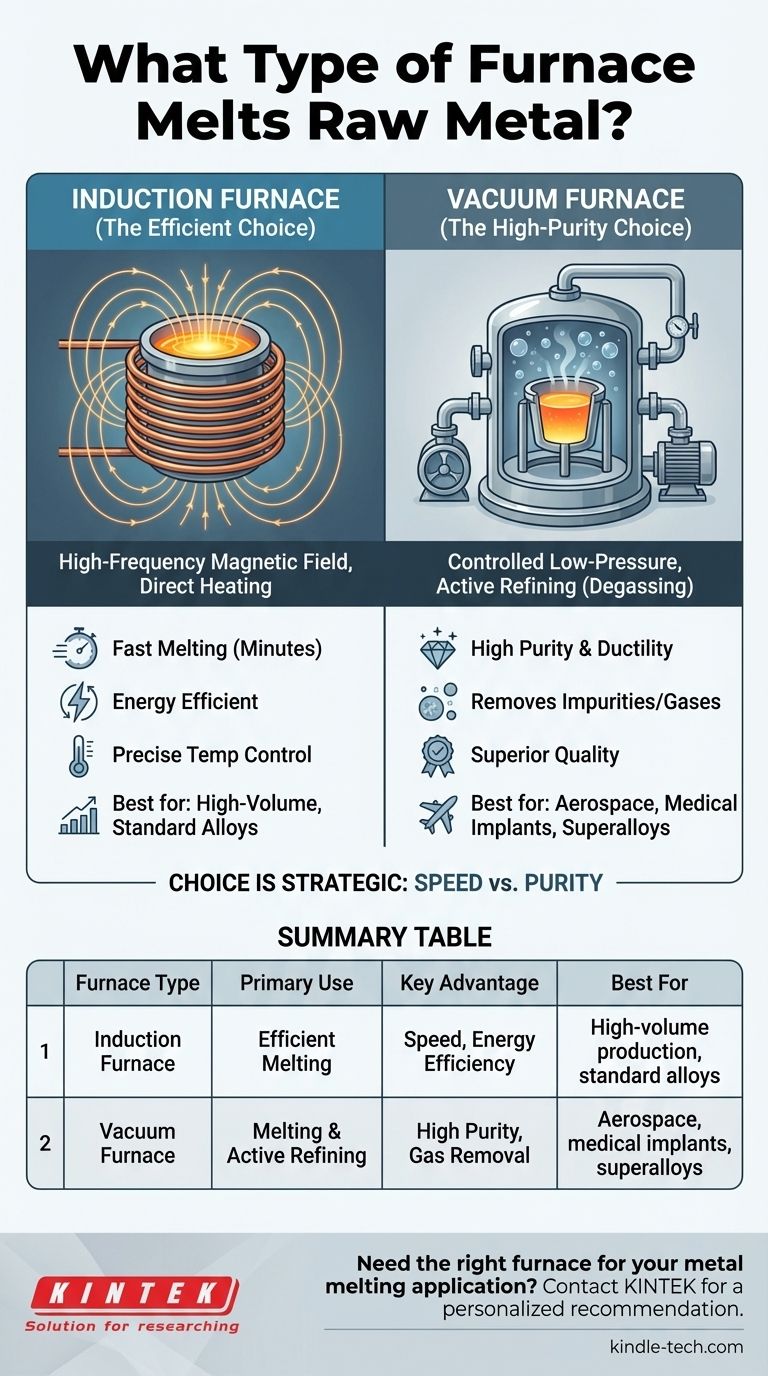
For melting raw metal, the most common and efficient technology used across the industry is the induction furnace. It works by using a powerful, high-frequency magnetic field to heat the metal directly without external flames or heating elements. While this is the standard for most applications, specialized processes requiring extremely high purity may use a high-temperature vacuum furnace.
The choice of furnace is not about a single "best" type, but a strategic decision based on the end goal. An induction furnace is chosen for efficient melting, while a vacuum furnace is chosen for active refining and purification.
