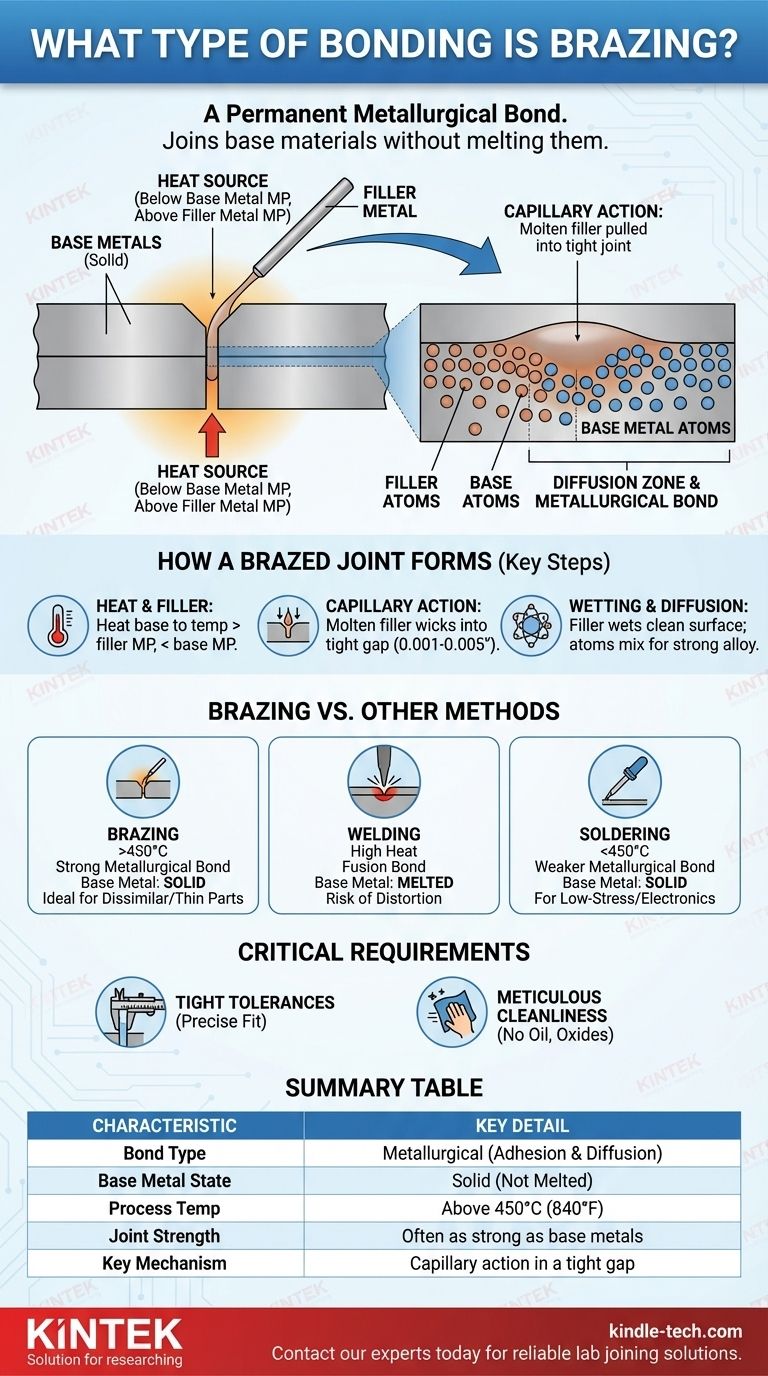
Brazing creates a permanent metallurgical bond by using a filler metal that melts and flows between two closely fitted parts. This process joins the base materials without melting them, instead relying on atomic-level interactions between the molten filler and the solid base metals to form a strong, continuous connection.
The core principle of brazing is not fusion, but adhesion and diffusion. A molten filler metal is drawn into a tight joint by capillary action, where it "wets" the base metal surfaces and forms a new, strong alloy at the interface.

How a Brazed Joint Forms
Brazing is a sophisticated process that leverages specific physical and chemical principles to create a joint that is often as strong as the materials it connects. Understanding each step reveals why it is such a reliable joining method.
