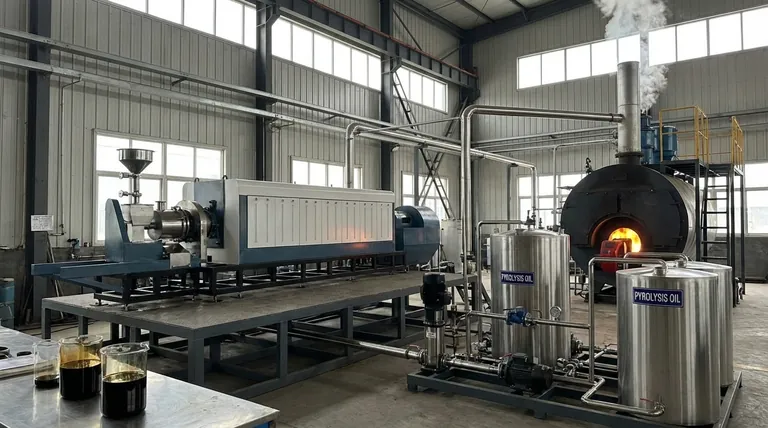
Pyrolysis oil serves primarily as a direct substitute for industrial fuel oil in stationary applications like boilers, furnaces, and power generation units. Beyond this immediate use, it can also be upgraded within existing refinery infrastructure to produce transportation fuels or serve as a valuable feedstock for creating bio-chemicals and other materials.
While pyrolysis oil offers a versatile pathway to convert waste into energy, its direct use is often confined to specific industrial applications. Realizing its full potential frequently requires upgrading and refining to overcome inherent chemical challenges like corrosiveness and instability.

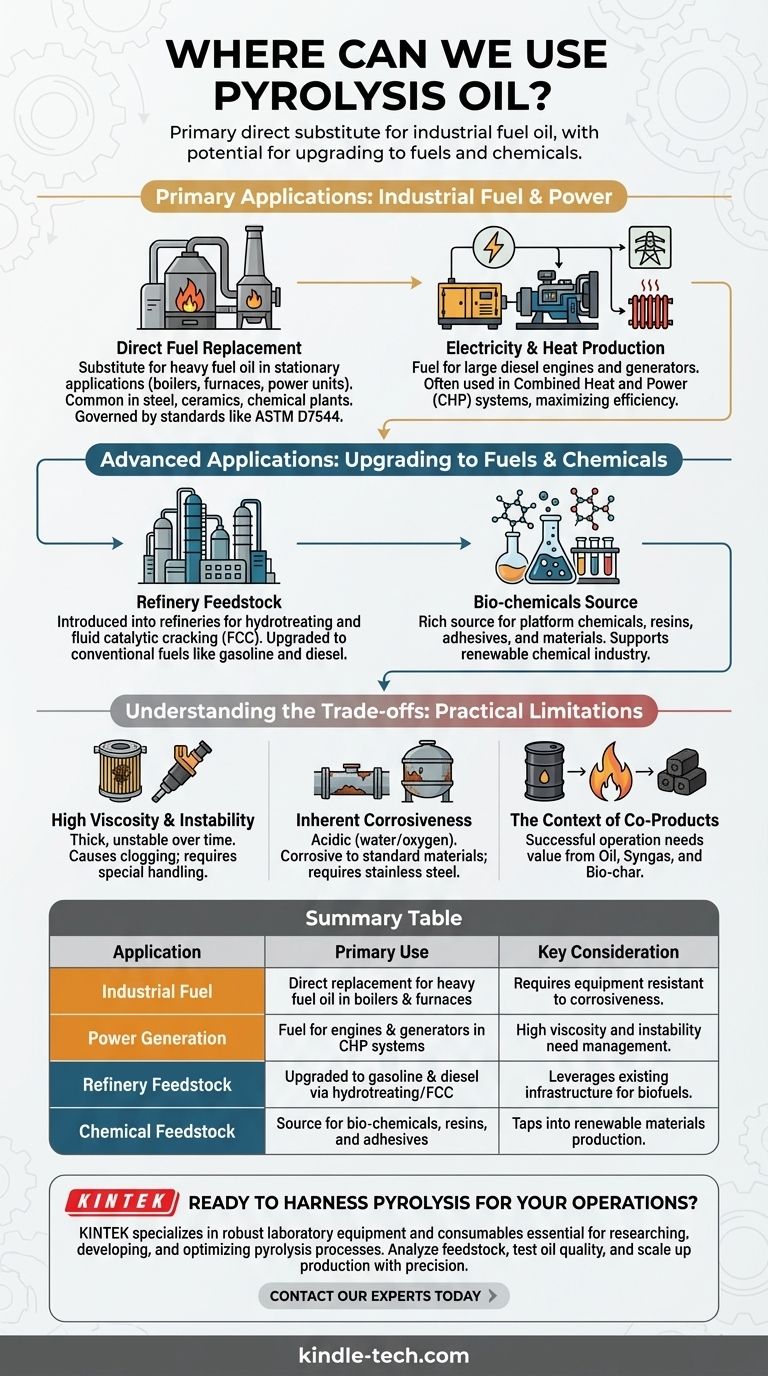
Primary Application: Industrial Fuel & Power
The most common and straightforward use for pyrolysis oil is as a direct energy source in controlled, industrial environments. It functions as a replacement for conventional heavy fuel oil or diesel.