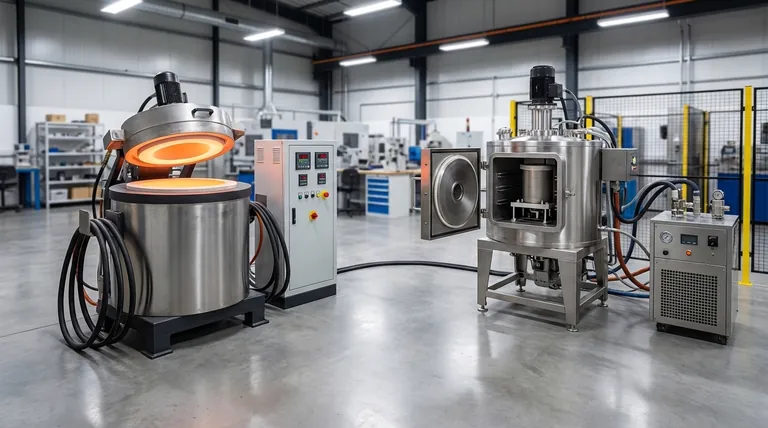

The Workhorse: How Induction Furnaces Operate
An induction furnace is the go-to solution for melting most metals, from steel and iron to copper and aluminum. Its design is based on efficiency and speed.
The Principle of Induction Heating
At the core of the furnace is a coil, typically made of copper, through which a strong alternating electrical current is passed. This current generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field around the metal placed inside a container called a crucible.
This magnetic field induces strong electrical currents directly within the metal itself. The metal's natural resistance to these internal currents generates immense heat, causing it to melt quickly from the inside out.
Key Advantages: Speed and Control
The primary benefit of induction melting is its speed. Because the heat is generated directly within the metal, there is very little wasted energy. A small induction furnace can melt a full batch of metal in a matter of minutes.
This direct heating also provides precise temperature control, which is critical for achieving consistent metallurgical properties in the final product.
When Purity is Paramount: The Vacuum Furnace
For specialized applications like aerospace components or medical implants, simply melting the metal is not enough. The material must be refined to an exceptional level of purity.
The Goal of Active Refining
A high-temperature vacuum furnace is designed for melting, refining, and casting metals under a controlled, low-pressure atmosphere. Its purpose extends beyond simply turning a solid into a liquid.
The main goal is to remove dissolved gases, like oxygen and hydrogen, and other trace impurities from the molten metal. These contaminants can introduce brittleness or other weaknesses into the final material.
How a Vacuum Improves Metal Quality
By melting the metal in a vacuum, unwanted gases are pulled out of the molten bath. This process, known as vacuum degassing, dramatically improves the metal's purity, ductility, and overall performance characteristics, resulting in a superior, high-quality material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these technologies involves a clear trade-off between speed, cost, and the required quality of the final product.
Induction Furnaces: The Efficient Choice
Induction furnaces are valued for their high speed, energy efficiency, and relatively clean operation. They are ideal for high-volume production where the primary goal is to melt raw material or scrap metal quickly and consistently.
However, a standard induction furnace does not actively refine the metal. The quality of the output is largely dependent on the quality of the input material.
Vacuum Furnaces: The High-Purity Choice
Vacuum furnaces are essential for producing the highest-purity metals and superalloys. The ability to remove impurities and gases is unmatched by other methods.
This superior quality comes at a cost. Vacuum furnaces are more complex, have slower cycle times, and are significantly more expensive to purchase and operate than their induction counterparts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your selection should be directly guided by the specifications of the final material you need to produce.
- If your primary focus is rapid, high-volume melting for casting standard parts: An induction furnace is the clear industry standard for its unmatched speed and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is producing mission-critical, high-performance alloys: A vacuum furnace is required to actively refine the metal and achieve the necessary purity and material properties.
Ultimately, the right furnace is the one that produces metal of the required quality in the most economical way for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Primary Use | Key Advantage | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Induction Furnace | Efficient Melting | Speed, Energy Efficiency | High-volume production, standard alloys |
| Vacuum Furnace | Melting & Active Refining | High Purity, Gas Removal | Aerospace, medical implants, superalloys |
Need the right furnace for your metal melting application? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Whether you require the rapid melting capabilities of an induction furnace or the ultra-pure results of a vacuum furnace, our experts can help you select the perfect solution to meet your quality and production goals. Contact us today to discuss your project and get a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- How does induction work in a vacuum? Achieve Ultra-Pure Metal Melting with VIM
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity



















