere around 2000-2050°F (1090-1120°C).
- If your primary focus is brazing aluminum components: You must use an aluminum-silicon filler and maintain a very tight temperature window, typically around 1050-1150°F (565-620°C), to avoid melting the parts.
- If your primary focus is joining stainless steel for aerospace: You will use a nickel-based filler in a vacuum furnace at temperatures often exceeding 1800°F (980°C).
Ultimately, successful furnace brazing is a function of precise thermal management tailored to your specific material combination.
Summary Table:
| Filler Metal Family | Typical Brazing Temperature Range (°F) | Typical Brazing Temperature Range (°C) | Common Base Materials |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum-Silicon (Al-Si) | 1050 - 1150°F | 565 - 620°C | Aluminum |
| Silver-Based Alloys | 1150 - 1800°F | 620 - 980°C | Steels, Copper, Brass |
| Copper | 2000 - 2050°F | 1090 - 1120°C | Steel, Carbide |
| Nickel-Based Alloys | 1800 - 2200°F | 980 - 1200°C | Stainless Steels, Superalloys |
Achieve Perfect Brazing Results with KINTEK
Precise temperature control is the cornerstone of successful furnace brazing. Whether you're working with aluminum, high-temperature alloys, or specialty steels, choosing the right equipment is critical to avoid costly failures like base metal erosion or incomplete joints.
KINTEK specializes in providing the reliable lab furnaces and consumables you need to master your brazing process. Our solutions help you maintain the exact thermal window required for your specific filler and base materials, ensuring strong, metallurgically sound joints every time.
Let our experts help you select the ideal furnace for your application.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your brazing requirements and discover how our equipment can enhance your lab's efficiency and results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- Where are vacuum furnaces used? Essential for High-Purity Heat Treatment in Critical Industries



















