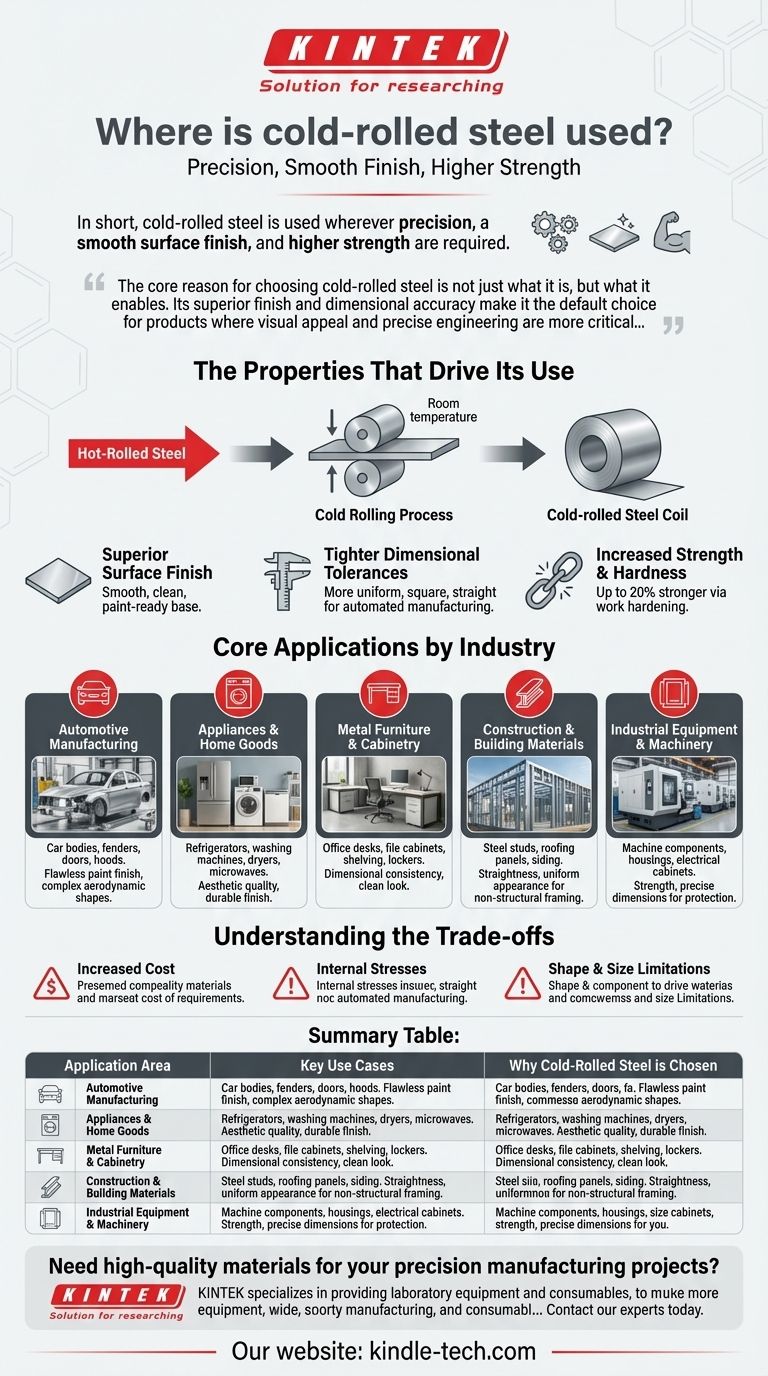
In short, cold-rolled steel is used wherever precision, a smooth surface finish, and higher strength are required. You will find it in applications ranging from automotive body panels and major home appliances to metal furniture, industrial equipment, and certain construction components.
The core reason for choosing cold-rolled steel is not just what it is, but what it enables. Its superior finish and dimensional accuracy make it the default choice for products where visual appeal and precise engineering are more critical than the lower cost of its rougher, hot-rolled counterpart.

The Properties That Drive Its Use
To understand where cold-rolled steel is used, you must first understand why it exists. It is not a different type of steel, but rather a different finishing process applied to steel.
The Cold Rolling Process
Cold-rolled steel starts as hot-rolled steel. After the hot-rolled steel cools, it is processed further by being rolled again at room temperature.
This additional compression and shaping without heat is what defines the "cold rolling" process. This seemingly simple step fundamentally changes the steel's characteristics.
Key Advantages Gained
This process imparts three critical properties:
- Superior Surface Finish: The steel becomes smooth, clean, and often slightly oily to the touch. This makes it an ideal base for painting and other high-quality finishes without extensive prep work.
