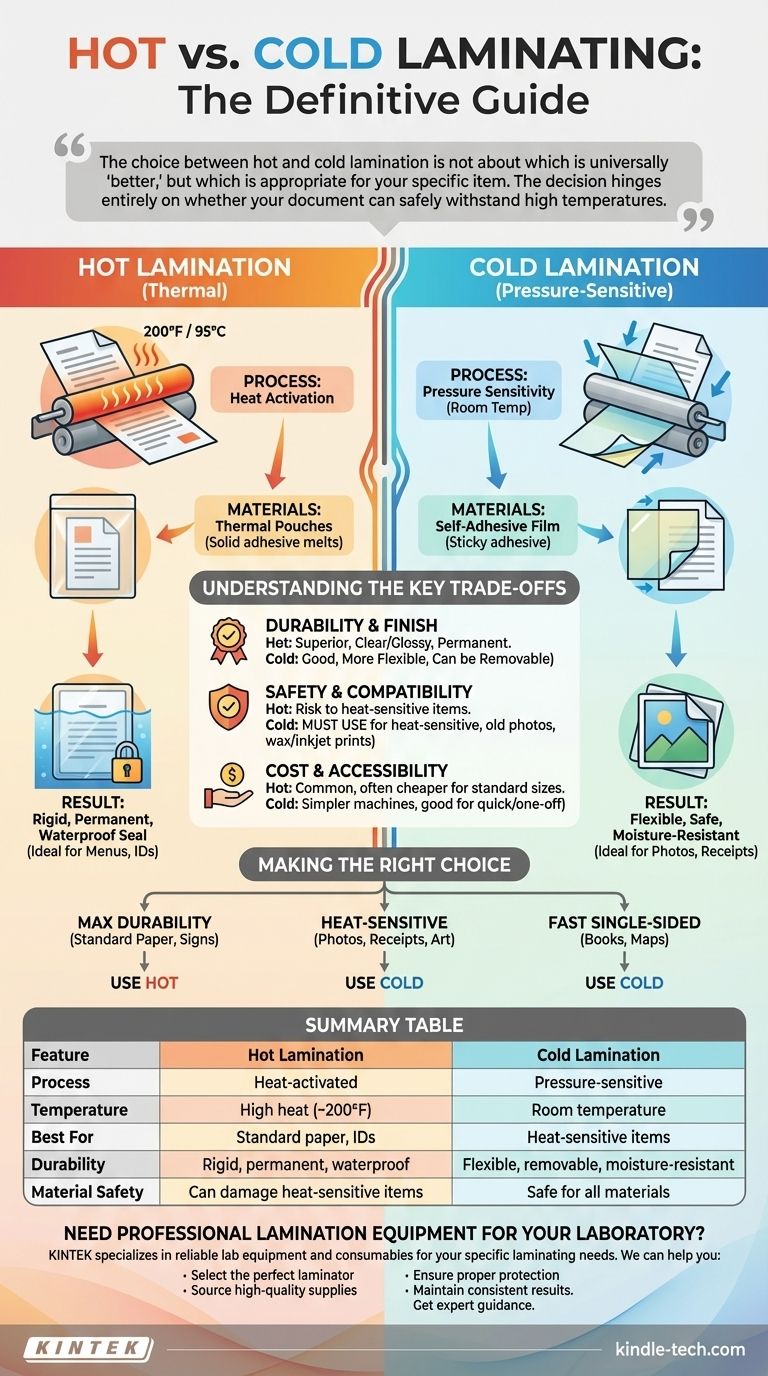
The fundamental difference is heat. Hot lamination uses thermal energy to activate a special adhesive, permanently sealing a document in plastic. In contrast, cold lamination functions like a high-quality sticker, using pressure to apply a self-adhesive film without any heat.
The choice between hot and cold lamination is not about which is universally "better," but which is appropriate for your specific item. The decision hinges entirely on whether your document can safely withstand high temperatures.
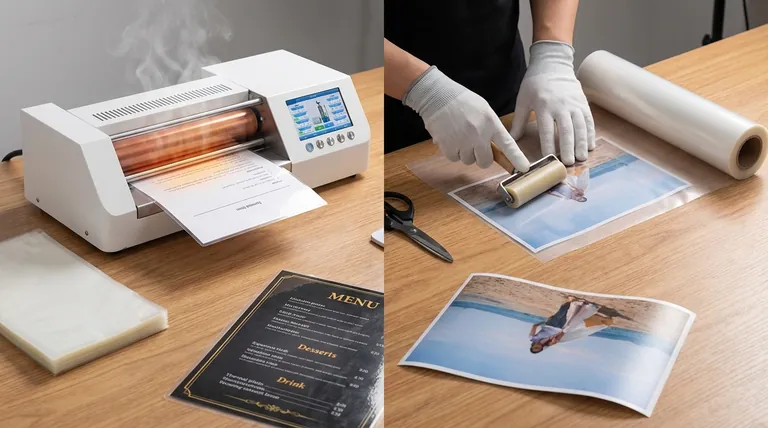

How Hot Lamination Works (The Industry Standard)
Hot lamination, also known as thermal lamination, is the most common method used for professional and everyday documents. It creates a rigid, highly durable, and permanent seal.
