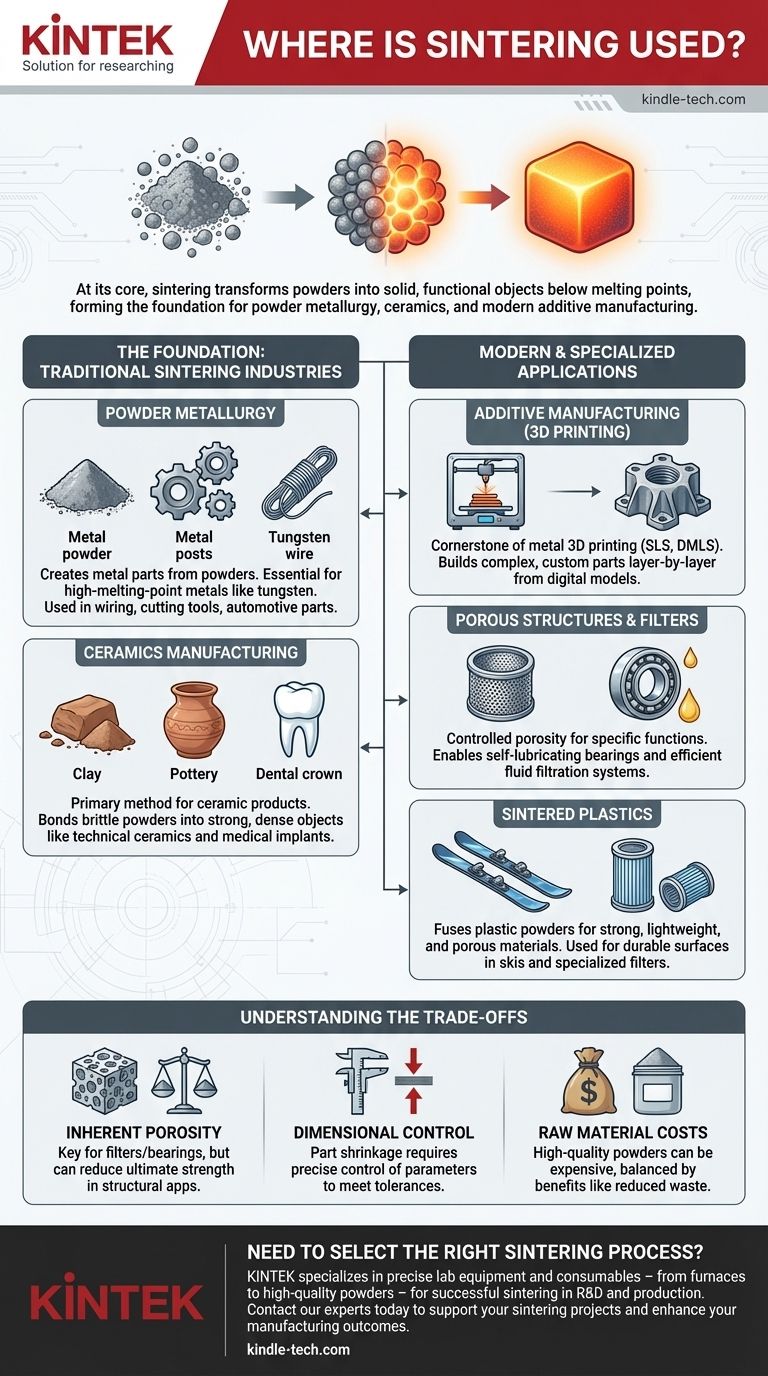
At its core, sintering is used across industries to transform powders into solid, functional objects without reaching their full melting point. It is the foundational process for powder metallurgy, the manufacturing of most ceramic goods, and a key technology in modern additive manufacturing. This method is chosen to create everything from structural steel parts and self-lubricating bearings to advanced dental implants and custom 3D-printed components.
Sintering's true value lies in its ability to solve problems that melting cannot. It allows for the creation of components from materials with extremely high melting points, the design of parts with controlled porosity, and the efficient mass-production of complex shapes.
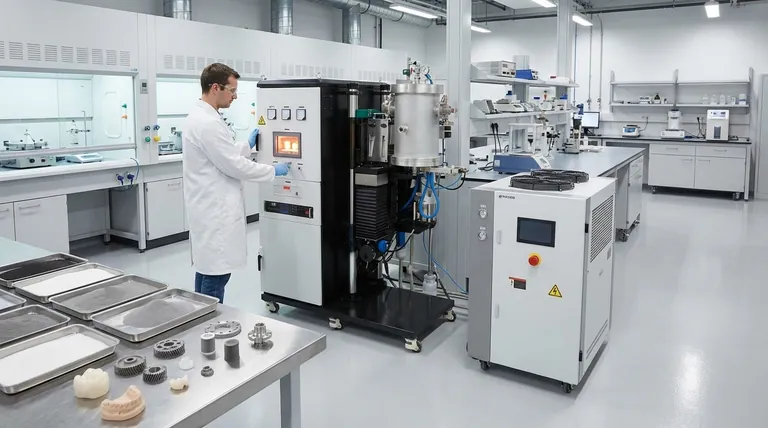

The Foundation: Traditional Sintering Industries
Sintering is not a new technology; its principles have been used for millennia. Today, it remains the backbone of two major industrial sectors.