A Direct Replacement for Fuel Oil
Pyrolysis oil, particularly from sources like rubber, can be burned in industrial furnaces and boilers. This is common in energy-intensive sectors like steel and iron manufacturing, ceramics, and chemical plants.
The use of pyrolysis oil as a commercial fuel blend is governed by standards such as ASTM D7544, which ensures quality and compatibility for these applications.
Electricity and Heat Production
The oil can be used as fuel in large diesel engines and generators to produce electricity. This is especially relevant for creating decentralized power or for facilities that want to generate their own power from waste streams.
In many cases, it's used in combined heat and power (CHP) systems, where both the electricity and the waste heat from the process are captured and utilized, maximizing energy efficiency.
Advanced Applications: Upgrading to Fuels & Chemicals
While direct burning is its primary use, the greater long-term value of pyrolysis oil lies in its potential as a renewable feedstock for higher-value products.
Feedstock for Existing Refineries
Pyrolysis oil can be introduced into traditional oil refineries. Through processes like hydrotreating and fluid catalytic cracking (FCC), it can be upgraded into conventional hydrocarbon fuels, such as gasoline and diesel.
This pathway leverages trillions of dollars of existing infrastructure, making it a compelling route for producing advanced biofuels without building entirely new facilities.
A Source for Bio-chemicals
The oil is not a single chemical but a complex mixture of hundreds of organic compounds. This complexity makes it a rich source for extracting or converting into platform chemicals, resins, adhesives, and other materials.
This application moves pyrolysis oil from being just a fuel source to becoming a cornerstone of a renewable chemical industry, reducing reliance on petroleum for materials production.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Practical Limitations
Objectivity requires acknowledging that pyrolysis oil is not a simple "drop-in" fuel. Its unique chemical properties present significant challenges that limit its widespread industrial application without pre-treatment.
High Viscosity and Instability
Pyrolysis oil is often thick and can become unstable over time, leading to polymerization and the formation of solids. This can clog fuel lines, filters, and injectors, requiring specialized handling and storage systems.
Inherent Corrosiveness
The oil is typically acidic due to its high water and oxygen content. This makes it corrosive to standard pipes, tanks, and engine components, necessitating the use of stainless steel or other resistant materials.
The Context of Co-Products
Pyrolysis doesn't just produce oil. It also creates syngas (a combustible gas) and bio-char (a solid carbon material). A successful pyrolysis operation depends on finding value for all three outputs, as the oil alone may not justify the economics. The syngas is often used to power the process itself, while the bio-char has applications in agriculture and filtration.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The best use for pyrolysis oil depends entirely on your technical capabilities, available infrastructure, and ultimate objective.
- If your primary focus is immediate waste-to-energy: Utilize the oil as a direct substitute for heavy fuel oil in stationary industrial boilers and furnaces where equipment modifications can be easily made.
- If your primary focus is producing higher-value products: Plan for a secondary upgrading process, potentially in partnership with a refinery, to convert the raw oil into stable transportation fuels or chemical feedstocks.
- If your primary focus is a holistic circular economy: Design a system that captures value from all outputs, using the syngas for process heat, the bio-char for soil amendment, and the oil for either power or as a chemical feedstock.
Understanding these distinct pathways and their associated challenges is the key to successfully leveraging pyrolysis oil as a valuable resource.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Use | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial Fuel | Direct replacement for heavy fuel oil in boilers & furnaces | Requires equipment resistant to corrosiveness |
| Power Generation | Fuel for engines & generators in CHP systems | High viscosity and instability need management |
| Refinery Feedstock | Upgraded to gasoline & diesel via hydrotreating/FCC | Leverages existing infrastructure for biofuels |
| Chemical Feedstock | Source for bio-chemicals, resins, and adhesives | Taps into renewable materials production |
Ready to harness the power of pyrolysis for your operations?
KINTEK specializes in providing robust laboratory equipment and consumables essential for researching, developing, and optimizing pyrolysis processes. Whether you are analyzing feedstock, testing oil quality, or scaling up production, our precise and durable tools help you overcome challenges like viscosity and corrosion.
Contact our experts today to find the right solutions for your laboratory's pyrolysis and biofuel research needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Culture Dish and Evaporation Dish
People Also Ask
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output