- Tighter Dimensional Tolerances: Cold rolling allows for much more precise control over the final shape and dimensions. The material is more uniform, square, and straight, which is critical for automated manufacturing and assembly.
- Increased Strength and Hardness: The process of compressing the steel at a low temperature, known as work hardening or strain hardening, realigns its crystal structure. This makes the final product up to 20% stronger and harder than the original hot-rolled steel.
Core Applications by Industry
These distinct properties make cold-rolled steel the ideal material for a wide range of applications where precision and finish are paramount.
Automotive Manufacturing
Cold-rolled sheets are essential for car bodies, fenders, doors, and hoods. The smooth surface is critical for achieving a flawless paint finish, and its formability allows for the complex, aerodynamic shapes of modern vehicles.
Appliances and Home Goods
The exterior casings of refrigerators, washing machines, dryers, and microwaves are almost always made from cold-rolled steel. The aesthetic quality and ability to hold a durable finish are the primary drivers for this choice.
Metal Furniture and Cabinetry
Office desks, file cabinets, shelving, and lockers rely on cold-rolled steel. Its dimensional consistency ensures that parts fit together perfectly during assembly, and its smooth surface provides a clean look.
Construction and Building Materials
While large structural beams are typically hot-rolled, cold-rolled steel is used for applications requiring more precision. This includes non-structural framing like steel studs, roofing panels, and high-end siding where straightness and a uniform appearance are important.
Industrial Equipment and Machinery
Many machine components, housings, and electrical cabinets are fabricated from cold-rolled steel. Its strength and precise dimensions are essential for protecting sensitive internal parts and ensuring a proper fit.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing cold-rolled steel is not without its compromises. An objective analysis requires acknowledging its limitations.
Increased Cost
The additional processing steps make cold-rolled steel significantly more expensive than hot-rolled steel. This is the single biggest factor when deciding between the two.
Internal Stresses
The work hardening process can create internal stresses within the material. For complex fabrication involving significant welding, bending, or machining, these stresses may need to be relieved through a separate heat treatment process like annealing.
Shape and Size Limitations
The cold rolling process is most effective for producing uniform cross-sections like sheets, strips, rounds, and bars. Creating more complex shapes is often impractical or prohibitively expensive compared to other methods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
The decision to use cold-rolled steel hinges entirely on your project's non-negotiable requirements.
- If your primary focus is aesthetics and surface quality: Choose cold-rolled steel for its smooth, paint-ready finish that requires minimal preparation.
- If your primary focus is precision and tight tolerances: Select cold-rolled steel when components must fit together perfectly, as in automated assembly or machinery.
- If your primary focus is raw strength and cost-effectiveness: Hot-rolled steel is the superior choice for large structural applications where surface finish is not a concern.
Ultimately, selecting the correct steel is about matching the material's inherent properties to the specific demands of your final product.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Use Cases | Why Cold-Rolled Steel is Chosen |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive Manufacturing | Car bodies, doors, hoods, fenders | Superior surface finish for painting, precise dimensions for assembly |
| Appliances & Home Goods | Refrigerators, washers, dryers, microwaves | Aesthetic quality, ability to hold a durable finish |
| Metal Furniture & Cabinetry | Desks, filing cabinets, shelving, lockers | Dimensional consistency for assembly, clean appearance |
| Construction & Building | Steel studs, roofing panels, siding | Straightness, uniform appearance for non-structural framing |
| Industrial Equipment | Machine housings, electrical cabinets | Strength, precise dimensions to protect internal components |
Need high-quality materials for your precision manufacturing projects? KINTEK specializes in providing laboratory equipment and consumables, including materials like cold-rolled steel, to meet the exacting standards of industries from automotive to industrial manufacturing. Our expertise ensures you get the right materials for superior finish, strength, and dimensional accuracy. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific application needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Cold Trap Chiller Indirect Cold Trap Chiller
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- 50L Chiller Water Bath Cooling Circulator Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
- 30L Chiller Water Bath Cooling Circulator Low Temperature Constant Temperature Reaction Bath
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
People Also Ask
- Why is a cold trap system containing isopropanol required for pyrolysis gas? Capture Elusive Volatiles Effectively
- What is the purpose of placing an ice water bath cold trap around a gas-liquid separator? Enhance Signal Accuracy
- What is the mechanism of a high-efficiency cold trap in pervaporation? Optimize Your Vapor Capture Efficiency
- What is the purpose of an immersion chilling accessory? Expand Lab Flexibility and Thermal Range
- What is the function of efficient cooling systems and cold traps in plastic pyrolysis? Maximize Yield and Purity



