Powder Metallurgy
Powder metallurgy is the science of creating metal parts from metal powders. Sintering is the critical step that fuses these powders into a coherent, strong mass.
This process is essential for metals with exceptionally high melting points, such as tungsten. Melting these materials is technically challenging and requires immense energy, whereas sintering achieves consolidation at a lower temperature.
Common applications include tungsten wiring for lighting, hardmetal cutting tools, and various structural steel parts used in automotive and industrial machinery.
Ceramics Manufacturing
Historically, sintering was first used to produce clay pottery and bricks, and it remains the primary method for creating nearly all ceramic products today.
Brittle ceramic powders are first compacted into a desired shape (the "green body") and then sintered in a furnace. This process bonds the particles, drastically increasing the strength and density of the final object.
Beyond traditional pottery, this is used for advanced technical ceramics found in electrical components, semiconductors, and medical products like dental crowns.
Modern and Specialized Applications
The principles of sintering have been adapted for cutting-edge manufacturing technologies and specialized materials, expanding its use far beyond traditional metals and ceramics.
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Sintering is a cornerstone of several metal 3D printing techniques, such as Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) and Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS).
In these processes, a laser selectively sinters thin layers of metal powder, one on top of the other, to build a complex, custom part from a digital model.
This enables the creation of intricate geometries that would be impossible or prohibitively expensive to produce with traditional machining, all while saving energy and material.
Porous Structures and Filters
Because sintering begins with individual particles, the final density of the part can be precisely controlled by adjusting process parameters. This is deliberately leveraged to create porous materials.
Self-lubricating bearings are made by sintering bronze powder to create a porous structure, which is then impregnated with oil. The bearing releases oil during operation.
This same principle is used to manufacture porous metal and plastic filters for separating solids from fluids in hydraulic systems, chemical processing, and other applications.
Sintered Plastics
Sintering is also applied to certain polymers. Fine plastic powder is heated until the surfaces of the particles fuse, creating a strong but lightweight material.
This is commonly used to produce durable, porous surfaces for the bases of high-performance skis and snowboards, which are designed to absorb wax efficiently. It is also used to create specialized plastic filters.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, sintering is not a universal solution. Choosing this process involves understanding its inherent compromises.
Inherent Porosity
Unless specific post-processing steps are taken, a sintered part almost always contains some residual porosity compared to a part made from molten material.
For structural applications, this can mean slightly lower ultimate strength or fatigue resistance compared to a forged or cast equivalent. However, for applications like filters or bearings, this porosity is a key feature.
Dimensional Control
During sintering, the part shrinks as the particles bond and the voids between them are reduced. Predicting and controlling this shrinkage is critical to achieving tight dimensional tolerances.
This requires precise control over powder characteristics, compaction pressure, and furnace temperature profiles. Imperfect control can lead to parts that are out of specification.
Raw Material Costs
The production of high-quality metal or ceramic powders suitable for sintering can be an expensive process. The powder must be of a specific size, shape, and purity to ensure consistent results.
This initial material cost must be weighed against the benefits, such as reduced energy consumption and minimal material waste (near-net-shape manufacturing).
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting sintering depends entirely on the material you are using and the desired properties of the final part.
- If your primary focus is working with high-melting-point metals: Sintering is the industry-standard method, allowing you to form parts from materials like tungsten without the extreme energy cost of melting.
- If your primary focus is creating parts with controlled porosity: Sintering offers unparalleled control over density, making it the ideal choice for producing self-lubricating bearings and filters.
- If your primary focus is mass-producing small, complex metal components: Powder metallurgy with sintering is a highly cost-effective process for creating near-net-shape parts with minimal waste.
- If your primary focus is creating custom, one-off metal prototypes: Sintering is the key technology in metal 3D printing, providing unmatched design freedom for complex geometries.
Ultimately, sintering is the go-to manufacturing process when melting is impractical, undesirable, or incapable of achieving the required final part characteristics.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Examples | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Powder Metallurgy | Tungsten wiring, Hardmetal tools, Automotive parts | Forms high-melting-point metals without full melting |
| Ceramics Manufacturing | Dental crowns, Electrical insulators, Semiconductors | Creates strong, dense objects from brittle powders |
| Additive Manufacturing | Custom 3D-printed metal prototypes, Complex geometries | Enables intricate designs with minimal waste |
| Porous Structures | Self-lubricating bearings, Metal/plastic filters | Provides controlled porosity for specific functions |
| Sintered Plastics | Ski/snowboard bases, Specialized filters | Produces strong, lightweight, and porous components |
Need to select the right sintering process for your materials and application goals?
KINTEK specializes in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables—from furnaces to high-quality powders—that are essential for successful sintering in R&D and production. Whether you're working with advanced metals, ceramics, or exploring additive manufacturing, our solutions help you achieve the desired density, strength, and complex geometries.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your sintering projects and enhance your manufacturing outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the factors influencing shrinkage during sintering? Control Dimensional Changes for Precision Parts
- Why is a high vacuum environment necessary in sintering equipment for TiAl alloys? Ensure High-Purity Metal Bonding
- Why must green bodies produced via binder jetting undergo treatment in a vacuum sintering furnace?
- Why is a high vacuum required for sintering Ti-43Al-4Nb-1Mo-0.1B? Ensure Purity & Fracture Toughness
- How does precise temperature control affect FeCoCrNiMnTiC high-entropy alloys? Master Microstructural Evolution



