The Process: Heat Activation
The document is placed inside a plastic pouch that is coated with a heat-activated adhesive. This pouch is then fed through a laminator, where heated rollers melt the adhesive and pressure bonds the film to the document and to itself around the edges.
The Materials: Thermal Pouches
The adhesive used in thermal pouches is solid and slightly cloudy at room temperature. The heat from the machine (often reaching 200°F / 95°C or higher) is what melts it, creating a crystal-clear, powerful bond.
The Result: Rigid and Durable
This process fully encapsulates the document, making it waterproof, tamper-proof, and stiff. It is the ideal choice for items that will be handled frequently, such as restaurant menus, ID badges, and classroom materials.
How Cold Lamination Works (The Gentle Alternative)
Cold lamination is a pressure-sensitive process that provides protection without any risk of heat damage. It is the go-to method for delicate or irreplaceable items.
The Process: Pressure Sensitivity
Cold lamination uses a plastic film with a sticky adhesive, much like a sticker or contact paper. The film is applied to the document, and a laminator with unheated, silicone rollers applies firm, even pressure to ensure a smooth, bubble-free bond. Some simple cold lamination can even be done by hand.
The Materials: Self-Adhesive Film
The adhesive on cold laminating film is active at room temperature and is protected by a peel-off backing liner. Because no heat is involved, the machines are simpler and do not require a warm-up period.
The Result: Flexible and Safe
Cold lamination offers excellent protection from moisture and surface damage but does not create the same rigid, permanent seal as hot lamination. The result is more flexible, and in some cases, the film can be removed. Its primary advantage is its complete safety for heat-sensitive materials.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Choosing the correct method requires understanding the compromises between durability, compatibility, and cost.
Durability and Finish
Hot lamination creates a superior bond that is more rigid and far more permanent than a cold lamination seal. The melted plastic often produces a clearer, glossier finish.
Safety and Compatibility
This is the most critical factor. You must use cold lamination for any item that could be damaged by heat. This includes thermal paper (like receipts), documents printed with certain inkjet or wax-based inks, old or valuable photographs, and anything with crayon, wax seals, or other low-melting-point materials.
Cost and Accessibility
For standard document sizes, hot laminators and their corresponding pouches are generally more common and less expensive than their cold counterparts. However, cold lamination can be more accessible for quick, one-off projects as it can sometimes be applied without a machine.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Your decision should be guided by the nature of the document you are protecting.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability for standard paper: Use hot lamination for its rigid, cost-effective, and permanent seal on items like signs, menus, and ID cards.
- If your primary focus is protecting heat-sensitive or irreplaceable items: Use cold lamination to avoid any risk of damage to things like old photos, thermal receipts, or certain art projects.
- If your primary focus is a fast, single-sided application: Use cold lamination, as self-adhesive sheets are perfect for quickly covering one side of a book, map, or sign without needing a machine to warm up.
Ultimately, understanding the heat sensitivity of your material is the single most important step in choosing the correct lamination method.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Hot Lamination | Cold Lamination |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Uses heat-activated adhesive | Uses pressure-sensitive adhesive |
| Temperature | High heat (~200°F / 95°C) | Room temperature (no heat) |
| Best For | Standard paper, ID badges, menus | Heat-sensitive items, photos, receipts |
| Durability | Rigid, permanent, waterproof | Flexible, removable, moisture-resistant |
| Material Safety | Can damage heat-sensitive items | Safe for all materials |
Need Professional Lamination Equipment for Your Laboratory?
Whether you're preserving important documents, creating durable ID badges, or protecting delicate materials, having the right laminating solution is crucial. KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables to meet your specific laminating needs.
We can help you: • Select the perfect laminator for your application (hot or cold) • Source high-quality laminating pouches and films • Ensure proper document protection for your laboratory materials • Maintain consistent results with professional-grade equipment
Get expert guidance on choosing the right laminating solution for your lab. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's document preservation needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- Why is it necessary to use high-precision temperature-controlled heating furnaces? Secure Natural Fiber Integrity.
- Does a hydraulic press have heat? How Heated Platens Unlock Advanced Molding and Curing
- What are the different types of press machines? Choose the Right Heating Tech for Your Application
- What is the hot press molding method? A Guide to Shaping Materials with Heat & Pressure
- What are the pros and cons of hot forging? Unlock Superior Strength for Critical Components



