The Role of Heat and Filler Metal
The entire process begins by heating the base metals (the parts being joined) to a specific brazing temperature.
Crucially, this temperature is always below the melting point of the base metals but above the melting point of the chosen filler metal. This distinction is the defining characteristic of brazing.
Capillary Action: The Driving Force
Once the base metals reach the correct temperature, the filler metal is introduced to the joint. It instantly melts and is pulled into the small gap between the parts through a force known as capillary action.
This is the same physical principle that causes a paper towel to wick up water. For it to work effectively, the gap between the parts, or joint clearance, must be precisely controlled.
Wetting and Diffusion: The Metallurgical Bond
As the molten filler flows into the joint, it must "wet" the surfaces of the base metals. Wetting is the ability of a liquid to maintain contact with a solid surface.
To ensure proper wetting, the base metals must be perfectly clean, which is why a chemical flux is often used. The flux removes oxides and prevents new ones from forming during heating, preparing the surface for bonding.
Once wetting occurs, atoms from the filler metal and the base metals begin to mix at the interface. This process, called diffusion, creates a new, thin layer of alloyed material, forming the strong, permanent metallurgical bond.
Brazing vs. Other Joining Methods
Understanding the unique bonding mechanism of brazing becomes clearer when compared to other common methods like welding and soldering.
Brazing vs. Welding
Welding works by melting the base metals along with a filler metal, fusing them directly together. This creates an extremely strong joint but generates intense heat that can distort, warp, or weaken the base metals.
Brazing, by not melting the base metals, preserves their original metallurgical properties, making it ideal for joining delicate or thin-walled components.
Brazing vs. Soldering
Soldering is mechanically very similar to brazing; both use a filler metal and capillary action without melting the base materials.
The primary difference is temperature. By definition, brazing occurs at temperatures above 450°C (840°F), while soldering occurs below this threshold. This higher temperature allows brazing to use stronger filler alloys, resulting in joints that are significantly stronger than soldered ones.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, brazing is not the solution for every scenario. The reliance on capillary action and clean surfaces introduces specific requirements that must be met for a successful joint.
The Need for Tight Tolerances
Capillary action only works effectively with very small gaps, typically between 0.001 and 0.005 inches (0.025 - 0.127 mm). Parts must be machined or formed to fit together precisely, which can increase manufacturing complexity.
The Critical Role of Cleanliness
Any surface contamination—such as oil, grease, or oxides—will prevent the filler metal from wetting the base metal, completely stopping the bonding process. Meticulous cleaning and proper fluxing are non-negotiable for a successful braze.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct joining method depends entirely on the materials, joint design, and performance requirements of your application.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar metals or thin components without distortion: Brazing is the ideal choice due to its lower process temperature and versatile metallurgical bond.
- If your primary focus is achieving the absolute highest strength on thick, similar metals: Welding is often the superior method because it fuses the base metals themselves.
- If your primary focus is joining heat-sensitive electronics or low-stress plumbing: Soldering provides a sufficient bond at much lower, safer temperatures.
By understanding the principles of the brazing bond, you can engineer joints with exceptional strength and reliability across a vast range of materials and applications.
Summary Table:
| Brazing Characteristic | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Bond Type | Metallurgical (adhesion & diffusion) |
| Base Metal State | Solid (not melted) |
| Process Temperature | Above 450°C (840°F) |
| Joint Strength | Often as strong as the base metals |
| Key Mechanism | Capillary action in a tight joint gap |
Need a reliable, high-strength joining solution for your lab equipment?
The metallurgical bond created by brazing is perfect for assembling durable lab instruments, sample holders, and custom components from dissimilar metals. KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and consumables that support precision manufacturing processes like brazing.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and ensure the integrity of your critical joins.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the cost of a vacuum brazing furnace? A guide to key factors and investment strategy
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- What are the different types of brazing welding? A Guide to Choosing the Right Heat Source
- What is the difference between welding and vacuum brazing? Choose the Right Joining Method for Your Project
- Can dissimilar metals be brazed or braze welded? A Guide to Strong, Reliable Joints



















